Quick Links
... all life forms were divided into two main categories, plants and animals. Organisms that photosynthesised and lacked mobility were classified as plants; those that had locomotion and ingested food were classified as animals. Bacteria were traditionally categorised as plants because many forms of bac ...
... all life forms were divided into two main categories, plants and animals. Organisms that photosynthesised and lacked mobility were classified as plants; those that had locomotion and ingested food were classified as animals. Bacteria were traditionally categorised as plants because many forms of bac ...
Wildflower Spot– April 2014 - Gloucester County Virginia
... drought. As needed, pruning can be done in late fall or early spring. Possumhaw viburnum ...
... drought. As needed, pruning can be done in late fall or early spring. Possumhaw viburnum ...
Scientific Name: Chenopodium murale L
... spikes, flowers inconspicuous, petals absent, perianth 5-lobed, greenish, mealy ,fleshy; stamens 5, pistil single with 2 stigmas. Fruit a single-seeded utricle; seeds black nutlets, keeled and pitted. Habitat & Distribution: Widespread all over the world in wet habitats. In U.A.E the plant is a fair ...
... spikes, flowers inconspicuous, petals absent, perianth 5-lobed, greenish, mealy ,fleshy; stamens 5, pistil single with 2 stigmas. Fruit a single-seeded utricle; seeds black nutlets, keeled and pitted. Habitat & Distribution: Widespread all over the world in wet habitats. In U.A.E the plant is a fair ...
plants n flowers ppt
... germinate. The seed absorbs water from the environment allowing the embryo to absorb food and start to grow. Germination (jur muh NAY shun) occurs when the embryo begins to grow and pushes out of the seed. First the root pushes downward. Next the stem and leaves push upward. Once you see the leaves ...
... germinate. The seed absorbs water from the environment allowing the embryo to absorb food and start to grow. Germination (jur muh NAY shun) occurs when the embryo begins to grow and pushes out of the seed. First the root pushes downward. Next the stem and leaves push upward. Once you see the leaves ...
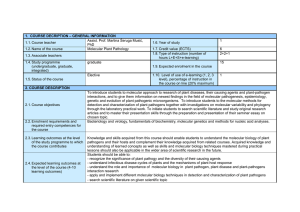
83820 Molecular Plant Pathology
... through the laboratory practical work. To initiate students to search scientific literature and study original research articles and to master their presentation skills through the preparation and presentation of their seminar essay on chosen topic. Bacteriology and virology, fundamentals of biochem ...
... through the laboratory practical work. To initiate students to search scientific literature and study original research articles and to master their presentation skills through the preparation and presentation of their seminar essay on chosen topic. Bacteriology and virology, fundamentals of biochem ...
Fordhook Giant Swiss Chard
... Big, beautiful and green, this chard is the most productive and longest lived that we know. Though technically a cool season veggie, Fordhook Giant produces through all seasons in our zone 8 garden (yes, right through the snow) and only slows down when it goes to seed in its second year. Now, that g ...
... Big, beautiful and green, this chard is the most productive and longest lived that we know. Though technically a cool season veggie, Fordhook Giant produces through all seasons in our zone 8 garden (yes, right through the snow) and only slows down when it goes to seed in its second year. Now, that g ...
Most mosses and ferns live in moist environments.
... You may have seen ferns growing in the woods or in a garden. The leaves of ferns, called fronds, are often included in a flower bouquet. The next time you have a chance to look at a fern frond, take a look at the back. You will probably see many small clusters similar to those shown to the right. Th ...
... You may have seen ferns growing in the woods or in a garden. The leaves of ferns, called fronds, are often included in a flower bouquet. The next time you have a chance to look at a fern frond, take a look at the back. You will probably see many small clusters similar to those shown to the right. Th ...
Most mosses and ferns live in moist environments.
... crowded. Some were pushed to the very edges of the water. Then, after a period of dry weather, the pond shrank. Some organisms at the edge were no longer in the water. The ones that were able to survive were now living on land. Scientists think that something like this took place in millions of wate ...
... crowded. Some were pushed to the very edges of the water. Then, after a period of dry weather, the pond shrank. Some organisms at the edge were no longer in the water. The ones that were able to survive were now living on land. Scientists think that something like this took place in millions of wate ...
92 - 97 - BAschools.org
... You may have seen ferns growing in the woods or in a garden. The leaves of ferns, called fronds, are often included in a flower bouquet. The next time you have a chance to look at a fern frond, take a look at the back. You will probably see many small clusters similar to those shown to the right. Th ...
... You may have seen ferns growing in the woods or in a garden. The leaves of ferns, called fronds, are often included in a flower bouquet. The next time you have a chance to look at a fern frond, take a look at the back. You will probably see many small clusters similar to those shown to the right. Th ...
Phytohormones - Napa Valley College
... sources to targets 2. Amplify the signal produced by the phytohormone Hormone, from the Greek word horman, meaning "to s:mulate”. Hormones control • Growth • Development • Movement. ...
... sources to targets 2. Amplify the signal produced by the phytohormone Hormone, from the Greek word horman, meaning "to s:mulate”. Hormones control • Growth • Development • Movement. ...
ethnobotanical survey,phytochemical analysis,bioassay and
... products, dietary supplements and ecological balance. Medicinal value- depends on chemical substance; produces definite physiological effect on the body Bioactive compounds: alkaloids, tannins, flavonoids, phenolics ...
... products, dietary supplements and ecological balance. Medicinal value- depends on chemical substance; produces definite physiological effect on the body Bioactive compounds: alkaloids, tannins, flavonoids, phenolics ...
Nitrogen
... 4. Lost to atmosphere through denitrification. 5. Lost to atmosphere through volatilization. ...
... 4. Lost to atmosphere through denitrification. 5. Lost to atmosphere through volatilization. ...
Plants
... produce their own food using energy from sunlight. Plants have green pigment called chlorophyll in their cells, mainly in the leaves. This pigment allows plants to make food from sunlight, water and carbon dioxide in a process called photosynthesis. Plants manufacture much more food than they can re ...
... produce their own food using energy from sunlight. Plants have green pigment called chlorophyll in their cells, mainly in the leaves. This pigment allows plants to make food from sunlight, water and carbon dioxide in a process called photosynthesis. Plants manufacture much more food than they can re ...
Aquatic Plants of Glen Lake
... Illinois pondweed is a common submersed plant. There are about 80 species of pondweeds in the world. Illinois pondweed grows equally well in swift-flowing rivers or quiet lake margins. Illinois pondweed has two primary leaf shapes: the floating leaves are more-or-less elliptic in shape, and are much ...
... Illinois pondweed is a common submersed plant. There are about 80 species of pondweeds in the world. Illinois pondweed grows equally well in swift-flowing rivers or quiet lake margins. Illinois pondweed has two primary leaf shapes: the floating leaves are more-or-less elliptic in shape, and are much ...
Plant Science Unit 4 Review – Plant Anatomy and Physiology 4.1
... _____14. A leaf that consists of a petiole and a leaf blade. _____15. The movement of water vapor through a stoma out of a plant. _____16. A pair of cells that regulate the opening and closing of the stomata. _____17. The process by which green plants convert solar energy into stored chemical energy ...
... _____14. A leaf that consists of a petiole and a leaf blade. _____15. The movement of water vapor through a stoma out of a plant. _____16. A pair of cells that regulate the opening and closing of the stomata. _____17. The process by which green plants convert solar energy into stored chemical energy ...
White Gerbera Daisy
... White Gerbera Daisy will grow to be about 12 inches tall at maturity extending to 16 inches tall with the flowers, with a spread of 12 inches. Its foliage tends to remain dense right to the ground, not requiring facer plants in front. Although it's not a true annual, this fast-growing plant can be e ...
... White Gerbera Daisy will grow to be about 12 inches tall at maturity extending to 16 inches tall with the flowers, with a spread of 12 inches. Its foliage tends to remain dense right to the ground, not requiring facer plants in front. Although it's not a true annual, this fast-growing plant can be e ...
Life Cycle of a Plant
... water from a rain storm or from a waterfall, the sperms swim through the water to the stems which support the eggs. After the sperm has fertilized an egg a spore case grows out of the moss on a stem. The spore case is often protected by a cap which blows off when the case ripens and dries out. The s ...
... water from a rain storm or from a waterfall, the sperms swim through the water to the stems which support the eggs. After the sperm has fertilized an egg a spore case grows out of the moss on a stem. The spore case is often protected by a cap which blows off when the case ripens and dries out. The s ...
Directed Reading A
... Some seeds are carried by the wind. Some fruits are eaten by animals, which discard the seeds. Some fruits, such as burrs, are carried by sticking to animal fur. ...
... Some seeds are carried by the wind. Some fruits are eaten by animals, which discard the seeds. Some fruits, such as burrs, are carried by sticking to animal fur. ...
Genetics Practice
... b. Phenotypic Ratio of Offspring = 17. In radishes, when a plant homozygous for red radishes is crossed with a plant for homozygous white radishes, plants bearing purple radishes are produced. a. What would the offspring look like is a cross between a purple and a white? ...
... b. Phenotypic Ratio of Offspring = 17. In radishes, when a plant homozygous for red radishes is crossed with a plant for homozygous white radishes, plants bearing purple radishes are produced. a. What would the offspring look like is a cross between a purple and a white? ...
Carpels
... carbohydrates in underground roots (carrots) or stems (onion) ○ In second year, stored carbohydrates are used to produce flowers and seeds Perennials live three or more years. ○ Typically flower every year, and keep growing for another season ○ In some species the reproductive cycle repeats each y ...
... carbohydrates in underground roots (carrots) or stems (onion) ○ In second year, stored carbohydrates are used to produce flowers and seeds Perennials live three or more years. ○ Typically flower every year, and keep growing for another season ○ In some species the reproductive cycle repeats each y ...
Whorled Rosinweed - Gloucester County
... Very tough and adaptable, preferring rich, welldrained soils, this plant is easy to grow in the home garden, in partial to full shade. Whorled Rosinweed spreads freely and fills in nicely around other shade perennials; it is drought tolerant once established. A native in eastern U.S. and most counti ...
... Very tough and adaptable, preferring rich, welldrained soils, this plant is easy to grow in the home garden, in partial to full shade. Whorled Rosinweed spreads freely and fills in nicely around other shade perennials; it is drought tolerant once established. A native in eastern U.S. and most counti ...
Royal Standard Hosta
... Royal Standard Hosta will grow to be about 16 inches tall at maturity extending to 28 inches tall with the flowers, with a spread of 4 feet. When grown in masses or used as a bedding plant, individual plants should be spaced approximately 4 feet apart. Its foliage tends to remain dense right to the ...
... Royal Standard Hosta will grow to be about 16 inches tall at maturity extending to 28 inches tall with the flowers, with a spread of 4 feet. When grown in masses or used as a bedding plant, individual plants should be spaced approximately 4 feet apart. Its foliage tends to remain dense right to the ...
Montrose White Dwarf Calamint*
... with the flowers, with a spread of 15 inches. It grows at a medium rate, and under ideal conditions can be expected to live for approximately 10 years. This plant does best in full sun to partial shade. It prefers to grow in average to moist conditions, and shouldn't be allowed to dry out. It is not ...
... with the flowers, with a spread of 15 inches. It grows at a medium rate, and under ideal conditions can be expected to live for approximately 10 years. This plant does best in full sun to partial shade. It prefers to grow in average to moist conditions, and shouldn't be allowed to dry out. It is not ...
Student 2. Steps within Tissue Culture that Provide
... Secondly these explants are taken and put through a strict sterilisation process involving glass that is heated under pressure, the heating under pressure is to render the glass aseptic. The sterilisation process of the explants involves them being rinsed in an alcohol or bleach solution, being swir ...
... Secondly these explants are taken and put through a strict sterilisation process involving glass that is heated under pressure, the heating under pressure is to render the glass aseptic. The sterilisation process of the explants involves them being rinsed in an alcohol or bleach solution, being swir ...
History of botany

The history of botany examines the human effort to understand life on Earth by tracing the historical development of the discipline of botany—that part of natural science dealing with organisms traditionally treated as plants.Rudimentary botanical science began with empirically-based plant lore passed from generation to generation in the oral traditions of paleolithic hunter-gatherers. The first written records of plants were made in the Neolithic Revolution about 10,000 years ago as writing was developed in the settled agricultural communities where plants and animals were first domesticated. The first writings that show human curiosity about plants themselves, rather than the uses that could be made of them, appears in the teachings of Aristotle's student Theophrastus at the Lyceum in ancient Athens in about 350 BC; this is considered the starting point for modern botany. In Europe, this early botanical science was soon overshadowed by a medieval preoccupation with the medicinal properties of plants that lasted more than 1000 years. During this time, the medicinal works of classical antiquity were reproduced in manuscripts and books called herbals. In China and the Arab world, the Greco-Roman work on medicinal plants was preserved and extended.In Europe the Renaissance of the 14th–17th centuries heralded a scientific revival during which botany gradually emerged from natural history as an independent science, distinct from medicine and agriculture. Herbals were replaced by floras: books that described the native plants of local regions. The invention of the microscope stimulated the study of plant anatomy, and the first carefully designed experiments in plant physiology were performed. With the expansion of trade and exploration beyond Europe, the many new plants being discovered were subjected to an increasingly rigorous process of naming, description, and classification.Progressively more sophisticated scientific technology has aided the development of contemporary botanical offshoots in the plant sciences, ranging from the applied fields of economic botany (notably agriculture, horticulture and forestry), to the detailed examination of the structure and function of plants and their interaction with the environment over many scales from the large-scale global significance of vegetation and plant communities (biogeography and ecology) through to the small scale of subjects like cell theory, molecular biology and plant biochemistry.