BIOL 273 Midterm #1 Notes
... This period is called the absolute refractory period, and it represents the time it takes for the Na gates to get to their original “starting positions”, from where they can open again and let more Na into the cell ...
... This period is called the absolute refractory period, and it represents the time it takes for the Na gates to get to their original “starting positions”, from where they can open again and let more Na into the cell ...
Actin in Axons: Stable Scaffolds and Dynamic Filaments
... are categorized by function: (1) sequester, or bind G-actin subunits; (2) nucleate actin polymerization; (3) cap F-actin barbed ends to inhibit polymerization; (4) cap pointed ends to inhibit depolymerization; (5) bind barbed ends to inhibit capping; (6) bind pointed ends to promote depolymerization ...
... are categorized by function: (1) sequester, or bind G-actin subunits; (2) nucleate actin polymerization; (3) cap F-actin barbed ends to inhibit polymerization; (4) cap pointed ends to inhibit depolymerization; (5) bind barbed ends to inhibit capping; (6) bind pointed ends to promote depolymerization ...
No Slide Title
... – have extensions (perivascular feet) that contact blood capillaries that stimulate them to form a tight seal called the blood-brain barrier – convert blood glucose to lactate and supply this to the neurons for nourishment – Secrete nerve growth factors, promote neuron growth and synapse formation – ...
... – have extensions (perivascular feet) that contact blood capillaries that stimulate them to form a tight seal called the blood-brain barrier – convert blood glucose to lactate and supply this to the neurons for nourishment – Secrete nerve growth factors, promote neuron growth and synapse formation – ...
PDF
... relationships as they enter the developing optic nerve (as they do in the zebra fish, Bodick & Levinthal, 1980), then pathways taken by pioneering fibres as they enter the optic stalk may determine the final organization of the optic nerve and may, in turn, order fibre projection to the tectum. Thus ...
... relationships as they enter the developing optic nerve (as they do in the zebra fish, Bodick & Levinthal, 1980), then pathways taken by pioneering fibres as they enter the optic stalk may determine the final organization of the optic nerve and may, in turn, order fibre projection to the tectum. Thus ...
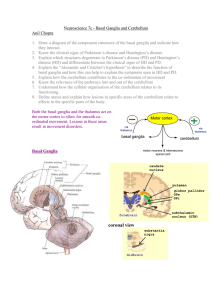
Neuroscience 7c – Basal Ganglia and Cerebellum
... Huntington’s disease is caused by a defective “Huntington Gene” on chromosome 4. This results in the degradation of the spiny GABAergic neurons in the striatum. It is an autosomal dominant disease. Symptoms of Huntington’s Disease Choreic movements (Chorea): Rapid jerky involuntary movements of th ...
... Huntington’s disease is caused by a defective “Huntington Gene” on chromosome 4. This results in the degradation of the spiny GABAergic neurons in the striatum. It is an autosomal dominant disease. Symptoms of Huntington’s Disease Choreic movements (Chorea): Rapid jerky involuntary movements of th ...
- Orange Coast College
... Myelinated preganglionic fibers exit spinal cord in ventral roots from T1 to L2 levels. Most sympathetic nerve fibers separate from somatic motor fibers and synapse with postganglionic neurons within paravertebral ganglia. ...
... Myelinated preganglionic fibers exit spinal cord in ventral roots from T1 to L2 levels. Most sympathetic nerve fibers separate from somatic motor fibers and synapse with postganglionic neurons within paravertebral ganglia. ...
Embryonic development of the Drosophila brain: formation of
... pathways are pioneered by axons that project across the neuronal cell bridge in close association with the row of longitudinal glial cells (Fig. 3J-L). Both descending and ascending axons are involved in pioneering the longitudinal pathway (Fig. 3A, arrows); they meet and fasciculate approximately h ...
... pathways are pioneered by axons that project across the neuronal cell bridge in close association with the row of longitudinal glial cells (Fig. 3J-L). Both descending and ascending axons are involved in pioneering the longitudinal pathway (Fig. 3A, arrows); they meet and fasciculate approximately h ...
Functions of the Nervous System
... When the central neuron is excited, the efferent impulse is conducted outward along the axon, at the same time, also can excite a inhibitory interneuron though its collateral branch, then cause the release of inhibitory neurotransmitter, which inhibit the previously excited neurons, this kind of inh ...
... When the central neuron is excited, the efferent impulse is conducted outward along the axon, at the same time, also can excite a inhibitory interneuron though its collateral branch, then cause the release of inhibitory neurotransmitter, which inhibit the previously excited neurons, this kind of inh ...
The Neuron - UPM EduTrain Interactive Learning
... Gene • The functional unit of the chromosome, which directs synthesis of one or more proteins. ...
... Gene • The functional unit of the chromosome, which directs synthesis of one or more proteins. ...
Chapter 13 - tanabe homepage
... • Nervous system – Allows for communication between cells through sensory input, integration of data, and motor output • 2 cell types: neurons and neuroglia ...
... • Nervous system – Allows for communication between cells through sensory input, integration of data, and motor output • 2 cell types: neurons and neuroglia ...
Microconnectomics of the Pretectum and Ventral Thalamus in the
... folia VIc–IXc in the cerebellum, which are related to visual and oculomotor responses (Freedman et al., 1975; Clarke, 1977). Nonretinal afferents to the GLv arise from the visual Wulst, TeO, GT, and VLT (Karten et al., 1973; Crossland and Uchwat, 1979; Vega-Zuniga et al., 2014). Although the role of ...
... folia VIc–IXc in the cerebellum, which are related to visual and oculomotor responses (Freedman et al., 1975; Clarke, 1977). Nonretinal afferents to the GLv arise from the visual Wulst, TeO, GT, and VLT (Karten et al., 1973; Crossland and Uchwat, 1979; Vega-Zuniga et al., 2014). Although the role of ...
The role of Pitx3 in survival of midbrain dopaminergic neurons
... psychiatric disorders. The A9 cell group located in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) has preferred projections to the dorsal striatum forming the nigrostriatal pathway, which is involved in the control of movement. The mDA system further includes the ventral tegmental area (VTA), located in ...
... psychiatric disorders. The A9 cell group located in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) has preferred projections to the dorsal striatum forming the nigrostriatal pathway, which is involved in the control of movement. The mDA system further includes the ventral tegmental area (VTA), located in ...
Chapter 12 Lecture Outline
... • About 1 trillion neurons in the nervous system • Neuroglia outnumber neurons by at least 10 to 1 • Neuroglia or glial cells – Protect neurons and help them function – Bind neurons together and form framework for nervous tissue – In fetus, guide migrating neurons to their destination – If mature ne ...
... • About 1 trillion neurons in the nervous system • Neuroglia outnumber neurons by at least 10 to 1 • Neuroglia or glial cells – Protect neurons and help them function – Bind neurons together and form framework for nervous tissue – In fetus, guide migrating neurons to their destination – If mature ne ...
Review of Thoracic and Abdominal Autonomics
... from the T1-T4 chain ganglia—some pass through cervical ganglia on their way to the heart. It may seem odd that some of the pathways to the heart start in the thoracic spinal cord, run all the way up to the superior cervical ganglion, synapse, and then descend again into the thorax. This is a holdov ...
... from the T1-T4 chain ganglia—some pass through cervical ganglia on their way to the heart. It may seem odd that some of the pathways to the heart start in the thoracic spinal cord, run all the way up to the superior cervical ganglion, synapse, and then descend again into the thorax. This is a holdov ...
Postnatal Development of the Corticospinal Tract in the Reeler Mouse
... Corticospinal tract (CST) neurons are located in layer V of the motor cortex, and send their axons to the spinal motoneurons, directly (5, 23) or indirectly (2, 35). The CST forms the longest axonal projection in the mammalian central nervous system (CNS). The development of CST axons is the latest ...
... Corticospinal tract (CST) neurons are located in layer V of the motor cortex, and send their axons to the spinal motoneurons, directly (5, 23) or indirectly (2, 35). The CST forms the longest axonal projection in the mammalian central nervous system (CNS). The development of CST axons is the latest ...
Introduction to the Nervous System
... ve and proviide a supportt system for the neuronss. They are a special typee of "connecctive tissue" for thhe nervous system. s ...
... ve and proviide a supportt system for the neuronss. They are a special typee of "connecctive tissue" for thhe nervous system. s ...
Nerve activates contraction
... Potassium ions rush out of the neuron after sodium ions rush in, which repolarizes the membrane The sodium-potassium pump restores the original configuration This action requires ATP ...
... Potassium ions rush out of the neuron after sodium ions rush in, which repolarizes the membrane The sodium-potassium pump restores the original configuration This action requires ATP ...
Chapter 15: Sense Organs
... Secretes Tears and Drains Them Across the Surface of the Eye and into the Nose Provides Moisture ...
... Secretes Tears and Drains Them Across the Surface of the Eye and into the Nose Provides Moisture ...
Slide 1
... Source: Modeling Future Heroes, A Practical Application of Heroic Values, By Roger F. Cram Source: NAMI–Family to Family Course, Class 6, Handout 2–Basic Neuro-transmission at the Synapse–page 6.23 Paragraph 3 ...
... Source: Modeling Future Heroes, A Practical Application of Heroic Values, By Roger F. Cram Source: NAMI–Family to Family Course, Class 6, Handout 2–Basic Neuro-transmission at the Synapse–page 6.23 Paragraph 3 ...
Electrical dimensions in cell science - Journal of Cell Science
... systems confirm that nerve growth in vivo is directed by endogenous electrical cues (Boxes 1 and 2, Fig. 2). Electrical control of neuronal migration It is clear that growth cones of differentiated neurons can be steered electrically in development and perhaps also following brain injury; however, d ...
... systems confirm that nerve growth in vivo is directed by endogenous electrical cues (Boxes 1 and 2, Fig. 2). Electrical control of neuronal migration It is clear that growth cones of differentiated neurons can be steered electrically in development and perhaps also following brain injury; however, d ...
Marieb_ch7a
... Potassium ions rush out of the neuron after sodium ions rush in, which repolarizes the membrane The sodium-potassium pump restores the original configuration This action requires ATP ...
... Potassium ions rush out of the neuron after sodium ions rush in, which repolarizes the membrane The sodium-potassium pump restores the original configuration This action requires ATP ...
Elastic instabilities in a layered cerebral cortex: A revised axonal
... Indirect evidence for each mechanism exists. For instance, in fetal brains where most of the tissue below the cortex is surgically ablated prior to folds developing, folds eventually do develop [5]. This observation is typically invoked to demonstrate that the intracortical buckling drives folding a ...
... Indirect evidence for each mechanism exists. For instance, in fetal brains where most of the tissue below the cortex is surgically ablated prior to folds developing, folds eventually do develop [5]. This observation is typically invoked to demonstrate that the intracortical buckling drives folding a ...
Neurons in the corpus callosum of the cat during postnatal
... Some of them have well-developed and differentiated processes and resemble pyramidal cells or interneurons. An axon-guiding function during the early postnatal period can not be excluded. ...
... Some of them have well-developed and differentiated processes and resemble pyramidal cells or interneurons. An axon-guiding function during the early postnatal period can not be excluded. ...
Chapter 15: Sense Organs I. SENSORY RECEPTORS (Receptors)
... Secretes Tears and Drains Them Across the Surface of the Eye and into the Nose Provides Moisture ...
... Secretes Tears and Drains Them Across the Surface of the Eye and into the Nose Provides Moisture ...