CS 291 – Dynamic Web Prog. With PHP
... ◦ Increased reliability graceful degradation fail-soft systems ...
... ◦ Increased reliability graceful degradation fail-soft systems ...
Operating System Concepts
... Each job is allocated a small portion of CPU time On-line communication between the user and the system is provided The CPU is multiplexed among several jobs that are kept in memory and on disk The CPU is allocated to a job only if the job is in memory A job is swapped in and out of memory t ...
... Each job is allocated a small portion of CPU time On-line communication between the user and the system is provided The CPU is multiplexed among several jobs that are kept in memory and on disk The CPU is allocated to a job only if the job is in memory A job is swapped in and out of memory t ...
Two Types of Software: System Software: Operating Systems
... Processor Management The operating system schedules the processes (tasks that come from the applications) that will be executed by the CPU. With a multi-tasking system, the operating system must arrange the execution of processes so that you believe that there are several things happening at once. I ...
... Processor Management The operating system schedules the processes (tasks that come from the applications) that will be executed by the CPU. With a multi-tasking system, the operating system must arrange the execution of processes so that you believe that there are several things happening at once. I ...
CPS120: Introduction to Computer Science
... controls the computer and its resources. An operating system keeps track of users, filenames and their location, and manages the computer's memory. • Other operating system functions include the allocation and monitoring of all devices and scheduling users' programs and tasks. • Also, the operating ...
... controls the computer and its resources. An operating system keeps track of users, filenames and their location, and manages the computer's memory. • Other operating system functions include the allocation and monitoring of all devices and scheduling users' programs and tasks. • Also, the operating ...
Memory Management – Thrashing, Segmentation and Paging
... Virtual memory is a way of introducing another level in our memory hierarchy in order to abstract away the amount of memory actually available on a particular system This is incredibly important for “ease-of-programming” Imagine having to explicitly check for size of physical memory and manage it ...
... Virtual memory is a way of introducing another level in our memory hierarchy in order to abstract away the amount of memory actually available on a particular system This is incredibly important for “ease-of-programming” Imagine having to explicitly check for size of physical memory and manage it ...
Operating Systems
... 1. Modern Operating Systems, Andrew S Tanenbaum 3rd Edition PHI. 2. Operating Systems A concept - based Approach, 2nd Edition, D. M. Dhamdhere, TMH. 3. Principles of Operating Systems, B. L. Stuart, Cengage learning, India Edition. 4. Operating Systems, A. S. Godbole, 2nd Edition, TMH 5. An Introduc ...
... 1. Modern Operating Systems, Andrew S Tanenbaum 3rd Edition PHI. 2. Operating Systems A concept - based Approach, 2nd Edition, D. M. Dhamdhere, TMH. 3. Principles of Operating Systems, B. L. Stuart, Cengage learning, India Edition. 4. Operating Systems, A. S. Godbole, 2nd Edition, TMH 5. An Introduc ...
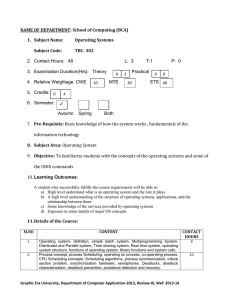
tbc 302 operating systems
... Distributed and Parallel system, Time sharing system, Real time system, operating system structure, functions of operating system, library functions and system calls. Process concept, process Scheduling, operating on process, co-operating process. CPU Scheduling concepts, Scheduling algorithms, proc ...
... Distributed and Parallel system, Time sharing system, Real time system, operating system structure, functions of operating system, library functions and system calls. Process concept, process Scheduling, operating on process, co-operating process. CPU Scheduling concepts, Scheduling algorithms, proc ...
I. Course code and Title OPERATING SYSTEM CONCEPTS II
... Space Types, Dynamic Loading/Linking & Shared Libraries. ...
... Space Types, Dynamic Loading/Linking & Shared Libraries. ...
Chapter 8: Operating Systems and Utility Programs
... Operating Systems • User Interface: controls how you enter data and instructions, and how information is displayed on the screen. ...
... Operating Systems • User Interface: controls how you enter data and instructions, and how information is displayed on the screen. ...
Introduction To Operating Systems
... After I/O starts, control returns to user program without waiting for I/O completion. Device controller later informs CPU that it has finished its operation by causing an interrupt. When an interrupt occur, current execution is put on hold; the CPU jumps to a service routine called “interrupt handle ...
... After I/O starts, control returns to user program without waiting for I/O completion. Device controller later informs CPU that it has finished its operation by causing an interrupt. When an interrupt occur, current execution is put on hold; the CPU jumps to a service routine called “interrupt handle ...
Slides10_30
... • We do not need all of a process in memory for it to run - We can swap in pages as required • So - we can now run processes that are bigger than total memory available! ...
... • We do not need all of a process in memory for it to run - We can swap in pages as required • So - we can now run processes that are bigger than total memory available! ...
PowerPoint - NYU Computer Science
... Requires changes in IRIX memory layout Flushes TLB when scheduling different virtual CPUs MIPS TLB is tagged (address space ID) Avoids virtualizing ASIDs ...
... Requires changes in IRIX memory layout Flushes TLB when scheduling different virtual CPUs MIPS TLB is tagged (address space ID) Avoids virtualizing ASIDs ...
1. OS_Overview
... A process contains three components: An executable program The associated data The execution context (or “process state”) Process registers Include information such as the process priority Internal data by which the OS is able to supervise and control the process ...
... A process contains three components: An executable program The associated data The execution context (or “process state”) Process registers Include information such as the process priority Internal data by which the OS is able to supervise and control the process ...
Operating System
... • Failed mutual exclusion • Nondeterminate program operation – Program should only depend on input to it, not on the activities of other programs ...
... • Failed mutual exclusion • Nondeterminate program operation – Program should only depend on input to it, not on the activities of other programs ...
OSTEP 13 Address Space
... Any address you can see as a programmer of a user-level program is a virtual address Only the OS, through its tricky techniques of virtualizing memory, that knows where in the physical memory of the machine these instructions and data values lie If you print out an address in a program, it’s a virtu ...
... Any address you can see as a programmer of a user-level program is a virtual address Only the OS, through its tricky techniques of virtualizing memory, that knows where in the physical memory of the machine these instructions and data values lie If you print out an address in a program, it’s a virtu ...
Chap 6: Virtual Memory
... • So - we can now run processes that are bigger than total memory available! • Main memory is called real memory • User/programmer sees much bigger memory virtual memory ...
... • So - we can now run processes that are bigger than total memory available! • Main memory is called real memory • User/programmer sees much bigger memory virtual memory ...
Test 1 Operating Systems and Networking CS
... I/O devices.” Is this a sufficient claim for a start as far as memory is concerned? Elaborate your answer. If processes within a system communicated via message passing without using shared memory, would we still insist on it? State your reason. Consider the following diagram that purports to depict ...
... I/O devices.” Is this a sufficient claim for a start as far as memory is concerned? Elaborate your answer. If processes within a system communicated via message passing without using shared memory, would we still insist on it? State your reason. Consider the following diagram that purports to depict ...
Chapter 10 – Operating Systems Roles of an Operating System
... - Virtual machine - illusion created by a time-sharing system that each user has his/her own machine - Real-time System - system in which response time is crucial given the nature of the application - Response time - time delay between receiving a stimulus and producing a response - Device driver - ...
... - Virtual machine - illusion created by a time-sharing system that each user has his/her own machine - Real-time System - system in which response time is crucial given the nature of the application - Response time - time delay between receiving a stimulus and producing a response - Device driver - ...
one.world — System Support for Pervasive Applications
... Recorded in per VM data structure (registers, TLB contents) Some traps (syscall, page fault) handled by guest OS’s trap handlers ...
... Recorded in per VM data structure (registers, TLB contents) Some traps (syscall, page fault) handled by guest OS’s trap handlers ...
Answer the following questions clearly but concisely. What is multiprogramming? 1.
... occurs, it takes 2 msec to handle the fault. If a program takes 60 sec to run, during which time it gets 15,000 page faults, how long would it take to run if twice as much memory were available? ...
... occurs, it takes 2 msec to handle the fault. If a program takes 60 sec to run, during which time it gets 15,000 page faults, how long would it take to run if twice as much memory were available? ...
08 Operating System Support
... It is better use of memory to load in just a few pages If the program references data or branches to an instruction on a page not in main memory, a page fault is triggered which tells the OS to bring in the desired page ...
... It is better use of memory to load in just a few pages If the program references data or branches to an instruction on a page not in main memory, a page fault is triggered which tells the OS to bring in the desired page ...
Training
... • C, D, E, F (25% - 60%) • Average of this class should be either B- or C+. • To pass this subject, the final exam should be >= 30. • To pass this subject, the overall score should be >= 35. • To get the “A” grade, the overall score should be at least 68. • Each person, each semester can have one su ...
... • C, D, E, F (25% - 60%) • Average of this class should be either B- or C+. • To pass this subject, the final exam should be >= 30. • To pass this subject, the overall score should be >= 35. • To get the “A” grade, the overall score should be at least 68. • Each person, each semester can have one su ...
Systems Software
... – These programs provide resource management services of many kinds such as the control and use of hardware resources including • disk space • memory • CPU time allocation and • peripheral devices. ...
... – These programs provide resource management services of many kinds such as the control and use of hardware resources including • disk space • memory • CPU time allocation and • peripheral devices. ...
2.4 The service and functions provided by an operating system can
... two main categories. Briefly describes the two categories and discuss how they differ. ANS: One class of services provided by an operating system is to enforce protection between different processes running concurrently in the system. Processes are allowed to access only those memory locations that ...
... two main categories. Briefly describes the two categories and discuss how they differ. ANS: One class of services provided by an operating system is to enforce protection between different processes running concurrently in the system. Processes are allowed to access only those memory locations that ...