OPERATING SYSTEM : AN OVERVIEW – [UNIT
... Computer software can be divided into two main categories: application software and system software. Application software consists of the programs for performing tasks particular to the machine’s utilisation. This software is designed to solve a particular problem for users. Examples of application ...
... Computer software can be divided into two main categories: application software and system software. Application software consists of the programs for performing tasks particular to the machine’s utilisation. This software is designed to solve a particular problem for users. Examples of application ...
Operating system/IT0307
... own address. It is a repository of quickly accessible data shared by the CPU and I/O devices. • Main memory is a volatile storage device. It loses its contents in the case of system failure. • The operating system is responsible for the following activities in connections with memory management ...
... own address. It is a repository of quickly accessible data shared by the CPU and I/O devices. • Main memory is a volatile storage device. It loses its contents in the case of system failure. • The operating system is responsible for the following activities in connections with memory management ...
Operating system hardware reconfiguration
... Originally, the mandate of DRDC Valcartier was to address the issue of various long-term support options that are available to the Navy should they decide to pursue the deployment of a Linux-based operating system aboard the frigates. This report is outlined in Report [1]. More specifically, with re ...
... Originally, the mandate of DRDC Valcartier was to address the issue of various long-term support options that are available to the Navy should they decide to pursue the deployment of a Linux-based operating system aboard the frigates. This report is outlined in Report [1]. More specifically, with re ...
Document
... 11. Explain the facilities provided by the following operating system 12. List out the services provided by operating systems to programs and to the 13. Define operating system and list out the function and component of operating system. 14. Explain in detail the modern computer system 15. Explain t ...
... 11. Explain the facilities provided by the following operating system 12. List out the services provided by operating systems to programs and to the 13. Define operating system and list out the function and component of operating system. 14. Explain in detail the modern computer system 15. Explain t ...
RAW 2003 Presentation - Louisiana State University
... Relocating a task at run-time from one type of processor to another one (e.g. from reconfigurable logic to ISP) with minimal interference ...
... Relocating a task at run-time from one type of processor to another one (e.g. from reconfigurable logic to ISP) with minimal interference ...
Lecture 8
... Solution to Critical-Section Problem MUST satisfy the following three requirements: 1. Mutual Exclusion - If process Pi is executing in its critical section, then no other processes can be executing in their critical sections 2. Progress - If no process is executing in its critical section and ther ...
... Solution to Critical-Section Problem MUST satisfy the following three requirements: 1. Mutual Exclusion - If process Pi is executing in its critical section, then no other processes can be executing in their critical sections 2. Progress - If no process is executing in its critical section and ther ...
ch4
... that the execution of the threads will be interleaved over time. On a system with multiple cores, however, concurrency means that some threads can run in parallel, because the system can assign a separate thread to each core ...
... that the execution of the threads will be interleaved over time. On a system with multiple cores, however, concurrency means that some threads can run in parallel, because the system can assign a separate thread to each core ...
Figure 5.01 - Texas A&M University
... •If a thread invokes the exec() system call, the program specified in the parameter to exec() will replace the entire process – including all threads. •If exec() is called immediately after forking, then duplicating all threads is unnecessary, as the program specified in the parameters to exec() wil ...
... •If a thread invokes the exec() system call, the program specified in the parameter to exec() will replace the entire process – including all threads. •If exec() is called immediately after forking, then duplicating all threads is unnecessary, as the program specified in the parameters to exec() wil ...
Application of Software Components in Operating System Design
... and also my individual contributions to the implementation of HelenOS. That being written, it is completely necessary to acknowledge that no human is an island and (almost) all ideas are always extensions and recombination of previous ideas. The current source code of HelenOS in its mainline branch ...
... and also my individual contributions to the implementation of HelenOS. That being written, it is completely necessary to acknowledge that no human is an island and (almost) all ideas are always extensions and recombination of previous ideas. The current source code of HelenOS in its mainline branch ...
Operating System
... utilization by organizing jobs so that the CPU always has one to execute. switches occur so frequently that the users may interact with each program while it is running. Time-sharing systems were developed to provide interactive use of a computer system at a reasonable cost. A time-shared operating ...
... utilization by organizing jobs so that the CPU always has one to execute. switches occur so frequently that the users may interact with each program while it is running. Time-sharing systems were developed to provide interactive use of a computer system at a reasonable cost. A time-shared operating ...
Disco: Running Commodity Operating Systems on Scalable
... machine monitor schedules the virtual resources (processor and memory) of the virtual machines on the physical resources of the scalable multiprocessor. Virtual machine monitors, in combination with commodity and specialized operating systems, form a flexible system software solution for these machi ...
... machine monitor schedules the virtual resources (processor and memory) of the virtual machines on the physical resources of the scalable multiprocessor. Virtual machine monitors, in combination with commodity and specialized operating systems, form a flexible system software solution for these machi ...
Project 2, Linux Kernel Hacking
... May be called from (almost) anywhere in kernel Same calling convention as printf() Writes to system log Output survives crashes (almost all of the time) ...
... May be called from (almost) anywhere in kernel Same calling convention as printf() Writes to system log Output survives crashes (almost all of the time) ...
* Abstract
... management decisions for the operating system. The physical memory manager of our virtual machine monitor implements first-touch allocation and dynamic migration or replication of “hot” memory pages [29]. These features are coupled with a physical CPU scheduler that is aware of memory locality issue ...
... management decisions for the operating system. The physical memory manager of our virtual machine monitor implements first-touch allocation and dynamic migration or replication of “hot” memory pages [29]. These features are coupled with a physical CPU scheduler that is aware of memory locality issue ...
Cellular Disco: resource management using
... management decisions for the operating system. The physical memory manager of our virtual machine monitor implements first-touch allocation and dynamic migration or replication of “hot” memory pages [29]. These features are coupled with a physical CPU scheduler that is aware of memory locality issue ...
... management decisions for the operating system. The physical memory manager of our virtual machine monitor implements first-touch allocation and dynamic migration or replication of “hot” memory pages [29]. These features are coupled with a physical CPU scheduler that is aware of memory locality issue ...
A Real-Time Linux
... whatever needs to be done in the real-time executive and then may pass the interrupt on to Linux. If the soft interrupt enable ag is set, then the stack is adjusted to t the needs of the Linux handler and control is passed, via a soft interrupt table, to the appropriate Linux \wrapper". The \wrapp ...
... whatever needs to be done in the real-time executive and then may pass the interrupt on to Linux. If the soft interrupt enable ag is set, then the stack is adjusted to t the needs of the Linux handler and control is passed, via a soft interrupt table, to the appropriate Linux \wrapper". The \wrapp ...
A Real-Time Linux
... whatever needs to be done in the real-time executive and then may pass the interrupt on to Linux. If the soft interrupt enable ag is set, then the stack is adjusted to t the needs of the Linux handler and control is passed, via a soft interrupt table, to the appropriate Linux \wrapper". The \wrapp ...
... whatever needs to be done in the real-time executive and then may pass the interrupt on to Linux. If the soft interrupt enable ag is set, then the stack is adjusted to t the needs of the Linux handler and control is passed, via a soft interrupt table, to the appropriate Linux \wrapper". The \wrapp ...
Processes
... modifiable part of the user space. May include program data, a heap area, and programs that may be modified. ...
... modifiable part of the user space. May include program data, a heap area, and programs that may be modified. ...
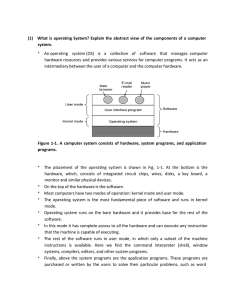
(1) What is operating System? Explain the abstract view of the
... In fact, a strong case can be made for putting as little as possible is kernel mode because bugs in the kernel can bring down the system instantly. In contrast, user processes can be set up to have less power so that a bug there may not be fatal. The basic idea behind the microkernel design is to ac ...
... In fact, a strong case can be made for putting as little as possible is kernel mode because bugs in the kernel can bring down the system instantly. In contrast, user processes can be set up to have less power so that a bug there may not be fatal. The basic idea behind the microkernel design is to ac ...
Benchmarking Real-time Operating Systems for use in Radio Base
... UART Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter, computer hardware component which ...
... UART Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter, computer hardware component which ...
A Taxonomy of Computer Program Security Flaws, with Examples
... This experience led researchers to seek better ways of building systems to meet security requirements in the first place instead of attempting to mend the flawed systems already installed. Although some success has been attained in identifying better strategies for building systems [12,13], these te ...
... This experience led researchers to seek better ways of building systems to meet security requirements in the first place instead of attempting to mend the flawed systems already installed. Although some success has been attained in identifying better strategies for building systems [12,13], these te ...
threads - Bilkent University Computer Engineering Department
... • thread-local: global inside the thread (thread-wide global), but not global for the whole process. Other threads can not access it. But all functions of the thread can. • But we don’t have language support to define such variables. – C can not do that. • Therefore thread API has special functions ...
... • thread-local: global inside the thread (thread-wide global), but not global for the whole process. Other threads can not access it. But all functions of the thread can. • But we don’t have language support to define such variables. – C can not do that. • Therefore thread API has special functions ...
P - Bilkent University Computer Engineering Department
... No Preemption – – A processing holding resources make requests: if request cannot be granted, release (preempt) the held resources, and try again later. – Preempted resources are added to the list of resources for which the process is waiting – Process will be restarted only when it can regain its o ...
... No Preemption – – A processing holding resources make requests: if request cannot be granted, release (preempt) the held resources, and try again later. – Preempted resources are added to the list of resources for which the process is waiting – Process will be restarted only when it can regain its o ...