Leaving Certificate Biology Topic iQuiz
... The pathway of a reflex arc involves the following structures: 1 – sense organ; 2 – spinal cord; 3 – motor neuron; 4 – muscle; 5 – sensory neurons. The correct sequence of events is … ...
... The pathway of a reflex arc involves the following structures: 1 – sense organ; 2 – spinal cord; 3 – motor neuron; 4 – muscle; 5 – sensory neurons. The correct sequence of events is … ...
Modeling and Imagery
... Intersensory integration and sensory dominance • Overall sense of what is going on dependent on information flowing from many receptors simultaneously • Occasionally they contradict each other • Vision is dominant…can lead to some amusing experiments (and experiences) ...
... Intersensory integration and sensory dominance • Overall sense of what is going on dependent on information flowing from many receptors simultaneously • Occasionally they contradict each other • Vision is dominant…can lead to some amusing experiments (and experiences) ...
ppt file
... the organization of cell types. The outermost layer of the cortex is called the molecular layer, and is nearly cell-free. Instead it is occupied mostly by axons and dendrites. The layer below that is a monolayer of large cells called Purkinje cells, central players in the circuitry of the cerebellum ...
... the organization of cell types. The outermost layer of the cortex is called the molecular layer, and is nearly cell-free. Instead it is occupied mostly by axons and dendrites. The layer below that is a monolayer of large cells called Purkinje cells, central players in the circuitry of the cerebellum ...
File - Mr. Jacobson`s Site
... by being pumped by membrane proteins or by simple diffusion through ion channels. ...
... by being pumped by membrane proteins or by simple diffusion through ion channels. ...
Document
... Input travels along several pathways Pathways are integrated in different CNS systems One stimulus promotes numerous responses ...
... Input travels along several pathways Pathways are integrated in different CNS systems One stimulus promotes numerous responses ...
NVCC Bio 211 - gserianne.com
... You should know which neurotransmitters are released, and the locations where they are released ...
... You should know which neurotransmitters are released, and the locations where they are released ...
Anatomical Terminology
... Rods and cones are distributed regionally. The center of the eye (i.e., the fovea) contains only cones. Peripheral retina consists primarily of rods with few cones. Central retina has approximately the same number of photoreceptor and ganglion. Peripheral retina has many photoreceptors (rods) conver ...
... Rods and cones are distributed regionally. The center of the eye (i.e., the fovea) contains only cones. Peripheral retina consists primarily of rods with few cones. Central retina has approximately the same number of photoreceptor and ganglion. Peripheral retina has many photoreceptors (rods) conver ...
Document
... undergo exchanges along the entire length of the axon Sodium and potassium pumps and channels are active only at each NODE OF RANVIER. This is where the axon can actually exchange ions with the ...
... undergo exchanges along the entire length of the axon Sodium and potassium pumps and channels are active only at each NODE OF RANVIER. This is where the axon can actually exchange ions with the ...
Smell and Taste
... mitral cells converge to one glomerulus), which accepts axons primary olfactory neurons. Axons of mitral cells make tzv. lateral olfactory tract. These axons give collaterals involved in pos. and neg. feedback control. The architecture of the bulb results in 1:1000 convergence of olfactory receptor ...
... mitral cells converge to one glomerulus), which accepts axons primary olfactory neurons. Axons of mitral cells make tzv. lateral olfactory tract. These axons give collaterals involved in pos. and neg. feedback control. The architecture of the bulb results in 1:1000 convergence of olfactory receptor ...
1. A unicellular protest may use a contractile vacuole to expel
... d. Ganglia adjacent to the spinal cord. e. None of the above. 28. After the depolarization of an action potential, the fall in the membrane potential occurs due to the a. Closing of sodium inactivation gates. b. Closing of potassium and sodium channels. c. Refractory period in which the membrane is ...
... d. Ganglia adjacent to the spinal cord. e. None of the above. 28. After the depolarization of an action potential, the fall in the membrane potential occurs due to the a. Closing of sodium inactivation gates. b. Closing of potassium and sodium channels. c. Refractory period in which the membrane is ...
Biology 2401 Anatomy and Physiology I notes
... *Why are malignant cells in nervous tissue from glial cells and not neurons? *Which two glial cells produce myelin for neurons and where is each located? Neurons are the communicating cells of the nervous system; link sensory receptors with brain and spinal cord, integration within brain and spinal ...
... *Why are malignant cells in nervous tissue from glial cells and not neurons? *Which two glial cells produce myelin for neurons and where is each located? Neurons are the communicating cells of the nervous system; link sensory receptors with brain and spinal cord, integration within brain and spinal ...
Candy Neurons
... Draw a picture of the neuron (with direction of a signal indicated) below: (must have candy neuron checked by me BEFORE DRAWING) ...
... Draw a picture of the neuron (with direction of a signal indicated) below: (must have candy neuron checked by me BEFORE DRAWING) ...
CNS: Brain and Spinal Cord
... *Before you move on to motor pathways, take a minute to draw the general routes of the sensory pathways. Where do 1st and 2nd order neurons generally synapse? (The posterior column pathway is an exception to this, but I will not focus on that). B. Somatic Motor (efferent) Pathways- remember, the alt ...
... *Before you move on to motor pathways, take a minute to draw the general routes of the sensory pathways. Where do 1st and 2nd order neurons generally synapse? (The posterior column pathway is an exception to this, but I will not focus on that). B. Somatic Motor (efferent) Pathways- remember, the alt ...
The Special Senses Throughout Life
... Special receptor cells • Are neuronlike epithelial cells or small peripheral neurons • Transfer sensory information to other neurons in afferent pathways The Chemical Senses: Taste and Smell ...
... Special receptor cells • Are neuronlike epithelial cells or small peripheral neurons • Transfer sensory information to other neurons in afferent pathways The Chemical Senses: Taste and Smell ...
Endocrine System: Overview
... Somatic Motor Pathways 9. What two main somatic motor pathways convey action potentials to skeletal muscles? ...
... Somatic Motor Pathways 9. What two main somatic motor pathways convey action potentials to skeletal muscles? ...
Seminars of Interest
... capabilities (such as the hands and face) occupy a greater amount of space than those that exhibit less precise motor control (such as the trunk). From: Functional Organization of the Primary Motor Cortex Copyright © 2001, Sinauer Associates, Inc. ...
... capabilities (such as the hands and face) occupy a greater amount of space than those that exhibit less precise motor control (such as the trunk). From: Functional Organization of the Primary Motor Cortex Copyright © 2001, Sinauer Associates, Inc. ...
excitatory neurotransmitter
... Mainly inhibitory – involved in the acid (GABA) sites experience of a range of emotions; acts as a hormone to stimulate the sympathetic NS. Glutamate Interneurons in many CNS Excitatory – communication between sites; cerebral cortex; spinal adjacent brain cells. Too little results in cord lack of si ...
... Mainly inhibitory – involved in the acid (GABA) sites experience of a range of emotions; acts as a hormone to stimulate the sympathetic NS. Glutamate Interneurons in many CNS Excitatory – communication between sites; cerebral cortex; spinal adjacent brain cells. Too little results in cord lack of si ...
Nervous Tissue - Manasquan Public Schools
... cell body - always are sensory neurons - originate in embryo as bipolar - during development, axon and dendrite fuse together into a single process - single process divides into two branches a short distance from cell body ...
... cell body - always are sensory neurons - originate in embryo as bipolar - during development, axon and dendrite fuse together into a single process - single process divides into two branches a short distance from cell body ...
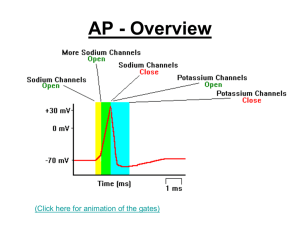
AP – All or nothing
... membrane, this is repolarisation • The membrane briefly becomes hyperpolarised (more negative on the inside than usual) • The Na+ / K+ channels close ...
... membrane, this is repolarisation • The membrane briefly becomes hyperpolarised (more negative on the inside than usual) • The Na+ / K+ channels close ...
A Functional Role for Intra-Axonal Protein Synthesis during Axonal
... Burlingame, CA). Immunofluorescence was analyzed by standard fluorescent microscopy or laser scanning confocal microscopy. In all experiments, samples (coverslips, membranes, or tissue sections) were incubated without primary antibody to rule out nonspecific signals from secondary antibodies. Specif ...
... Burlingame, CA). Immunofluorescence was analyzed by standard fluorescent microscopy or laser scanning confocal microscopy. In all experiments, samples (coverslips, membranes, or tissue sections) were incubated without primary antibody to rule out nonspecific signals from secondary antibodies. Specif ...
Flatworm nervous system as drug target
... • A truncated one, which has the glutamate-binding site but lacks the seven transmembrane domains characterizing the metabotropic glutamate receptors (Taman and Ribeiro 2011). ...
... • A truncated one, which has the glutamate-binding site but lacks the seven transmembrane domains characterizing the metabotropic glutamate receptors (Taman and Ribeiro 2011). ...
2014 nervous system ppt
... • Peripheral Nervous System • Sense stimuli (receptors - dendrite of neuron) • Motor responses using effectors (muscles, organs, glands) • Transmit information to and from CNS • Sensory and motor neurons • Groups of cell bodies of PNS called ganglia ...
... • Peripheral Nervous System • Sense stimuli (receptors - dendrite of neuron) • Motor responses using effectors (muscles, organs, glands) • Transmit information to and from CNS • Sensory and motor neurons • Groups of cell bodies of PNS called ganglia ...
2 neurons in parasympathetic nervous syste
... continue through the trunk and synapse with the postganglionic neurons at the target tissue. What is the function of visceral afferent neurons? Provide sensory information from viscera. Sense distension of viscera. Cause sensing of visceral pain. How do visceral afferent neurons reach the CNS? They ...
... continue through the trunk and synapse with the postganglionic neurons at the target tissue. What is the function of visceral afferent neurons? Provide sensory information from viscera. Sense distension of viscera. Cause sensing of visceral pain. How do visceral afferent neurons reach the CNS? They ...