Phosphorus retention in forest soils and the functioning of
... Phosphorus (P) retention properties of soils typical for boreal forest, i.e. podzolic soil and peat soils, vary significantly, but the range of this variation has not been sufficiently documented. To assess the usefulness of buffer zones used in forestry in removing P from the discharge by chemical ...
... Phosphorus (P) retention properties of soils typical for boreal forest, i.e. podzolic soil and peat soils, vary significantly, but the range of this variation has not been sufficiently documented. To assess the usefulness of buffer zones used in forestry in removing P from the discharge by chemical ...
the nutritive significance of the amino acids
... the functions of these amino acids was conducted by Henriques and Hansen (50). These authors reported that the removal of arginine, hist!idine, and lysine from an enzyme digest of a protein yields a mixture of amino acids which is adequate for the maintenance of positive nitrogen balance. Their conc ...
... the functions of these amino acids was conducted by Henriques and Hansen (50). These authors reported that the removal of arginine, hist!idine, and lysine from an enzyme digest of a protein yields a mixture of amino acids which is adequate for the maintenance of positive nitrogen balance. Their conc ...
Organic and Inorganic Dietary Phosphorus and Its Management in
... during the later stages of treatment is frequently underappreciated. For example, one study found that a 4-hour hemodialysis treatment removed an average of 923 ± 12 mg of phosphorus versus 1127 ± 15 mg in a 5-hour session.50 In comparison, phosphorus removal with continuous ambulatory peritoneal di ...
... during the later stages of treatment is frequently underappreciated. For example, one study found that a 4-hour hemodialysis treatment removed an average of 923 ± 12 mg of phosphorus versus 1127 ± 15 mg in a 5-hour session.50 In comparison, phosphorus removal with continuous ambulatory peritoneal di ...
Traditional agroforestry in the eastern Himalayan region
... Abstract: Large scale land use transition for maximizing the benefits to meet the rising demands for food and other ecosystem services for the well being of the societies has been the main problem confronting sustainable development in the mountain areas. Agroforestry is one of the favoured land man ...
... Abstract: Large scale land use transition for maximizing the benefits to meet the rising demands for food and other ecosystem services for the well being of the societies has been the main problem confronting sustainable development in the mountain areas. Agroforestry is one of the favoured land man ...
Asif, M., 2015. Pharmacological activities and
... Solanaceae (Weinmann, 1997; Matern et al, 1999). Many monocotyledonous plants, especially the Gramineae and orchids, also contain large amounts of coumarins. Although mainly synthesised in the leaves, coumarins occur at the highest levels in the fruits, followed by the roots and stems. In addition, ...
... Solanaceae (Weinmann, 1997; Matern et al, 1999). Many monocotyledonous plants, especially the Gramineae and orchids, also contain large amounts of coumarins. Although mainly synthesised in the leaves, coumarins occur at the highest levels in the fruits, followed by the roots and stems. In addition, ...
Studies of the Physiology, Pharmacology, and Biochemistry of the
... now known to be principally IAA (64), is stable to heating in acid in crude extracts of cabbage leaves and for this reason was once held to be an auxin different from IAA[Link et al. (81)]. Several new and powerful methods are now available for the chemical characterization of a native plant growth ...
... now known to be principally IAA (64), is stable to heating in acid in crude extracts of cabbage leaves and for this reason was once held to be an auxin different from IAA[Link et al. (81)]. Several new and powerful methods are now available for the chemical characterization of a native plant growth ...
Medicinal Uses - esculenta.org
... and 1600's are full of recipes and uses for plantain. It was considered to be almost a panacea - a cure-all, and a quick search shows that is has historically been recommended as a treatment for just about everything, up to and including dog bites, ulcers, ringworm, jaundice, epilepsy, liver obstruc ...
... and 1600's are full of recipes and uses for plantain. It was considered to be almost a panacea - a cure-all, and a quick search shows that is has historically been recommended as a treatment for just about everything, up to and including dog bites, ulcers, ringworm, jaundice, epilepsy, liver obstruc ...
Practical - UAHS-S
... The plants are shrubs; levees are simple, shiny with auricles. Flowers are star shaped; Flowers used as loose flowers and in the production of perfumers, peak flowering in rainy season. Varieties (TNAU, Coimbatore): Parimullai, CO-1 Mullai and CO-2 Mullai ...
... The plants are shrubs; levees are simple, shiny with auricles. Flowers are star shaped; Flowers used as loose flowers and in the production of perfumers, peak flowering in rainy season. Varieties (TNAU, Coimbatore): Parimullai, CO-1 Mullai and CO-2 Mullai ...
Soil profile CO2 concentrations variations from forested and clear
... Subsurface soil CO2 concentration is an important component of the terrestrial C budget and site specific information on the spatial and temporal variability and how it responds to forest management is needed for accurately estimating ecosystem C budgets. The objectives of this study were to examine ...
... Subsurface soil CO2 concentration is an important component of the terrestrial C budget and site specific information on the spatial and temporal variability and how it responds to forest management is needed for accurately estimating ecosystem C budgets. The objectives of this study were to examine ...
Development 128, 1771-1783 - The Company of Biologists
... 1774 E. Semiarti and others leaves had obvious humps at the base of the leaf lamina (Fig. 1B,C), which also resulted in an asymmetric lamina (Fig. 2B). The juvenile leaves of wild-type plants had no obvious serrations (Poethig, 1997; Hamada et al., 2000). The allelic mutations as22 and as2-4 also g ...
... 1774 E. Semiarti and others leaves had obvious humps at the base of the leaf lamina (Fig. 1B,C), which also resulted in an asymmetric lamina (Fig. 2B). The juvenile leaves of wild-type plants had no obvious serrations (Poethig, 1997; Hamada et al., 2000). The allelic mutations as22 and as2-4 also g ...
Native Flowers and all Grasses
... Native flowers are marked with the native symbol ˜ and the source of the plant stock or seed used to grow these plants is given. Those without the Minnesota symbol are selections or cultivated varieties bred from the Minnesota species. In those cases, the term “cultivar,” “selected,” or “selection” ...
... Native flowers are marked with the native symbol ˜ and the source of the plant stock or seed used to grow these plants is given. Those without the Minnesota symbol are selections or cultivated varieties bred from the Minnesota species. In those cases, the term “cultivar,” “selected,” or “selection” ...
SelenoPrecise
... Selenium in the agricultural soil is inorganic. Once it gets absorbed by plants (and ends up in animals) it gets converted to organic selenium. The selenium we get from our diet can be bound to amino acids such as methionine and cystein. In contrast, selenium in supplements can either organic or ino ...
... Selenium in the agricultural soil is inorganic. Once it gets absorbed by plants (and ends up in animals) it gets converted to organic selenium. The selenium we get from our diet can be bound to amino acids such as methionine and cystein. In contrast, selenium in supplements can either organic or ino ...
Lessons - Upper Kuskokwim
... something after you have disturbed them, and praying while collecting and preparing medicinal plants. Others say that you should talk to the plant and tell it what you are going to use it for. The time of year for harvesting some plants really matters. The parts of some plants are stronger at differ ...
... something after you have disturbed them, and praying while collecting and preparing medicinal plants. Others say that you should talk to the plant and tell it what you are going to use it for. The time of year for harvesting some plants really matters. The parts of some plants are stronger at differ ...
Meristem
... Most angiosperm shoot apical meristems can be described by the tunica-corpus theory of meristem organization, where outer cell layers or the tunica covers the inner body or corpus layers of the meristem. The tunica layers are characterized by having anticlinal (perpendicular to the surface) cell div ...
... Most angiosperm shoot apical meristems can be described by the tunica-corpus theory of meristem organization, where outer cell layers or the tunica covers the inner body or corpus layers of the meristem. The tunica layers are characterized by having anticlinal (perpendicular to the surface) cell div ...
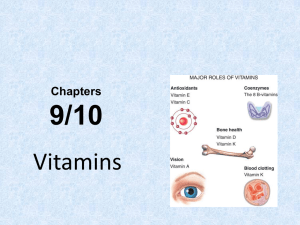
Chapter 9: Vitamins: Vital Keys to Health
... precursors that the body can convert to the active vitamin form. Growing conditions, storage, processing, and cooking all affect the amounts of vitamins in foods. • For at the last 3,000 years, there has been an empirical understanding that some diseases (which we now call vitamin deficiency disease ...
... precursors that the body can convert to the active vitamin form. Growing conditions, storage, processing, and cooking all affect the amounts of vitamins in foods. • For at the last 3,000 years, there has been an empirical understanding that some diseases (which we now call vitamin deficiency disease ...
Phytochemical and Pharmacological activity of Genus Plumeria: An
... isolated from leaves. Peckolt and Boorsma have successfully isolated Fulvoplummierin, Plumericin along with three new compounds isoplumericin, β-dihydroplumericin and β-dihydroplumericinic acid from roots of Plumeria acuminata. The steam distillate of Plumeria acuminata yields an essential oil (0.04 ...
... isolated from leaves. Peckolt and Boorsma have successfully isolated Fulvoplummierin, Plumericin along with three new compounds isoplumericin, β-dihydroplumericin and β-dihydroplumericinic acid from roots of Plumeria acuminata. The steam distillate of Plumeria acuminata yields an essential oil (0.04 ...
Organic selenium with 89% bioavailability
... Selenium in the agricultural soil is inorganic. Once it gets absorbed by plants (and ends up in animals) it gets converted to organic selenium. The selenium we get from our diet can be bound to amino acids such as methionine and cystein. In contrast, selenium in supplements can either be organic or ...
... Selenium in the agricultural soil is inorganic. Once it gets absorbed by plants (and ends up in animals) it gets converted to organic selenium. The selenium we get from our diet can be bound to amino acids such as methionine and cystein. In contrast, selenium in supplements can either be organic or ...
Effects of WClMV and root-flooding on white clover
... as cropping practises. WClMV infection may strongly impact white clover’s performance, hence affecting its ability to compete with other plants in the pasture. In the field, the legume may also experience important stress induced by excess water in soils mainly due to over-irrigation or heavy rainfa ...
... as cropping practises. WClMV infection may strongly impact white clover’s performance, hence affecting its ability to compete with other plants in the pasture. In the field, the legume may also experience important stress induced by excess water in soils mainly due to over-irrigation or heavy rainfa ...
VITAMINS
... Vitamin E is absorbed along with fat in the small intestine. Bile salts are necessary for the absorption. In the liver, it is incorporated into lipoproteins (VLDL and LDL) and transported. Vitamin E is stored in adipose tissue, liver and muscle. The normal plasma level of tocopherol in less than 1 m ...
... Vitamin E is absorbed along with fat in the small intestine. Bile salts are necessary for the absorption. In the liver, it is incorporated into lipoproteins (VLDL and LDL) and transported. Vitamin E is stored in adipose tissue, liver and muscle. The normal plasma level of tocopherol in less than 1 m ...
controlling volunteer cotton
... may be a useful strategy, killing some plants, but also buying time. Applying Spray.Seed to cotton plants will defoliate the plants, burning off most or all the leaves, setting plant growth back by many weeks. This will greatly reduce the growth rate of the plants, greatly reduce the moisture use of ...
... may be a useful strategy, killing some plants, but also buying time. Applying Spray.Seed to cotton plants will defoliate the plants, burning off most or all the leaves, setting plant growth back by many weeks. This will greatly reduce the growth rate of the plants, greatly reduce the moisture use of ...
Mustard Production Manual - Saskatchewan Mustard Development
... recommendations should be based on realistic target yields which will vary with the type and variety of mustard and are based on available soil moisture reserves and an estimation of the growing season precipitation. Nitrogen Nitrogen (N) is essential for vigorous growth, high yield and quality of m ...
... recommendations should be based on realistic target yields which will vary with the type and variety of mustard and are based on available soil moisture reserves and an estimation of the growing season precipitation. Nitrogen Nitrogen (N) is essential for vigorous growth, high yield and quality of m ...
In This Issue - The Cycad Society
... dinosaurs were still roaming the earth. Today, the ±180 remaining species are restricted to specific tropical and subtropical regions of the Old and the New Worlds. Recent recommendations of the World Conservation Union (IUCN) include encouraging extensive propagation and culture of these magnificen ...
... dinosaurs were still roaming the earth. Today, the ±180 remaining species are restricted to specific tropical and subtropical regions of the Old and the New Worlds. Recent recommendations of the World Conservation Union (IUCN) include encouraging extensive propagation and culture of these magnificen ...
Carbon dioxide metabolism and ecological significance
... 45% of global net primary production per year. Carbon fixation resulting from Rubisco’s activity forms more than 1011 tons of atmospheric CO2 annually [16]. Its catalytic activity is chiefly associated with the central part of the Calvin-Benson-Basham (CBB) reductive pentose phosphate pathway. Rubis ...
... 45% of global net primary production per year. Carbon fixation resulting from Rubisco’s activity forms more than 1011 tons of atmospheric CO2 annually [16]. Its catalytic activity is chiefly associated with the central part of the Calvin-Benson-Basham (CBB) reductive pentose phosphate pathway. Rubis ...
Deficiency in plastidic glutamine synthetase alters proline
... degradation of proline occurs in the mitochondria and involves oxidation to pyrroline-5-carboxylate (P5C) by proline oxidase (also called proline dehydrogenase, PDH), and subsequent conversion into glutamate by pyrroline-5carboxylate dehydrogenase (P5CDH) (Székely et al., 2008 and references therei ...
... degradation of proline occurs in the mitochondria and involves oxidation to pyrroline-5-carboxylate (P5C) by proline oxidase (also called proline dehydrogenase, PDH), and subsequent conversion into glutamate by pyrroline-5carboxylate dehydrogenase (P5CDH) (Székely et al., 2008 and references therei ...
Plant nutrition
.jpg?width=300)
Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds that are necessary for plant growth, and also of their external supply and internal metabolism. In 1972, E. Epstein defined two criteria for an element to be essential for plant growth: in its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle; or that the element is part of some essential plant constituent or metabolite.This is in accordance with Liebig's law of the minimum. There are 14 essential plant nutrients. Carbon and oxygen are absorbed from the air, while other nutrients including water are typically obtained from the soil (exceptions include some parasitic or carnivorous plants).Plants must obtain the following mineral nutrients from the growing media: the primary macronutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K) the three secondary macronutrients: calcium (Ca), sulfur (S), magnesium (Mg) the micronutrients/trace minerals: boron (B), chlorine (Cl), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni)The macronutrients are consumed in larger quantities and are present in plant tissue in quantities from 0.2% to 4.0% (on a dry matter weight basis). Micro nutrients are present in plant tissue in quantities measured in parts per million, ranging from 5 to 200 ppm, or less than 0.02% dry weight.Most soil conditions across the world can provide plants with adequate nutrition and do not require fertilizer for a complete life cycle. However, humans can artificially modify soil through the addition of fertilizer to promote vigorous growth and increase yield. The plants are able to obtain their required nutrients from the fertilizer added to the soil. A colloidal carbonaceous residue, known as humus, can serve as a nutrient reservoir. Even with adequate water and sunshine, nutrient deficiency can limit growth.Nutrient uptake from the soil is achieved by cation exchange, where root hairs pump hydrogen ions (H+) into the soil through proton pumps. These hydrogen ions displace cations attached to negatively charged soil particles so that the cations are available for uptake by the root.Plant nutrition is a difficult subject to understand completely, partly because of the variation between different plants and even between different species or individuals of a given clone. An element present at a low level may cause deficiency symptoms, while the same element at a higher level may cause toxicity. Further, deficiency of one element may present as symptoms of toxicity from another element. An abundance of one nutrient may cause a deficiency of another nutrient. For example, lower availability of a given nutrient such as SO42− can affect the uptake of another nutrient, such as NO3−. As another example, K+ uptake can be influenced by the amount of NH4+ available.The root, especially the root hair, is the most essential organ for the uptake of nutrients. The structure and architecture of the root can alter the rate of nutrient uptake. Nutrient ions are transported to the center of the root, the stele in order for the nutrients to reach the conducting tissues, xylem and phloem. The Casparian strip, a cell wall outside the stele but within the root, prevents passive flow of water and nutrients, helping to regulate the uptake of nutrients and water. Xylem moves water and inorganic molecules within the plant and phloem accounts for organic molecule transportation. Water potential plays a key role in a plants nutrient uptake. If the water potential is more negative within the plant than the surrounding soils, the nutrients will move from the region of higher solute concentration—in the soil—to the area of lower solute concentration: in the plant.There are three fundamental ways plants uptake nutrients through the root: simple diffusion, occurs when a nonpolar molecule, such as O2, CO2, and NH3 follows a concentration gradient, moving passively through the cell lipid bilayer membrane without the use of transport proteins. facilitated diffusion, is the rapid movement of solutes or ions following a concentration gradient, facilitated by transport proteins. Active transport, is the uptake by cells of ions or molecules against a concentration gradient; this requires an energy source, usually ATP, to power molecular pumps that move the ions or molecules through the membrane. Nutrients are moved inside a plant to where they are most needed. For example, a plant will try to supply more nutrients to its younger leaves than to its older ones. When nutrients are mobile, symptoms of any deficiency become apparent first on the older leaves. However, not all nutrients are equally mobile. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are mobile nutrients, while the others have varying degrees of mobility. When a less mobile nutrient is deficient, the younger leaves suffer because the nutrient does not move up to them but stays in the older leaves. This phenomenon is helpful in determining which nutrients a plant may be lacking.Many plants engage in symbiosis with microorganisms. Two important types of these relationship are with bacteria such as rhizobia, that carry out biological nitrogen fixation, in which atmospheric nitrogen (N2) is converted into ammonium (NH4); and with mycorrhizal fungi, which through their association with the plant roots help to create a larger effective root surface area. Both of these mutualistic relationships enhance nutrient uptake. Though nitrogen is plentiful in the Earth's atmosphere, relatively few plants harbor nitrogen fixing bacteria, so most plants rely on nitrogen compounds present in the soil to support their growth. These can be supplied by mineralization of soil organic matter or added plant residues, nitrogen fixing bacteria, animal waste, or through the application of fertilizers.Hydroponics, is a method for growing plants in a water-nutrient solution without the use of nutrient-rich soil. It allows researchers and home gardeners to grow their plants in a controlled environment. The most common solution, is the Hoagland solution, developed by D. R. Hoagland in 1933, the solution consists of all the essential nutrients in the correct proportions necessary for most plant growth. An aerator is used to prevent an anoxic event or hypoxia. Hypoxia can affect nutrient uptake of a plant because without oxygen present, respiration becomes inhibited within the root cells. The Nutrient film technique is a variation of hydroponic technique. The roots are not fully submerged, which allows for adequate aeration of the roots, while a ""film"" thin layer of nutrient rich water is pumped through the system to provide nutrients and water to the plant.