Plants Worksheet_answer key - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
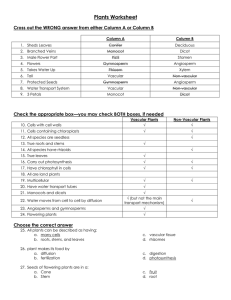
... 12. All species are seedless 13. True roots and stems ...
... 12. All species are seedless 13. True roots and stems ...
World of Plants – Summary
... ovules become seeds with seed coats, food stores and embryos. The ovary wall becomes the rest of the fruit, which surrounds the seeds. Depending on the plant the ovary wall may become fleshy (cherry, grape) or dry and hard (sycamore). 19. It is vital that seeds are dispersed away from each other and ...
... ovules become seeds with seed coats, food stores and embryos. The ovary wall becomes the rest of the fruit, which surrounds the seeds. Depending on the plant the ovary wall may become fleshy (cherry, grape) or dry and hard (sycamore). 19. It is vital that seeds are dispersed away from each other and ...
Plant Reproduction
... *Some flowers are only female, some flowers are only male and some flowers have both male and female gametes (pollen and ovuole). ...
... *Some flowers are only female, some flowers are only male and some flowers have both male and female gametes (pollen and ovuole). ...
Seed plants
... The term gymnosperm comes from a Greek word meaning “naked seed.” Gymnosperms do not produce true flowers or fruit, and therefore the seeds of gymnosperms are not enclosed in flowers or fruit. The seeds of most gymnosperms develop on the surface of the scales of female cones. Gymnosperms are thought ...
... The term gymnosperm comes from a Greek word meaning “naked seed.” Gymnosperms do not produce true flowers or fruit, and therefore the seeds of gymnosperms are not enclosed in flowers or fruit. The seeds of most gymnosperms develop on the surface of the scales of female cones. Gymnosperms are thought ...
Plant Reproduction & Development
... Flowers are the reproductive structure of angiosperms Sepals: Enclose the bud before it opens Protect flower while it’s developing ...
... Flowers are the reproductive structure of angiosperms Sepals: Enclose the bud before it opens Protect flower while it’s developing ...
Plant adaptations guided notes
... 5. The jobs of the ____________ are to anchor the plant and absorb water. Some roots are even modified to store ____________ (like carrots!). a. To help absorb ____________, plants have tiny extensions for more surface. These are called __________ ______________. ...
... 5. The jobs of the ____________ are to anchor the plant and absorb water. Some roots are even modified to store ____________ (like carrots!). a. To help absorb ____________, plants have tiny extensions for more surface. These are called __________ ______________. ...
Native Plants and Wildflowers Study Guide for Midterm 1
... 4. Provide definitions for each of the following terms; complete flower, incomplete flower, perfect flower, imperfect flower. ...
... 4. Provide definitions for each of the following terms; complete flower, incomplete flower, perfect flower, imperfect flower. ...
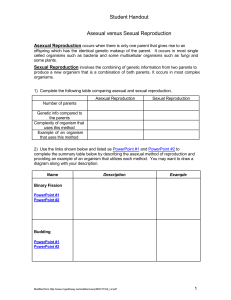
Student Handout Asexual versus Sexual Reproduction
... fertilization pattern occurs when the gametes (sex cells) meet outside the bodies of both parents. To keep the sperm and egg moist it must occur in an aquatic environment. Internal fertilization occurs inside the female body in terrestrial or land animals. The sperm is transferred using a specialize ...
... fertilization pattern occurs when the gametes (sex cells) meet outside the bodies of both parents. To keep the sperm and egg moist it must occur in an aquatic environment. Internal fertilization occurs inside the female body in terrestrial or land animals. The sperm is transferred using a specialize ...
Mosses and Liverworts (Non
... like minerals to be transported quickly and effectively throughout the entire body of the plant. Even though they have tube-like cells, ferns and their relatives reproduce using spores. They need standing water so that their sperm can swim to find eggs to fertilize during reproduction. Ferns can gro ...
... like minerals to be transported quickly and effectively throughout the entire body of the plant. Even though they have tube-like cells, ferns and their relatives reproduce using spores. They need standing water so that their sperm can swim to find eggs to fertilize during reproduction. Ferns can gro ...
petal 22.2 Reproduction in Flowering Plants TEKS 6G, 10B
... • Animal pollinated flowers have larger flowers and less pollen. – many flowering plants pollinated by animal pollinators ...
... • Animal pollinated flowers have larger flowers and less pollen. – many flowering plants pollinated by animal pollinators ...
22.2 Reproduction in Flowering Plants TEKS 6G
... • Animal pollinated flowers have larger flowers and less pollen. – many flowering plants pollinated by animal pollinators ...
... • Animal pollinated flowers have larger flowers and less pollen. – many flowering plants pollinated by animal pollinators ...
Araceae Family - Missouri State University
... o mostly alternate but may be opposite or whorled o simple or compound o sometimes highly reduced o colored leaves (bracts) often mistaken as the flowers Flowers o specialized type of miniature inflorescence called a cyathium occurs in about 1,500 of the species in the genera Euphorbia and Chamaesyc ...
... o mostly alternate but may be opposite or whorled o simple or compound o sometimes highly reduced o colored leaves (bracts) often mistaken as the flowers Flowers o specialized type of miniature inflorescence called a cyathium occurs in about 1,500 of the species in the genera Euphorbia and Chamaesyc ...
Slide 1
... b) Chemicals that act as insect hormones—disrupt normal growth and development c) Thorns/thistles—undesirable or hard to eat ...
... b) Chemicals that act as insect hormones—disrupt normal growth and development c) Thorns/thistles—undesirable or hard to eat ...
Influence of Temperature on Pollen Germination
... B. When the pollen of a plant pollinates the flower on another plant of the same species, it is said to be cross-pollination. C. Once pollen lands on the stigma, it grows a pollen tube down the style to the ovary. The cell within the grain of pollen divides to form two sperm nuclei, which travel dow ...
... B. When the pollen of a plant pollinates the flower on another plant of the same species, it is said to be cross-pollination. C. Once pollen lands on the stigma, it grows a pollen tube down the style to the ovary. The cell within the grain of pollen divides to form two sperm nuclei, which travel dow ...
The Life Cycle of A Plant
... Gather materials for planting the seeds. (Soil, lima beans, cups, dropper, water). Show the materials. Discuss the proper use of the materials. On chart paper, list the 5 Senses with students and remind them that scientists do not use their sense of taste. Explain to the children that they are going ...
... Gather materials for planting the seeds. (Soil, lima beans, cups, dropper, water). Show the materials. Discuss the proper use of the materials. On chart paper, list the 5 Senses with students and remind them that scientists do not use their sense of taste. Explain to the children that they are going ...
Plant Divisions
... 4. Specialized structures for reproduction including spores & seeds that do not dry out ...
... 4. Specialized structures for reproduction including spores & seeds that do not dry out ...
Bryophytes and Ferns
... 2. Which of the following is diploid? a. the archegonia of a moss b. a cell in the gametangia of a moss c. a cell that is part of the stalk of a moss sporophyte d. a spore produced by a sporophyte 3. In moss, _____ produce sperm. a. sporangia b. antheridia c. embryos d. archegonia 4. Fertilization i ...
... 2. Which of the following is diploid? a. the archegonia of a moss b. a cell in the gametangia of a moss c. a cell that is part of the stalk of a moss sporophyte d. a spore produced by a sporophyte 3. In moss, _____ produce sperm. a. sporangia b. antheridia c. embryos d. archegonia 4. Fertilization i ...
Flower Parts - Fort Bend ISD
... else – the stunning evolutionary success of angiosperms, or flowering plants.” ...
... else – the stunning evolutionary success of angiosperms, or flowering plants.” ...
Kingdom Plantae
... Getting Water and Nutrients Aquatic plants are surrounded by water and nutrients so most cells can just absorb them the environment. Terrestrial plants require a system for collecting and transporting water. Plants developed root systems that can collect and transport water. Some plants have shal ...
... Getting Water and Nutrients Aquatic plants are surrounded by water and nutrients so most cells can just absorb them the environment. Terrestrial plants require a system for collecting and transporting water. Plants developed root systems that can collect and transport water. Some plants have shal ...
Leaves have many functions
... It consists of three parts: • The stigma -- the pollen grains stick to this small sticky pad • The style -- the pollen grains grow down through this stem-like cylinder • The ovary -- this is where the young seeds (eggs) wait for the chromosomes in the pollen (sperm), and where they grow into mature ...
... It consists of three parts: • The stigma -- the pollen grains stick to this small sticky pad • The style -- the pollen grains grow down through this stem-like cylinder • The ovary -- this is where the young seeds (eggs) wait for the chromosomes in the pollen (sperm), and where they grow into mature ...
apical meristems
... • Plants exhibit a phenomena known as alternation of generations - this phenomena is shared with some green algae as well • Plants alternate between a diploid generation - the sporophyte; and a haploid generation - the gametophyte • The names refer to the reproductive structures produced by each gen ...
... • Plants exhibit a phenomena known as alternation of generations - this phenomena is shared with some green algae as well • Plants alternate between a diploid generation - the sporophyte; and a haploid generation - the gametophyte • The names refer to the reproductive structures produced by each gen ...
Plant reproduction

Plant reproduction is the production of new individuals or offspring in plants, which can be accomplished by sexual or asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction produces offspring by the fusion of gametes, resulting in offspring genetically different from the parent or parents. Asexual reproduction produces new individuals without the fusion of gametes, genetically identical to the parent plants and each other, except when mutations occur. In seed plants, the offspring can be packaged in a protective seed, which is used as an agent of dispersal.