AP Biology Review Chapters 23-27 Review Questions Chapter 23
... 2005 Question 3 Angiosperms (flowering plants) have wide distribution in the biosphere and the largest number of species in the plant kingdom. a) Discuss the function of four structures for reproduction found in angiosperms and the adaptive (evolutionary) significance of each. b) Mosses (bryophytes ...
... 2005 Question 3 Angiosperms (flowering plants) have wide distribution in the biosphere and the largest number of species in the plant kingdom. a) Discuss the function of four structures for reproduction found in angiosperms and the adaptive (evolutionary) significance of each. b) Mosses (bryophytes ...
ID Guide
... is comprised of two petal lobes and the lower “lip” is comprised of three small lobes. The flowers are bisexual, which means they have both male and female reproductive organs. At the peak of flowering, the flower clusters will include closed buds, open fresh flowers, and drying flowers that are dev ...
... is comprised of two petal lobes and the lower “lip” is comprised of three small lobes. The flowers are bisexual, which means they have both male and female reproductive organs. At the peak of flowering, the flower clusters will include closed buds, open fresh flowers, and drying flowers that are dev ...
Plant Reproduction
... Hypocotyl: Develops into roots and in some species lower stem. Radical: Develops in roots Epicotyl: Develops into leaves and upper stem Cotyledon: Stored food for early development of embryo (seed leaves) ...
... Hypocotyl: Develops into roots and in some species lower stem. Radical: Develops in roots Epicotyl: Develops into leaves and upper stem Cotyledon: Stored food for early development of embryo (seed leaves) ...
Plant Divisions
... they have no vascular system? • What is the most common example in this division and how do they reproduce? • Why are mosses so small? • What is the division of plants that contain a vascular system? • What did a vascular system do for plants size-wise? • How are mosses and ferns different? • How ar ...
... they have no vascular system? • What is the most common example in this division and how do they reproduce? • Why are mosses so small? • What is the division of plants that contain a vascular system? • What did a vascular system do for plants size-wise? • How are mosses and ferns different? • How ar ...
Plants Unit Test SBI 3U Openbook
... in the space below, correct the FALSE statements (1 additional mark for each corrected false statement). 1. Petioles are structures in the seeds of flowering plants that store and supply nutrients to the embryo. ___________ 2. A petiole is the flat part of a leaf. ____________________ 3. A cotyledon ...
... in the space below, correct the FALSE statements (1 additional mark for each corrected false statement). 1. Petioles are structures in the seeds of flowering plants that store and supply nutrients to the embryo. ___________ 2. A petiole is the flat part of a leaf. ____________________ 3. A cotyledon ...
Gymnosperms Gymnosperms are non-flowering plants that do not
... There are many different kinds of plants. These can be found in almost every type of habitat and come in a variety of sizes and shapes. Plants are an important source of nutrition for mankind and many of the herbs can be used as medicine. A few examples of different plant types are given below. Angi ...
... There are many different kinds of plants. These can be found in almost every type of habitat and come in a variety of sizes and shapes. Plants are an important source of nutrition for mankind and many of the herbs can be used as medicine. A few examples of different plant types are given below. Angi ...
Golgi- Packages and transports proteins outside the cell
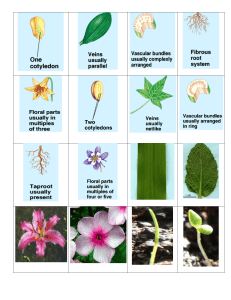
... The last distinct difference between monocots and dicots are their flowers (if present). Monocot flowers usually form in threes whereas dicot flowers occur in groups of four or five. ...
... The last distinct difference between monocots and dicots are their flowers (if present). Monocot flowers usually form in threes whereas dicot flowers occur in groups of four or five. ...
An Introduction to Potentially Invasive
... (NDCC Chapter 63-01.1). Internet and catalog sales have made a large variety of plants available to everyone, including ND noxious weeds and potential invasive ornaments. It is your responsibility to know what kind of plant ornamentals you are getting before you purchase, exchange, or dig up a plant ...
... (NDCC Chapter 63-01.1). Internet and catalog sales have made a large variety of plants available to everyone, including ND noxious weeds and potential invasive ornaments. It is your responsibility to know what kind of plant ornamentals you are getting before you purchase, exchange, or dig up a plant ...
A plant is a(an)
... 1. conifers only 2. conifers and cycads only 3. conifers and ginkgoes only 4. conifers, cycads, gnetophytes, and ginkgoes ...
... 1. conifers only 2. conifers and cycads only 3. conifers and ginkgoes only 4. conifers, cycads, gnetophytes, and ginkgoes ...
CHAPTER 16
... In both divisions, daughter cells containing the same types of chromosomes as the original cell are formed and replication of the chromosomes (forming chromatids joined at the centromere) occurs before the process begins. In mitosis there is a single nuclear division, the chromatid pairs join joins ...
... In both divisions, daughter cells containing the same types of chromosomes as the original cell are formed and replication of the chromosomes (forming chromatids joined at the centromere) occurs before the process begins. In mitosis there is a single nuclear division, the chromatid pairs join joins ...
plants in the tropical rainforests
... More than two thirds of the world's plant species are found in the warm and humid tropical rainforests. There are plants such as white trillium, rainforest buttercup, bougainvillea, opium poppies and over 20,000 different species of orchids. Most tropical rainforest plants are exotic and very beauti ...
... More than two thirds of the world's plant species are found in the warm and humid tropical rainforests. There are plants such as white trillium, rainforest buttercup, bougainvillea, opium poppies and over 20,000 different species of orchids. Most tropical rainforest plants are exotic and very beauti ...
plants vascular systems
... brown. Sepals are leaf like structures that surround and protect the flower before it blooms. Color the sepals green. Petals are the colorful part of the flower that attracts insects and even other small animals, such as mice, birds, and bats. Color the petals a bright color of your choice. All flow ...
... brown. Sepals are leaf like structures that surround and protect the flower before it blooms. Color the sepals green. Petals are the colorful part of the flower that attracts insects and even other small animals, such as mice, birds, and bats. Color the petals a bright color of your choice. All flow ...
Plant Packet
... plant has. “Seed leaves” are called Cotyledons: A cotyledon is… ______________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ ...
... plant has. “Seed leaves” are called Cotyledons: A cotyledon is… ______________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ ...
1 - BY 124 SI
... 21. Of the following, which is a difference in how reproduction occurs in gymnosperms compared to angiosperms? A. Only angiosperms have reduced gametophytes. B. Double fertilization only occurs in gymnosperms. C. Only angiosperm pollen grains form pollen tubes. D. Only gymnosperms can contain male a ...
... 21. Of the following, which is a difference in how reproduction occurs in gymnosperms compared to angiosperms? A. Only angiosperms have reduced gametophytes. B. Double fertilization only occurs in gymnosperms. C. Only angiosperm pollen grains form pollen tubes. D. Only gymnosperms can contain male a ...
1 - BY 124 SI
... 21. Of the following, which is a difference in how reproduction occurs in gymnosperms compared to angiosperms? A. Only angiosperms have reduced gametophytes. B. Double fertilization only occurs in gymnosperms. C. Only angiosperm pollen grains form pollen tubes. D. Only gymnosperms can contain male a ...
... 21. Of the following, which is a difference in how reproduction occurs in gymnosperms compared to angiosperms? A. Only angiosperms have reduced gametophytes. B. Double fertilization only occurs in gymnosperms. C. Only angiosperm pollen grains form pollen tubes. D. Only gymnosperms can contain male a ...
Seed plants - Michigan State University
... In pteridophytes, gymnosperms, and angiosperms the sporophyte form is the dominant. The fern plant most of us are familiar with is the diploid sporophyte. The gametophyte is a tiny plant. In gymnosperms & angiosperms the gametophyte is retained within the sporophyte. ...
... In pteridophytes, gymnosperms, and angiosperms the sporophyte form is the dominant. The fern plant most of us are familiar with is the diploid sporophyte. The gametophyte is a tiny plant. In gymnosperms & angiosperms the gametophyte is retained within the sporophyte. ...
Year 5 (Entry into Year 6) 10 Hour Revision
... 3. Seed Dispersal – the fruit grows around the seed, its job is to carry the seed as far away as possible. a. Animals can either eat the fruit and pass the seed out later (eg Apples) or the fruit gets hooked on the fur of a passing animal (eg Burdock) b. The wind can also be used to make the seed tr ...
... 3. Seed Dispersal – the fruit grows around the seed, its job is to carry the seed as far away as possible. a. Animals can either eat the fruit and pass the seed out later (eg Apples) or the fruit gets hooked on the fur of a passing animal (eg Burdock) b. The wind can also be used to make the seed tr ...
LORELEI: Guiding the Fate of Male Gametes
... close proximity to the egg cell and the central cell, and double fertilization ensues. Signals from the female gametophyte are known to be critical for pollen tube guidance, but the molecular mechanisms involved are not fully understood (Higashiyama and Hamamura, 2008; Punwani and Drews, 2008). Capr ...
... close proximity to the egg cell and the central cell, and double fertilization ensues. Signals from the female gametophyte are known to be critical for pollen tube guidance, but the molecular mechanisms involved are not fully understood (Higashiyama and Hamamura, 2008; Punwani and Drews, 2008). Capr ...
30LecturePresentation
... Angiosperm Diversity • The two main groups of angiosperms are monocots (one cotyledon) and eudicots (“true” dicots) • Basal angiosperms - less derived and include the flowering plants belonging to the oldest lineages (Eg. Amborella trichopoda, water lilies, and star anise) • Magnoliids - share some ...
... Angiosperm Diversity • The two main groups of angiosperms are monocots (one cotyledon) and eudicots (“true” dicots) • Basal angiosperms - less derived and include the flowering plants belonging to the oldest lineages (Eg. Amborella trichopoda, water lilies, and star anise) • Magnoliids - share some ...
137 CHAPTER 10 – REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS
... Inside each ovule, a large, diploid, spore mother cell develops. This cell divides by meiosis to produce four haploid cells. All but one of these degenerates and the one surviving haploid cell then develops into an embryo sac. The embryo sac absorbs nutrients from the nucleus and grows larger. Its n ...
... Inside each ovule, a large, diploid, spore mother cell develops. This cell divides by meiosis to produce four haploid cells. All but one of these degenerates and the one surviving haploid cell then develops into an embryo sac. The embryo sac absorbs nutrients from the nucleus and grows larger. Its n ...
ch 29-30 plant diversity notes-2007
... angiosperms include flowers and fruits • Angiosperms are flowering plants • These seed plants have reproductive structures called flowers and fruits • They are the most widespread and diverse of all ...
... angiosperms include flowers and fruits • Angiosperms are flowering plants • These seed plants have reproductive structures called flowers and fruits • They are the most widespread and diverse of all ...
Flowering plant

The flowering plants (angiosperms), also known as Angiospermae or Magnoliophyta, are the most diverse group of land plants. Angiosperms are seed-producing plants like the gymnosperms and can be distinguished from the gymnosperms by characteristics including flowers, endosperm within the seeds, and the production of fruits that contain the seeds. Etymologically, angiosperm means a plant that produces seeds within an enclosure, in other words, a fruiting plant.The ancestors of flowering plants diverged from gymnosperms around 245–202 million years ago, and the first flowering plants known to exist are from 160 million years ago. They diversified enormously during the Lower Cretaceous and became widespread around 120 million years ago, but replaced conifers as the dominant trees only around 60–100 million years ago.