collinsnervoussystem (1)
... released that cross the synapse to the next cell • B. a chemical change occurs within the cell, the change causes an electric charge to be produced and the charge jumps the gap between the nerve cells. • C. the electric charge produced chemically inside a group of neurons causes chemical changes in ...
... released that cross the synapse to the next cell • B. a chemical change occurs within the cell, the change causes an electric charge to be produced and the charge jumps the gap between the nerve cells. • C. the electric charge produced chemically inside a group of neurons causes chemical changes in ...
Test 3
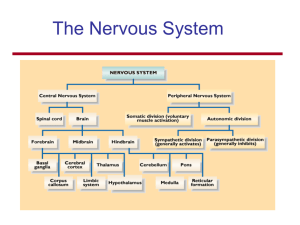
... 1. List the structural and functional divisions of the nervous system, and describe their relationship to each other. Nervous system, CNS, PNS, Somatic, ANS. Sensory, integration, motor 2. Describe the types of glial cells, Schwann, oligodendrocyte 3. Explain the physiological characteristics of mat ...
... 1. List the structural and functional divisions of the nervous system, and describe their relationship to each other. Nervous system, CNS, PNS, Somatic, ANS. Sensory, integration, motor 2. Describe the types of glial cells, Schwann, oligodendrocyte 3. Explain the physiological characteristics of mat ...
Conference Outline 1
... The cerebral hemispheres can be divided into four lobes (frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal). Some scientists though have added a fifth lobe that is the grouping of several medial structures that are involved in memory and emotions. This lobe is called the Limbic lobe. Carpenter in addition r ...
... The cerebral hemispheres can be divided into four lobes (frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal). Some scientists though have added a fifth lobe that is the grouping of several medial structures that are involved in memory and emotions. This lobe is called the Limbic lobe. Carpenter in addition r ...
Section: Nervous system
... 8. Electrical messages, called __________________--, may travel as fast as 150 m/s or as slow as 0.2 m/s. Match the correct description with the correct term. Write the letter in the space provided. ______ 9. allows the neuron to receive information a. cell body ______10. a long fiber that transmits ...
... 8. Electrical messages, called __________________--, may travel as fast as 150 m/s or as slow as 0.2 m/s. Match the correct description with the correct term. Write the letter in the space provided. ______ 9. allows the neuron to receive information a. cell body ______10. a long fiber that transmits ...
Q 1
... Q29: Explain the three main factors in addiction: genetic predisposition, social factors and dopamine secretion. ...
... Q29: Explain the three main factors in addiction: genetic predisposition, social factors and dopamine secretion. ...
Document
... Monocular Cues – one eye depth cues • Monocular Cues: – Relative Size: two objects the same size; if one appears larger then it’s closer to us ...
... Monocular Cues – one eye depth cues • Monocular Cues: – Relative Size: two objects the same size; if one appears larger then it’s closer to us ...
Chapter 11 Marieb
... 1. Action potential reaches axon terminal, causing the voltageAll cells pump calcium gated calcium channels to open, so… out of the cell! 2. Calcium rushes in! 3. Calcium influx stimulates exocytosis of vesicles containing neurotransmitter. This mechanism is not clear. 4. Neurotransmitter is release ...
... 1. Action potential reaches axon terminal, causing the voltageAll cells pump calcium gated calcium channels to open, so… out of the cell! 2. Calcium rushes in! 3. Calcium influx stimulates exocytosis of vesicles containing neurotransmitter. This mechanism is not clear. 4. Neurotransmitter is release ...
BASAL GANGLIA
... A: An injection of antergograde tracer was made in a small site in the motor cortex (area 4) representing the foot. In the same hemisphere , a small site in the pallidum was injected with retrograde tracer. Both the labeled axon projections from the cortex to terminal sites in the striatum and the ...
... A: An injection of antergograde tracer was made in a small site in the motor cortex (area 4) representing the foot. In the same hemisphere , a small site in the pallidum was injected with retrograde tracer. Both the labeled axon projections from the cortex to terminal sites in the striatum and the ...
Microscopy of myelination - Formatex Research Center
... Experiments using knockout mice have shown the actin cytoskeleton to play a crucial role in process outgrowth. A single oligodendrocyte may myelinate as many as 40 axon segments [26]. Oligodendrocytes are believed to generate an excess of processes at first, with only those in contact with an axon b ...
... Experiments using knockout mice have shown the actin cytoskeleton to play a crucial role in process outgrowth. A single oligodendrocyte may myelinate as many as 40 axon segments [26]. Oligodendrocytes are believed to generate an excess of processes at first, with only those in contact with an axon b ...
The autonomic nervous system
... - It regulates bodily functions such as heart rate, digestion, urination, respiratory rate etc. - Within the brain, the ANS regulated by the hypothalamus ...
... - It regulates bodily functions such as heart rate, digestion, urination, respiratory rate etc. - Within the brain, the ANS regulated by the hypothalamus ...
Chapter 17 Part A
... - central nervous system (CNS) - nerves within spinal cord and brain - peripheral nervous system (PNS) - all nerves outside the CNS ...
... - central nervous system (CNS) - nerves within spinal cord and brain - peripheral nervous system (PNS) - all nerves outside the CNS ...
The Nervous System and Neurons
... 2. List the 4 main parts and describe the purpose of the 4 main parts of a neuron. 3. The nervous system is divided into 2 parts. What are they and what do they include? 4. Describe the internal and external environment of a neuron in resting potential. How is resting potential reached? 5. What is a ...
... 2. List the 4 main parts and describe the purpose of the 4 main parts of a neuron. 3. The nervous system is divided into 2 parts. What are they and what do they include? 4. Describe the internal and external environment of a neuron in resting potential. How is resting potential reached? 5. What is a ...
New Insights into Neuron-Glia Communication
... environment shared by these two cell types. Advanced imaging methods, which allow observation of changes in intracellular and extracellular signaling molecules in real time, show that glia communicate with one another and with neurons primarily through chemical signals rather than electrical signals ...
... environment shared by these two cell types. Advanced imaging methods, which allow observation of changes in intracellular and extracellular signaling molecules in real time, show that glia communicate with one another and with neurons primarily through chemical signals rather than electrical signals ...
Media:oreilly_genpsych_ch2_neuron
... E = driving potential (pull down for inhibition, up for excitation) Vm = the “flag” – reflects net balance between two sides ...
... E = driving potential (pull down for inhibition, up for excitation) Vm = the “flag” – reflects net balance between two sides ...
Nervous
... 4 The sensory neurons communicate with motor neurons that supply the quadriceps. The motor neurons convey signals to the quadriceps, causing it to contract and jerking the lower leg forward. Gray matter 5 Sensory neurons from the quadriceps also communicate with interneurons in the spinal cord. ...
... 4 The sensory neurons communicate with motor neurons that supply the quadriceps. The motor neurons convey signals to the quadriceps, causing it to contract and jerking the lower leg forward. Gray matter 5 Sensory neurons from the quadriceps also communicate with interneurons in the spinal cord. ...
Types of Neuron and their function - Click here
... Neurons are microscopic in size and can be one of three types: sensory, motor and relay. They typically consist of a cell body, dendrites and an axon but each type of neuron has a unique structure related to its function within the nervous system. The cell body consists of a number of short branchin ...
... Neurons are microscopic in size and can be one of three types: sensory, motor and relay. They typically consist of a cell body, dendrites and an axon but each type of neuron has a unique structure related to its function within the nervous system. The cell body consists of a number of short branchin ...
Current concepts in central nervous system regeneration
... dependencies also varies accordingly. It has been postulated that neurons are programmed before differentiation to switch chemotrophic dependencies at the right time, irrespective of external signals.6 This can also be demonstrated in vitro (Figs 1, 2). Neurotrophins are not only restricted to the s ...
... dependencies also varies accordingly. It has been postulated that neurons are programmed before differentiation to switch chemotrophic dependencies at the right time, irrespective of external signals.6 This can also be demonstrated in vitro (Figs 1, 2). Neurotrophins are not only restricted to the s ...
nervous system
... • Neuron receives external stimulus • ______ channel opens on cell membrane • Na+ flow into cell by passive _____________ • Down the concentration gradient ...
... • Neuron receives external stimulus • ______ channel opens on cell membrane • Na+ flow into cell by passive _____________ • Down the concentration gradient ...
Sensory receptors
... • Supporting cells contain enzymes that oxidize hydrophobic volatile odorants. • Bipolar sensory neurons located within olfactory epithelium are pseudostratified. • Axon projects directly up into olfactory bulb of cerebrum. • Olfactory bulb projects to olfactory cortex, hippocampus, and amygdaloid n ...
... • Supporting cells contain enzymes that oxidize hydrophobic volatile odorants. • Bipolar sensory neurons located within olfactory epithelium are pseudostratified. • Axon projects directly up into olfactory bulb of cerebrum. • Olfactory bulb projects to olfactory cortex, hippocampus, and amygdaloid n ...
atterning the nervous system through development and evolution: a
... As a final note, Wilson reported the preliminary results of a screen for mutations that prevent habenula lateralization, either due to impaired parapineal lateralization, to impaired parapineal to habenula signaling, or to more general impairment of body lateralization. He observed that delateraliz ...
... As a final note, Wilson reported the preliminary results of a screen for mutations that prevent habenula lateralization, either due to impaired parapineal lateralization, to impaired parapineal to habenula signaling, or to more general impairment of body lateralization. He observed that delateraliz ...
1. Impulse Conduction
... Example: can be compare to a gun firing: If you pull the trigger the gun wil fire (bullet will not go faster because you pull the trigger harder) & if you do not pull the trigger the gun wil not fire ...
... Example: can be compare to a gun firing: If you pull the trigger the gun wil fire (bullet will not go faster because you pull the trigger harder) & if you do not pull the trigger the gun wil not fire ...
ANPS 019 Beneyto-Santonja 10-29
... Partial crushing of the vertebral column leads to compression of the spinal cord, but symptoms will vary depending on which part of spinal cord is injured. Composition of a Peripheral Nerve Nerves contain both sensory and motor axons and both somatic and autonomic fibers Connective Tissue Compon ...
... Partial crushing of the vertebral column leads to compression of the spinal cord, but symptoms will vary depending on which part of spinal cord is injured. Composition of a Peripheral Nerve Nerves contain both sensory and motor axons and both somatic and autonomic fibers Connective Tissue Compon ...
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
... General organization Sympathetic Division • Thoracolumbar division- Preganglionic neurons originate from the thoracic and lumbar levels of the spinal cord (T1-L2). • Sympathetic ganglia: Sympathetic trunk (vertebral chain) ganglia. Prevertebral (collateral) ganglia: celiac, ...
... General organization Sympathetic Division • Thoracolumbar division- Preganglionic neurons originate from the thoracic and lumbar levels of the spinal cord (T1-L2). • Sympathetic ganglia: Sympathetic trunk (vertebral chain) ganglia. Prevertebral (collateral) ganglia: celiac, ...