Lab 7 - De Anza
... 4. Remove a stamen and touch the anther to a drop of water on a slide. If nothing comes off in the water, crush the anther a little to squeeze out some of its contents. Place a cover slip on the drop and observe with low and high powers of the microscope. The spherical cells with thick walls are pol ...
... 4. Remove a stamen and touch the anther to a drop of water on a slide. If nothing comes off in the water, crush the anther a little to squeeze out some of its contents. Place a cover slip on the drop and observe with low and high powers of the microscope. The spherical cells with thick walls are pol ...
Gymnosperms Ch. 24 Notes
... – Thick, waxy cuticles with stomata • Water-conserving • Enable to retain leaves year round ...
... – Thick, waxy cuticles with stomata • Water-conserving • Enable to retain leaves year round ...
Lesson 1: What is Motion
... pollination- the movement of pollen from stamen to pistol fertilization- the process in which a sperm cell and an egg cell combine germinate- to start to grow NOTES An important function of plants is to reproduce, or make more of the same kind of plant. Parts of a Flower Most flowers have 4 main ...
... pollination- the movement of pollen from stamen to pistol fertilization- the process in which a sperm cell and an egg cell combine germinate- to start to grow NOTES An important function of plants is to reproduce, or make more of the same kind of plant. Parts of a Flower Most flowers have 4 main ...
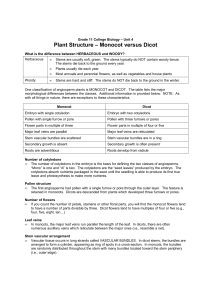
Unit 4 - Lesson 6 - Monocot and Dicot
... • The number of cotyledons in the embryo is the basis for defining the two classes of angiosperms. “Mono” is one and “di” is two. The cotyledons are the “seed leaves” produced by the embryo. The cotyledons absorb nutrients packaged in the seed until the seedling is able to produce its first true lea ...
... • The number of cotyledons in the embryo is the basis for defining the two classes of angiosperms. “Mono” is one and “di” is two. The cotyledons are the “seed leaves” produced by the embryo. The cotyledons absorb nutrients packaged in the seed until the seedling is able to produce its first true lea ...
ppt
... Lycopodiophytes: vascular tissue and dominance of the sporophyte (tall) Monilophytes: true leaves Gymnosperms: Seeds and pollen Angiosperms: Flowers and fruit ...
... Lycopodiophytes: vascular tissue and dominance of the sporophyte (tall) Monilophytes: true leaves Gymnosperms: Seeds and pollen Angiosperms: Flowers and fruit ...
Lesson Observation Proforma - plantreproductionfieldtrip
... direct wind). Inside petals are reprod organs stamens and pistol Male parts – stamen – filament & anther. Anther contains pollen sacs. Pollen like a box containing 2 or 3 cells. Anther releases pollen. Anther site of meiosis Female parts – pistol – stigma, style and ovary. Stigma catches pollen, sty ...
... direct wind). Inside petals are reprod organs stamens and pistol Male parts – stamen – filament & anther. Anther contains pollen sacs. Pollen like a box containing 2 or 3 cells. Anther releases pollen. Anther site of meiosis Female parts – pistol – stigma, style and ovary. Stigma catches pollen, sty ...
Kingdom Plantae
... Plants developed root systems that can collect and transport water. Some plants have shallow roots which spread out to collect water. Water carrying minerals from the roots can travel to all parts of the plant and food made in the leaves can travel to non-photosynthetic parts of the ...
... Plants developed root systems that can collect and transport water. Some plants have shallow roots which spread out to collect water. Water carrying minerals from the roots can travel to all parts of the plant and food made in the leaves can travel to non-photosynthetic parts of the ...
Kingdom Plantae
... ) اﻷﻧﺒﻮﺑﻴﺔgrows down the style toward an ovule. There are two sperm cells inside the pollen tube. ...
... ) اﻷﻧﺒﻮﺑﻴﺔgrows down the style toward an ovule. There are two sperm cells inside the pollen tube. ...
PLANT DIVISIONS
... • What division of plants has no vascular tissue? • What is made by the archegonium? • What part of the flower “catches the pollen? • What is one gymnosperm other than ...
... • What division of plants has no vascular tissue? • What is made by the archegonium? • What part of the flower “catches the pollen? • What is one gymnosperm other than ...
Angiosperms and Gymnosperms
... sperm meets with the egg in the ovule and fertilization occurs. The fertilized egg will become a seed and the ovary will become a protective fruit. Fertilization ...
... sperm meets with the egg in the ovule and fertilization occurs. The fertilized egg will become a seed and the ovary will become a protective fruit. Fertilization ...
All About Plants
... Seeds • Seeds may be dormant (inactive) for weeks or years protected by their seed coat • Seeds contain a plant embryo and endosperm ...
... Seeds • Seeds may be dormant (inactive) for weeks or years protected by their seed coat • Seeds contain a plant embryo and endosperm ...
What is a Plant? - Jordan High School
... History & Evolution of Plants • Ancestors of modern plants were waterdwelling organisms similar to algae • Early land plants were centimeters tall – Grew close to the ground to obtain water ...
... History & Evolution of Plants • Ancestors of modern plants were waterdwelling organisms similar to algae • Early land plants were centimeters tall – Grew close to the ground to obtain water ...
Plant Reproduction & Development
... Carries out long-distance transport of materials within the plant Xylem and phloem are examples of vascular tissues ...
... Carries out long-distance transport of materials within the plant Xylem and phloem are examples of vascular tissues ...
Photosynthesis
... Phloem conducts sucrose and other organic compounds throughout the plant Lignin strengthens walls of conducting cells in xylem All seed plants are heterosporous and have male and female gametophytes ...
... Phloem conducts sucrose and other organic compounds throughout the plant Lignin strengthens walls of conducting cells in xylem All seed plants are heterosporous and have male and female gametophytes ...
Seed Plants connection lesson - biology-rocks
... – Abundant sunlight for photosynthesis – Continuous free movement of gases (O2/CO2) ...
... – Abundant sunlight for photosynthesis – Continuous free movement of gases (O2/CO2) ...
Jeopardyplants
... The process by which pollen is carried from the male part of a flower to the female part of another flower ...
... The process by which pollen is carried from the male part of a flower to the female part of another flower ...
Slide 1
... In this stage plants make spores. In damp soil, many spores may grow. These new plans are called gametohytes. ...
... In this stage plants make spores. In damp soil, many spores may grow. These new plans are called gametohytes. ...
Unit 4 Notes #3Terrestrial Plants and Their - Mr. Lesiuk
... environments. They are still limited to environments that are at least seasonally wet, as they use flagellated sperm to swim to the eggs. Adaptations: 1) Have vascular tissues. a) Xylem: Tissue that includes dead Tracheid cells (hence Tracheophyta), these cells transports water and dissolved nutrien ...
... environments. They are still limited to environments that are at least seasonally wet, as they use flagellated sperm to swim to the eggs. Adaptations: 1) Have vascular tissues. a) Xylem: Tissue that includes dead Tracheid cells (hence Tracheophyta), these cells transports water and dissolved nutrien ...
Flowering Plant Reproduction (p. 403)
... 2. Both microgametophytes (male gametophytes) and megagametophytes (female gametophytes) are housed within the same structure, the flower. 3. Flower production is seasonal and not a permanent feature of the mature sporophyte. 4. Pollen grains are the male gametophytes while embryo sacs are the femal ...
... 2. Both microgametophytes (male gametophytes) and megagametophytes (female gametophytes) are housed within the same structure, the flower. 3. Flower production is seasonal and not a permanent feature of the mature sporophyte. 4. Pollen grains are the male gametophytes while embryo sacs are the femal ...
THE GREAT PLANT ESCAPE
... A plant that lives for 3 or more years. It can grow, flower, and set seed for many years. Examples: daisies, chrysanthemums, and ...
... A plant that lives for 3 or more years. It can grow, flower, and set seed for many years. Examples: daisies, chrysanthemums, and ...
SEED PLANTS: ANGIOSPERMS First land plants appeared
... The paleoherbs are a small group of flowering plants which have traditionally been classified as dicots, but which have many characters in common with monocots. “Even after the general acceptance of Monocots and Dicots as the primary groups of flowering plants, botanists did not always agree upon th ...
... The paleoherbs are a small group of flowering plants which have traditionally been classified as dicots, but which have many characters in common with monocots. “Even after the general acceptance of Monocots and Dicots as the primary groups of flowering plants, botanists did not always agree upon th ...
Gymnosperm fossils
... cupule.These cupules bear capitate glands.The ovule is Orthotropous and consists of well developed nucellus .The nucellus apex has a hollow pollen chamber(Lagenostome). • The pollen chamber in this ovule is conical in shape and has a central core of tissue,shaped like inverted bell.This is known as ...
... cupule.These cupules bear capitate glands.The ovule is Orthotropous and consists of well developed nucellus .The nucellus apex has a hollow pollen chamber(Lagenostome). • The pollen chamber in this ovule is conical in shape and has a central core of tissue,shaped like inverted bell.This is known as ...
Flowering plant

The flowering plants (angiosperms), also known as Angiospermae or Magnoliophyta, are the most diverse group of land plants. Angiosperms are seed-producing plants like the gymnosperms and can be distinguished from the gymnosperms by characteristics including flowers, endosperm within the seeds, and the production of fruits that contain the seeds. Etymologically, angiosperm means a plant that produces seeds within an enclosure, in other words, a fruiting plant.The ancestors of flowering plants diverged from gymnosperms around 245–202 million years ago, and the first flowering plants known to exist are from 160 million years ago. They diversified enormously during the Lower Cretaceous and became widespread around 120 million years ago, but replaced conifers as the dominant trees only around 60–100 million years ago.