Plant Adaptation Notes
... • Flowers can be pollinated by wind, insects, birds, & other animals • Many flowers are ____________ colored to attract birds & insects that aid in pollination ...
... • Flowers can be pollinated by wind, insects, birds, & other animals • Many flowers are ____________ colored to attract birds & insects that aid in pollination ...
plant kingdom
... It is thallus-like and prostrate or erect, and attached to the substratum by unicellular or multicellular rhizoids. They lack true roots, stem or leaves. They may possess root-like, leaf-like or stem-like structures. The main plant body of the bryophyte is haploid. It produces gametes, hence is call ...
... It is thallus-like and prostrate or erect, and attached to the substratum by unicellular or multicellular rhizoids. They lack true roots, stem or leaves. They may possess root-like, leaf-like or stem-like structures. The main plant body of the bryophyte is haploid. It produces gametes, hence is call ...
Common Name: TAYLOR`S FILMY FERN Scientific Name
... gametophyte phase consists of tiny, ground-hugging plants that produce egg and sperm which unite to produce a larger, leafy plant called the sporophyte. The sporophyte phase consists of a plant that, in most ferns, produces spores which develop into gametophytes, thus completing the cycle. Almost al ...
... gametophyte phase consists of tiny, ground-hugging plants that produce egg and sperm which unite to produce a larger, leafy plant called the sporophyte. The sporophyte phase consists of a plant that, in most ferns, produces spores which develop into gametophytes, thus completing the cycle. Almost al ...
Seedless Vascular Plants
... c. Absorptive structures called rhizoids; “leaflike” blades/leaves d. Typically separate male and female gametophytic plants; sperm must swim through a thin film of water to fertilize the egg; a diploid zygote forms and grows into a mature moss sporophyte; spores will be released from the sporophyte ...
... c. Absorptive structures called rhizoids; “leaflike” blades/leaves d. Typically separate male and female gametophytic plants; sperm must swim through a thin film of water to fertilize the egg; a diploid zygote forms and grows into a mature moss sporophyte; spores will be released from the sporophyte ...
Lab 08: Plant Diversity
... prevents water loss). Commercially, most of our lumber and paper pulp comes from the wood of conifers. D) Seed bearing vascular plants: Angiosperms The angiosperms are recognized as the “flowering plants.” In addition to pollen and seeds, the angiosperms developed two other distinctive traits: 1) fl ...
... prevents water loss). Commercially, most of our lumber and paper pulp comes from the wood of conifers. D) Seed bearing vascular plants: Angiosperms The angiosperms are recognized as the “flowering plants.” In addition to pollen and seeds, the angiosperms developed two other distinctive traits: 1) fl ...
Seeds - Fulton County Schools
... dissolved minerals up from roots out to the plant. Hyphae may or may not have septa. The septa of many species have pores, which allows cytoplasm to flow freely from one cell to the next. Cytoplasmic movement within the hypha provides a means to transport of materials. ...
... dissolved minerals up from roots out to the plant. Hyphae may or may not have septa. The septa of many species have pores, which allows cytoplasm to flow freely from one cell to the next. Cytoplasmic movement within the hypha provides a means to transport of materials. ...
Balloon vine - Cape Town Invasives
... • Pull out by hand or dig young plants out, ensuring roots are removed. • Cut mature plants at base, leaving top growth to die off, then dig roots out. • Combine with herbicide application; take care to prevent contamination of water. • WARNING: Herbicides should only be applied by suitably trai ...
... • Pull out by hand or dig young plants out, ensuring roots are removed. • Cut mature plants at base, leaving top growth to die off, then dig roots out. • Combine with herbicide application; take care to prevent contamination of water. • WARNING: Herbicides should only be applied by suitably trai ...
WS 3 Meiosis
... 2. How many cells does mitosis produce from 1 cell?______ 3. Are the cells produced by mitosis exact copies of the original cell? yes or no 4. How many cells does meiosis produce from 1 cell?___________ 5. If a cell has 4 chromosomes before meiosis, how many chromosomes do each of the gametes (new c ...
... 2. How many cells does mitosis produce from 1 cell?______ 3. Are the cells produced by mitosis exact copies of the original cell? yes or no 4. How many cells does meiosis produce from 1 cell?___________ 5. If a cell has 4 chromosomes before meiosis, how many chromosomes do each of the gametes (new c ...
Bio 101: Plant Evolution (Karoly) Midterm Review
... Be prepared to describe the historical context in which the different major plant groups (10 phyla) arose and diversified. What is a plant and how do they differ from their algal relatives? How has the reproductive biology of the major plant groups contributed to their success in the terrestrial env ...
... Be prepared to describe the historical context in which the different major plant groups (10 phyla) arose and diversified. What is a plant and how do they differ from their algal relatives? How has the reproductive biology of the major plant groups contributed to their success in the terrestrial env ...
Section 22-1 Introduction to Plants (pages 551-555)
... 8. What are the four basic needs of plants? a. b. c. d. 9. Why are plant leaves typically broad and flat? 10. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about the basic needs of plants. a. Plants require oxygen to support cellular respiration. b. Plants must get rid of water as quickly as possi ...
... 8. What are the four basic needs of plants? a. b. c. d. 9. Why are plant leaves typically broad and flat? 10. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about the basic needs of plants. a. Plants require oxygen to support cellular respiration. b. Plants must get rid of water as quickly as possi ...
Chapter 30-Plant Evolution and Classification
... by the presence of a flower and fruit. • Angiosperms can be herbaceous plants like violets or shrubs like rose bushes. Still others are vines, like grapes and ivy. • Oak, aspen, and birch trees are all flowering plants that have woody stems, although the small flower are almost undetectable. Likewis ...
... by the presence of a flower and fruit. • Angiosperms can be herbaceous plants like violets or shrubs like rose bushes. Still others are vines, like grapes and ivy. • Oak, aspen, and birch trees are all flowering plants that have woody stems, although the small flower are almost undetectable. Likewis ...
Life Processes
... Plants release energy through their life processes like growth and photosynthesis. ...
... Plants release energy through their life processes like growth and photosynthesis. ...
Arboretum Botanical Vampires! Parasitic and Carnivorous Plants in
... underside. In spring a long stem produces several flowers which are pollinated by male wasps which mistake the flowers for female wasps. This pollination strategy is called sexual deception. The orchids produce dust‐ like seeds and with almost no reserves stored Cryptostylis erecta in flower ...
... underside. In spring a long stem produces several flowers which are pollinated by male wasps which mistake the flowers for female wasps. This pollination strategy is called sexual deception. The orchids produce dust‐ like seeds and with almost no reserves stored Cryptostylis erecta in flower ...
Matthiola incana Height: 30 inches Spread: 18 inches Spacing: 14
... Stock will grow to be about 24 inches tall at maturity, with a spread of 18 inches. When grown in masses or used as a bedding plant, individual plants should be spaced approximately 14 inches apart. It grows at a fast rate, and tends to be biennial, meaning that it puts on vegetative growth the firs ...
... Stock will grow to be about 24 inches tall at maturity, with a spread of 18 inches. When grown in masses or used as a bedding plant, individual plants should be spaced approximately 14 inches apart. It grows at a fast rate, and tends to be biennial, meaning that it puts on vegetative growth the firs ...
Plant classification
... In order to study the billions of different organisms living on Earth, scientists have sorted and classified them based on their similarities and differences. This system of classification is also called taxonomy and usually features both English and Latin names for different divisions. It is always ...
... In order to study the billions of different organisms living on Earth, scientists have sorted and classified them based on their similarities and differences. This system of classification is also called taxonomy and usually features both English and Latin names for different divisions. It is always ...
Plant classification
... In order to study the billions of different organisms living on Earth, scientists have sorted and classified them based on their similarities and differences. This system of classification is also called taxonomy and usually features both English and Latin names for different divisions. It is always ...
... In order to study the billions of different organisms living on Earth, scientists have sorted and classified them based on their similarities and differences. This system of classification is also called taxonomy and usually features both English and Latin names for different divisions. It is always ...
dendrobium orchid - Super Floral Retailing
... tight during repotting. GROOMING Remove individual flowers as they fade. If lower leaves turn yellow, they can be removed without damaging the plants. ...
... tight during repotting. GROOMING Remove individual flowers as they fade. If lower leaves turn yellow, they can be removed without damaging the plants. ...
Unit 7 - Plants
... • The sperm cell that does NOT fertilize the egg has a triploid (3n) nucleus and becomes the endosperm, a food supply for the developing plant embryo. • The process in which one sperm fertilizes an egg and the other forms a triploid cell is called double fertilization. o Only happens in flowering pl ...
... • The sperm cell that does NOT fertilize the egg has a triploid (3n) nucleus and becomes the endosperm, a food supply for the developing plant embryo. • The process in which one sperm fertilizes an egg and the other forms a triploid cell is called double fertilization. o Only happens in flowering pl ...
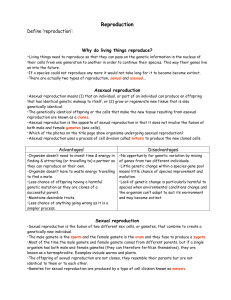
Sexual reproduction
... •Asexual reproduction means (1) that an individual, or part of an individual can produce an offspring that has identical genetic makeup to itself, or (2) grow or regenerate new tissue that is also genetically identical. •The genetically identical offspring or the cells that make the new tissue resul ...
... •Asexual reproduction means (1) that an individual, or part of an individual can produce an offspring that has identical genetic makeup to itself, or (2) grow or regenerate new tissue that is also genetically identical. •The genetically identical offspring or the cells that make the new tissue resul ...
Lesson 03B What`s your Classification? PPT
... LIFE CYCLE is the amount of time it takes for the plant to go from a germinating seed until the resulting plant produces another seed. *Seed to seed* ...
... LIFE CYCLE is the amount of time it takes for the plant to go from a germinating seed until the resulting plant produces another seed. *Seed to seed* ...
Imperata cylindrica - SE-EPPC
... and bobwhite quail, as well as the endangered gopher tortoise, which depends on native grasses and legumes. While cogongrass roots are very fire tolerant, the plant is extremely flammable, and can cause fast-moving wildfires (to more than 840o F) that consume native plants and animals and disrupt th ...
... and bobwhite quail, as well as the endangered gopher tortoise, which depends on native grasses and legumes. While cogongrass roots are very fire tolerant, the plant is extremely flammable, and can cause fast-moving wildfires (to more than 840o F) that consume native plants and animals and disrupt th ...
Plant reproduction

Plant reproduction is the production of new individuals or offspring in plants, which can be accomplished by sexual or asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction produces offspring by the fusion of gametes, resulting in offspring genetically different from the parent or parents. Asexual reproduction produces new individuals without the fusion of gametes, genetically identical to the parent plants and each other, except when mutations occur. In seed plants, the offspring can be packaged in a protective seed, which is used as an agent of dispersal.