Seed Vascular Plants
... - they protect seeds and aid in dispersal - pollination triggers a hormone change that causes the ovary walls to thicken and become pericarp. ...
... - they protect seeds and aid in dispersal - pollination triggers a hormone change that causes the ovary walls to thicken and become pericarp. ...
Plant Divisions1 - Turner
... • What did plants have to overcome to live on land? • What is the most primitive division of plants because they have no vascular system? • What is the most common example in this division and how do they reproduce? • Why are mosses so small? • What is the division of plants that contain a vascular ...
... • What did plants have to overcome to live on land? • What is the most primitive division of plants because they have no vascular system? • What is the most common example in this division and how do they reproduce? • Why are mosses so small? • What is the division of plants that contain a vascular ...
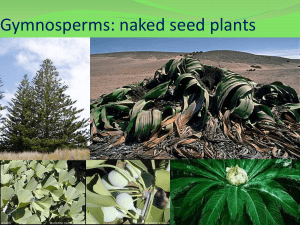
Gymnosperms
... B. Possession of a true seed. C. Contain secondary growth that forms woody stems D. No water necessary for sperm to reach egg. E. Leaves usually needle-like; exceptions exist. F. Sweden’s pines produce 75,000 tons of pollen each Spring. ...
... B. Possession of a true seed. C. Contain secondary growth that forms woody stems D. No water necessary for sperm to reach egg. E. Leaves usually needle-like; exceptions exist. F. Sweden’s pines produce 75,000 tons of pollen each Spring. ...
Plant Outline Notes
... All living organisms share the following characteristics: o They obtain and use resources for energy All organisms must obtain resources, such as food, oxygen, and water This provides required energy to perform the basic processes of life Autotrophs (for example plants) provide their own food ...
... All living organisms share the following characteristics: o They obtain and use resources for energy All organisms must obtain resources, such as food, oxygen, and water This provides required energy to perform the basic processes of life Autotrophs (for example plants) provide their own food ...
Asexual and Sexual Reproduction Study Guide
... Chromosome copied cell divides much like mitosis, but then divides again without making another copy resulting in 4 daughter cells with ½ the chromosomes of the parent cells. These cells become sex cells and are used in sexual reproduction resulting in offspring that is unique to both parents as eac ...
... Chromosome copied cell divides much like mitosis, but then divides again without making another copy resulting in 4 daughter cells with ½ the chromosomes of the parent cells. These cells become sex cells and are used in sexual reproduction resulting in offspring that is unique to both parents as eac ...
Answers to REVISION QUESTIONS File
... 14. This is the process where pollen from the anther is transferred to the stigma. This can be between plants (cross pollination) or within the same flower (self pollination). 15. Feathery stigma, stamens that hang out of the flower, lots of light weight pollen, dull, small. 16. Large, brightly colo ...
... 14. This is the process where pollen from the anther is transferred to the stigma. This can be between plants (cross pollination) or within the same flower (self pollination). 15. Feathery stigma, stamens that hang out of the flower, lots of light weight pollen, dull, small. 16. Large, brightly colo ...
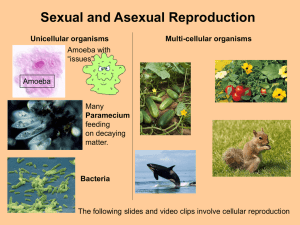
Sexual and Asexual Reproduction
... Asexual Reproduction are: Strawberry Runners. These are stems which grow from the base of strawberry plants. When they touch the ground they form new plants Daffodil Bulbs. These increase in number each year. Producing Clones of the original plant. Plant Cuttings. If you take a cutting from a Gerani ...
... Asexual Reproduction are: Strawberry Runners. These are stems which grow from the base of strawberry plants. When they touch the ground they form new plants Daffodil Bulbs. These increase in number each year. Producing Clones of the original plant. Plant Cuttings. If you take a cutting from a Gerani ...
Section 22.3 Summary – pages 588 - 597
... • Identify and analyze the characteristics of seed plants. • Analyze the advantages of seed and fruit production. ...
... • Identify and analyze the characteristics of seed plants. • Analyze the advantages of seed and fruit production. ...
Plant Reproduction - Cal State LA
... 2. Explain the difference between the angiosperm sporophyte and gametophyte 3. Describe the series of events that occur in the angiosperm life cycle from spore production to seed germination 4. Describe some modes of plant asexual reproduction and ...
... 2. Explain the difference between the angiosperm sporophyte and gametophyte 3. Describe the series of events that occur in the angiosperm life cycle from spore production to seed germination 4. Describe some modes of plant asexual reproduction and ...
07 - Plant Reproduction (ch.38)
... – this expands the seed, rupturing its coat, and triggers metabolic changes that cause the embryo to resume growth • The embryonic root, or radicle, is the first structure to emerge from the germinating seed • Next, the embryonic shoot breaks through the soil ...
... – this expands the seed, rupturing its coat, and triggers metabolic changes that cause the embryo to resume growth • The embryonic root, or radicle, is the first structure to emerge from the germinating seed • Next, the embryonic shoot breaks through the soil ...
Sample
... almost exclusively native to the tropics and subtropics of America, with one species occurring in western Africa. Many species are now cultivated around the globe, however. The most economically important species is the familiar pineapple. A few species are sources of fiber, others are cultivated fo ...
... almost exclusively native to the tropics and subtropics of America, with one species occurring in western Africa. Many species are now cultivated around the globe, however. The most economically important species is the familiar pineapple. A few species are sources of fiber, others are cultivated fo ...
Asexual vs. Sexual Reproduction
... No, not all animals have two parents. When necessary, some animals can be produced from just one parent. Some reptiles, such as this Komodo dragon, have only one parent. The process of creating offspring from just one individual is called asexual reproduction. Reproduction ...
... No, not all animals have two parents. When necessary, some animals can be produced from just one parent. Some reptiles, such as this Komodo dragon, have only one parent. The process of creating offspring from just one individual is called asexual reproduction. Reproduction ...
Chapter 12: Diversification of the Eukaryotes: Plants and Fungi
... The first vascular plants—the earliest ferns, horsetails, and some related forms—were able to grow much taller than their non-vascular predecessors. The evolution of vascular tissue made large plants possible because it made water and nutrient delivery more efficient. Like a circulatory system, ve ...
... The first vascular plants—the earliest ferns, horsetails, and some related forms—were able to grow much taller than their non-vascular predecessors. The evolution of vascular tissue made large plants possible because it made water and nutrient delivery more efficient. Like a circulatory system, ve ...
Chapter 21 - 22
... stems, and leaves (ferns) Vascular, seed – vascular tissue and true roots, stems, and leaves; also produce seeds for reproduction (4 phyla of gymnosperms, 1 phyla of angiosperms) ...
... stems, and leaves (ferns) Vascular, seed – vascular tissue and true roots, stems, and leaves; also produce seeds for reproduction (4 phyla of gymnosperms, 1 phyla of angiosperms) ...
Kingdom Animalia
... • Adult male and female animals produce haploid gametes by meiosis • Fertilization: an egg and a sperm fuse to form a diploid zygote • Zygote undergoes mitosis • Zygote embryo fetus ...
... • Adult male and female animals produce haploid gametes by meiosis • Fertilization: an egg and a sperm fuse to form a diploid zygote • Zygote undergoes mitosis • Zygote embryo fetus ...
APPLYING PRINCIPLES OF PLANT SCIENCE
... • LEAVES - Make food for the plant through a process known as photosynthesis. • STEMS - Transport water and other material between the leaves and roots; supports the leaves, fruit and other structures. • ROOTS - Anchors the plant; takes in water and minerals and stores food. August 2008 ...
... • LEAVES - Make food for the plant through a process known as photosynthesis. • STEMS - Transport water and other material between the leaves and roots; supports the leaves, fruit and other structures. • ROOTS - Anchors the plant; takes in water and minerals and stores food. August 2008 ...
APPLYING PRINCIPLES OF PLANT SCIENCE
... • LEAVES - Make food for the plant through a process known as photosynthesis. • STEMS - Transport water and other material between the leaves and roots; supports the leaves, fruit and other structures. • ROOTS - Anchors the plant; takes in water and minerals and stores food. August 2008 ...
... • LEAVES - Make food for the plant through a process known as photosynthesis. • STEMS - Transport water and other material between the leaves and roots; supports the leaves, fruit and other structures. • ROOTS - Anchors the plant; takes in water and minerals and stores food. August 2008 ...
Native Dandelions Common Dandelion Is An Introduced Weed How
... Native plants are species that occur naturally in an area. There are several native dandelions in North America, but only one of these, a small alpine species called northern dandelion (Taraxacum ceratophorum), grows in Alberta. ...
... Native plants are species that occur naturally in an area. There are several native dandelions in North America, but only one of these, a small alpine species called northern dandelion (Taraxacum ceratophorum), grows in Alberta. ...
Parts of a Plant - The Lesson Locker
... Pollen is produced by the stamen. Pollen moves away from the plant via the wind or other pollinators (birds & bees) The pollen lands on the pistil of another plant and fertilizes the eggs within the ovary The flower petals fall off, the ovary develops into a FRUIT that encloses the seeds Fruits are ...
... Pollen is produced by the stamen. Pollen moves away from the plant via the wind or other pollinators (birds & bees) The pollen lands on the pistil of another plant and fertilizes the eggs within the ovary The flower petals fall off, the ovary develops into a FRUIT that encloses the seeds Fruits are ...
Plants - Cloudfront.net
... 1) Why do moss grow so low to the ground? 2) Which stage is the main stage of moss: sporophyte or gametophyte? 3) How do moss reproduce? 4) What is the major difference between moss and ...
... 1) Why do moss grow so low to the ground? 2) Which stage is the main stage of moss: sporophyte or gametophyte? 3) How do moss reproduce? 4) What is the major difference between moss and ...
Frontline SMS
... To control sorghum anthracnose, add 85 gms of cut garlic to 50 ml of vegetable oil, and keep for 24 hours. Add about 2 litres of water and stir. Dilute 1 part of the mixture with 9 parts of water and spray on the crops. 15TH To control sorghum downy mildew, mix 2 garlic bulbs, match-box size piece o ...
... To control sorghum anthracnose, add 85 gms of cut garlic to 50 ml of vegetable oil, and keep for 24 hours. Add about 2 litres of water and stir. Dilute 1 part of the mixture with 9 parts of water and spray on the crops. 15TH To control sorghum downy mildew, mix 2 garlic bulbs, match-box size piece o ...
pollination - Projekt EU
... A strong gust of wind can transport pollen grains to another plant of the same species. This type of pollination typically occurs in plants that don't produce flowers, such as ragweed and conifers. Windpollinated flowers tend to have very little scent and don't produce nectar. However, these plants ...
... A strong gust of wind can transport pollen grains to another plant of the same species. This type of pollination typically occurs in plants that don't produce flowers, such as ragweed and conifers. Windpollinated flowers tend to have very little scent and don't produce nectar. However, these plants ...
as an RTF file
... Obtain food and water: Make their food with photosynthesis; mine the soil for water with roots or root like structures: Getting water is a hard thing to do when you live on land: land plants have many adaptations associated with getting water, transporting water, and conserving water. Reproduction: ...
... Obtain food and water: Make their food with photosynthesis; mine the soil for water with roots or root like structures: Getting water is a hard thing to do when you live on land: land plants have many adaptations associated with getting water, transporting water, and conserving water. Reproduction: ...
Lycopodiophyta - People Server at UNCW
... – Stomatal density of Asteroxylon is about 10X more than Aglaophyton – Unlike other Rhynie Chert plants, could likely survive in temporarily drier environments ...
... – Stomatal density of Asteroxylon is about 10X more than Aglaophyton – Unlike other Rhynie Chert plants, could likely survive in temporarily drier environments ...
You just read that there are 4 main groups of gymnosperms but the
... seeds. The seeds have a tough seed coat covering them. However, they are “naked” because they are not enclosed in a fruit. Three basic facts about gymnosperm plants that you MUST know are: • seeds not enclosed in fruit • do not make flowers • Have male and female cones that are used in the reproduct ...
... seeds. The seeds have a tough seed coat covering them. However, they are “naked” because they are not enclosed in a fruit. Three basic facts about gymnosperm plants that you MUST know are: • seeds not enclosed in fruit • do not make flowers • Have male and female cones that are used in the reproduct ...
Plant reproduction

Plant reproduction is the production of new individuals or offspring in plants, which can be accomplished by sexual or asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction produces offspring by the fusion of gametes, resulting in offspring genetically different from the parent or parents. Asexual reproduction produces new individuals without the fusion of gametes, genetically identical to the parent plants and each other, except when mutations occur. In seed plants, the offspring can be packaged in a protective seed, which is used as an agent of dispersal.