Five Essential Components to the Reflex Arc
... descending tracts, which consist of axons conducting impulses away from the brain. ...
... descending tracts, which consist of axons conducting impulses away from the brain. ...
Facial whisker pattern is not sufficient to instruct a
... sensory trigeminal nucleus (dPrV). Input from mystacial whiskers is relayed by the maxillary branch and forms a topographic representation of rows and whiskers in the ventral PrV (vPrV). To investigate peripheral organisation in imposing a brain topographic pattern, we analysed Edn1−/− mice, which p ...
... sensory trigeminal nucleus (dPrV). Input from mystacial whiskers is relayed by the maxillary branch and forms a topographic representation of rows and whiskers in the ventral PrV (vPrV). To investigate peripheral organisation in imposing a brain topographic pattern, we analysed Edn1−/− mice, which p ...
Fig. - Development - The Company of Biologists
... sensory trigeminal nucleus (dPrV). Input from mystacial whiskers is relayed by the maxillary branch and forms a topographic representation of rows and whiskers in the ventral PrV (vPrV). To investigate peripheral organisation in imposing a brain topographic pattern, we analysed Edn1−/− mice, which p ...
... sensory trigeminal nucleus (dPrV). Input from mystacial whiskers is relayed by the maxillary branch and forms a topographic representation of rows and whiskers in the ventral PrV (vPrV). To investigate peripheral organisation in imposing a brain topographic pattern, we analysed Edn1−/− mice, which p ...
Emerging roles of Axin in cerebral cortical development
... with a leading process pointing toward the apical pia and a trailing process extending toward the ventricle. Directed by their leading processes, neurons migrate toward the cortical (i.e., pial) surface in an orderly progression to occupy their proper positions (Tsai and Gleeson, 2005). Each wave of ...
... with a leading process pointing toward the apical pia and a trailing process extending toward the ventricle. Directed by their leading processes, neurons migrate toward the cortical (i.e., pial) surface in an orderly progression to occupy their proper positions (Tsai and Gleeson, 2005). Each wave of ...
Do cortical areas emerge from a protocottex?
... 2). However, barrels are not apparent as the cortex is assembled, but emerge later from an initially uniform cortical plate38. Another example of uniformity in the developing neocortex can be taken from the development of area-specific outputs. In the adult neocortex, the unique outputs of specific ...
... 2). However, barrels are not apparent as the cortex is assembled, but emerge later from an initially uniform cortical plate38. Another example of uniformity in the developing neocortex can be taken from the development of area-specific outputs. In the adult neocortex, the unique outputs of specific ...
Association of type I neurons positive for NADPH
... morphology, these neurons exhibit distinct heterogeneity. In one subpopulation, the cell body is narrowly attenuated (7–10 μm in width). These have bipolar dendrites, extending 300–800 μm from the cell body. One or both of the dendrites is often closely associated with blood vessels and tends to be ...
... morphology, these neurons exhibit distinct heterogeneity. In one subpopulation, the cell body is narrowly attenuated (7–10 μm in width). These have bipolar dendrites, extending 300–800 μm from the cell body. One or both of the dendrites is often closely associated with blood vessels and tends to be ...
Lateral Zone
... Cerebellum does not initiate movement but controls sequence and timing of successive movements that lead to smooth progression from one movement to next. • Lateral zone has extra motor function. • Predictive Function: it helps individual to predict how rapidly movement will occur. • Intermediate Zon ...
... Cerebellum does not initiate movement but controls sequence and timing of successive movements that lead to smooth progression from one movement to next. • Lateral zone has extra motor function. • Predictive Function: it helps individual to predict how rapidly movement will occur. • Intermediate Zon ...
Lectin and Peptide Expression in Nodose
... afferents and their terminals (5, 21, 6). Furthermore, it has been reported that the majority of peripheral unmyelinated somatosensory afferents are specifically labeled by lectins (12). In the present study, it was found that GSA I-B4-positive neurons were smaller than unlabeled neurons in NG. Henc ...
... afferents and their terminals (5, 21, 6). Furthermore, it has been reported that the majority of peripheral unmyelinated somatosensory afferents are specifically labeled by lectins (12). In the present study, it was found that GSA I-B4-positive neurons were smaller than unlabeled neurons in NG. Henc ...
RESEARCH LETTERS 3 Marwood RP. Disappearance of
... filamentous projections. 39.9% of the DAT* neurons were found in the putamen, 11.6% in the caudate nucleus, 16.3% in the globus pallidus externa, 6.2% in the globus pallidus interna, and 25.9% in the adjacent internal capsule and in particular the ansa lenticularis. In eight of the ten brains from p ...
... filamentous projections. 39.9% of the DAT* neurons were found in the putamen, 11.6% in the caudate nucleus, 16.3% in the globus pallidus externa, 6.2% in the globus pallidus interna, and 25.9% in the adjacent internal capsule and in particular the ansa lenticularis. In eight of the ten brains from p ...
Principle of Superposition-free Memory - Deep Blue
... of firing. The problem of memory is thus to reconstruct this pattern, but in response to a secondary pattern of firing concomitant to an event other than the original input (for example, part of the original input or some other input with which it has been associated). Presumably this means that at ...
... of firing. The problem of memory is thus to reconstruct this pattern, but in response to a secondary pattern of firing concomitant to an event other than the original input (for example, part of the original input or some other input with which it has been associated). Presumably this means that at ...
1 How the Nervous System Works
... synapse between the axon tip of one neuron and the dendrite of another neuron. Notice that a small gap separates these two structures. For a nerve impulse to be carried along at a synapse, it must cross the gap between the axon and the next structure. The axon tips release chemicals that carry the i ...
... synapse between the axon tip of one neuron and the dendrite of another neuron. Notice that a small gap separates these two structures. For a nerve impulse to be carried along at a synapse, it must cross the gap between the axon and the next structure. The axon tips release chemicals that carry the i ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM
... During the period of the rising and falling phases of the action potential the system is selfperpetuating. The voltage-gated Na+ channels can not reopen until they return to their original shape. As a result, the membrane can not be excited to generate another action potential at this site until the ...
... During the period of the rising and falling phases of the action potential the system is selfperpetuating. The voltage-gated Na+ channels can not reopen until they return to their original shape. As a result, the membrane can not be excited to generate another action potential at this site until the ...
Chapter 7 - Faculty Web Sites
... At an inhibitory synapse, binding of the neurotransmitter to the receptor opens different ion channels The postsynaptic cell’s interior becomes more negatively charged than usual, reducing the likelihood that an action potential will begin ...
... At an inhibitory synapse, binding of the neurotransmitter to the receptor opens different ion channels The postsynaptic cell’s interior becomes more negatively charged than usual, reducing the likelihood that an action potential will begin ...
Synapses and Synaptic Transmission
... The CNS contains more than 100 billion neurons. Incoming signals enter the neuron through synapses located mostly on the neuronal dendrites, but also on the cell body. For different types of neurons, there may be only a few hundred or as many as 200,000 such synaptic connections from input fibers. C ...
... The CNS contains more than 100 billion neurons. Incoming signals enter the neuron through synapses located mostly on the neuronal dendrites, but also on the cell body. For different types of neurons, there may be only a few hundred or as many as 200,000 such synaptic connections from input fibers. C ...
Morris_2007_Macrosto..
... organized in a way that resembles a typical invertebrate ganglion. Neuronal cell bodies form an external cell layer, the cortex, and processes of the predominantly unipolar neurons form a neuropile in the brain center. A system of nerves, called orthogon (due to its orthogonal arrangement of longitu ...
... organized in a way that resembles a typical invertebrate ganglion. Neuronal cell bodies form an external cell layer, the cortex, and processes of the predominantly unipolar neurons form a neuropile in the brain center. A system of nerves, called orthogon (due to its orthogonal arrangement of longitu ...
Microsoft Word 97 - 2003 Document
... major group, the arthropods. Additions of more nerve cells and greater concentrations of these in specific body areas allow arthropods to become aware of and to respond more quickly to stimuli. ...
... major group, the arthropods. Additions of more nerve cells and greater concentrations of these in specific body areas allow arthropods to become aware of and to respond more quickly to stimuli. ...
Interneurons and triadic circuitry of the thalamus
... Effects on voltage-sensitive properties Because activation of the triadic circuit via activation of mGlu5 receptors has a long-lasting effect on membrane potential, it can affect the ‘play’ of the voltage-sensitive properties of a cell. There are many voltage-gated conductances that can be so affect ...
... Effects on voltage-sensitive properties Because activation of the triadic circuit via activation of mGlu5 receptors has a long-lasting effect on membrane potential, it can affect the ‘play’ of the voltage-sensitive properties of a cell. There are many voltage-gated conductances that can be so affect ...
The mind`s mirror
... But that story is just at its beginning. Researchers haven't yet been able to prove that humans have individual mirror neurons like monkeys, although they have shown that humans have a more general mirror system. And researchers are just beginning to branch out from the motor cortex to try to figure ...
... But that story is just at its beginning. Researchers haven't yet been able to prove that humans have individual mirror neurons like monkeys, although they have shown that humans have a more general mirror system. And researchers are just beginning to branch out from the motor cortex to try to figure ...
A & P 240: Overview of the Human Nervous System
... 1. One major function of the spinal cord is to convey sensory impulses from the periphery to the brain and to conduct motor impulses from the brain to the periphery. 2. The other major function is to serve as a REFLEX CENTER. The posterior root, posterior root ganglion, and anterior root (aka: the d ...
... 1. One major function of the spinal cord is to convey sensory impulses from the periphery to the brain and to conduct motor impulses from the brain to the periphery. 2. The other major function is to serve as a REFLEX CENTER. The posterior root, posterior root ganglion, and anterior root (aka: the d ...
The hidden side of the UPR signalling pathway - Reflexions
... "We asked ourselves whether the UPR had a physiological function for the control of this transition during corticogenesis", the scientist continues. "And this is indeed the case! We isolated the apical progenitors at different stages of development and we showed that there is indeed an UPR pathway t ...
... "We asked ourselves whether the UPR had a physiological function for the control of this transition during corticogenesis", the scientist continues. "And this is indeed the case! We isolated the apical progenitors at different stages of development and we showed that there is indeed an UPR pathway t ...
nerves
... carry information from the central nervous system Human Anatomy, 3rd edition Prentice Hall, © 2001 ...
... carry information from the central nervous system Human Anatomy, 3rd edition Prentice Hall, © 2001 ...
Structures and Learning Simulations
... input layer 4, receives information from the thalamus, senses; output layers 5/6, subcortical centers, motor commands; hidden layers 2/3, transform local information and information from distant neuron groups, coming through axons on layer 1. ...
... input layer 4, receives information from the thalamus, senses; output layers 5/6, subcortical centers, motor commands; hidden layers 2/3, transform local information and information from distant neuron groups, coming through axons on layer 1. ...
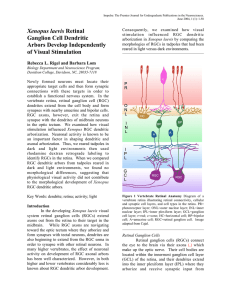
Xenopus laevis Retinal Ganglion Cell Dendritic Arbors Develop
... dendritic arbors in developing X e n o p u s . Because neurons may become desensitized when exposed to a continuous stimulus, it is possible that tadpoles reared in the light became accustomed to the light and that retinal neurons ceased or altered their firing in response to constant light stimuli. ...
... dendritic arbors in developing X e n o p u s . Because neurons may become desensitized when exposed to a continuous stimulus, it is possible that tadpoles reared in the light became accustomed to the light and that retinal neurons ceased or altered their firing in response to constant light stimuli. ...
AXOTOMIZED SPINAL COMMISSURAL INTERNEURONS OF THE ADULT FELINE:
... To my parents: thank you for your unwavering love and support for twenty-twoand-a-bit years of education. Mom and Dad, you gave me everything I needed growing up and I think it’s starting to pay off. To the Shirtliff’s: Thank you for coming to visit us and allowing us to visit you so often, we may l ...
... To my parents: thank you for your unwavering love and support for twenty-twoand-a-bit years of education. Mom and Dad, you gave me everything I needed growing up and I think it’s starting to pay off. To the Shirtliff’s: Thank you for coming to visit us and allowing us to visit you so often, we may l ...
increase in osmiophilia of axonal membranes of crayfish as a result
... membranes' reactivity for osmium . An unmasking of SH groups could explain such increased osmiophilia, since SH groups are very reactive with osmium, while disulfide bonds are considerably less reactive . This hypothesis was tested by treating control, glutaraldehydefixed nerve cords with disulfide ...
... membranes' reactivity for osmium . An unmasking of SH groups could explain such increased osmiophilia, since SH groups are very reactive with osmium, while disulfide bonds are considerably less reactive . This hypothesis was tested by treating control, glutaraldehydefixed nerve cords with disulfide ...