The UNIX Operating System - Niagara College Technology
... The kernel allocates and frees memory for each process. ...
... The kernel allocates and frees memory for each process. ...
Chapter 2 – Operating System Overview
... 7. The central theme of modern operating systems, based on the concept of switching among multiple programs in memory, is called __________________. ...
... 7. The central theme of modern operating systems, based on the concept of switching among multiple programs in memory, is called __________________. ...
PowerPoint XP
... Resource sharing and management Long term data storage Protection, security, accounting Real time support, parallelism, human interface ...
... Resource sharing and management Long term data storage Protection, security, accounting Real time support, parallelism, human interface ...
Multi-Tasking/Multi-Programming Operating Systems
... development of more powerful CPU’ s, more memory and large, cheap disk drives, operating system’ s have been developed that allow more than one PROGRAM or TASK to run at the same time. This is known as Multi-tasking or Multi-programming. A single processor cannot really process more that one task at ...
... development of more powerful CPU’ s, more memory and large, cheap disk drives, operating system’ s have been developed that allow more than one PROGRAM or TASK to run at the same time. This is known as Multi-tasking or Multi-programming. A single processor cannot really process more that one task at ...
Frequently Asked Questions - Operating System Concepts
... 32. What is the difference between Hard and Soft real-time systems ? 33. What is a mission critical system ? 34. What is the important aspect of a real-time system ? 35. If two processes which shares same system memory and system clock in a distributed system, What is it called? 36. What is the stat ...
... 32. What is the difference between Hard and Soft real-time systems ? 33. What is a mission critical system ? 34. What is the important aspect of a real-time system ? 35. If two processes which shares same system memory and system clock in a distributed system, What is it called? 36. What is the stat ...
Introduction - University of Pennsylvania
... Compiler assigns logical addresses, say Add1 and Add2, for program variables in P’s data space When P is loaded in memory, OS assigns a physical base address to ...
... Compiler assigns logical addresses, say Add1 and Add2, for program variables in P’s data space When P is loaded in memory, OS assigns a physical base address to ...
Operating systems
... the course The acquisition of basic knowledge of operating systems and work in them. Knowledge of modern operating systems. Understanding the key differences between objectoriented, modular, layered or systems based on a microkernel. Knowledge of the mechanisms of competitive execution and the probl ...
... the course The acquisition of basic knowledge of operating systems and work in them. Knowledge of modern operating systems. Understanding the key differences between objectoriented, modular, layered or systems based on a microkernel. Knowledge of the mechanisms of competitive execution and the probl ...
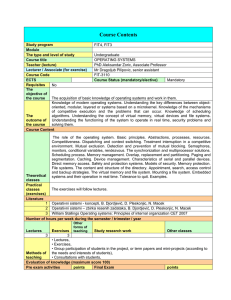
Course Content File
... 6. Prerequisites: Computer Organization, Object-Oriented Programming, Data Structures and Algorithm, Systems Software 7. Foundation for: Technical Electives 8. Abstract Content: The course aims to introduce the fundamental concepts of operating system. The course relates these fundamentals with the ...
... 6. Prerequisites: Computer Organization, Object-Oriented Programming, Data Structures and Algorithm, Systems Software 7. Foundation for: Technical Electives 8. Abstract Content: The course aims to introduce the fundamental concepts of operating system. The course relates these fundamentals with the ...
Computer Operating Systems (COP 4610)
... To learn the basic elements of Operating Systems To understand basic concepts of the structure and architecture of an operating system To learn how processes are managed including, scheduling, creation, and termination To learn basic process synchronization mechanisms To understand the problem of de ...
... To learn the basic elements of Operating Systems To understand basic concepts of the structure and architecture of an operating system To learn how processes are managed including, scheduling, creation, and termination To learn basic process synchronization mechanisms To understand the problem of de ...
Chapter 2 Operating System Overview
... – Prevents a job from monopolizing the system (when allocated time is up, job is stopped) ...
... – Prevents a job from monopolizing the system (when allocated time is up, job is stopped) ...
Operating System Software The OS
... • Each process must have enough memory in which to execute, and it can neither run into the memory space of another process nor be run into by another process. ...
... • Each process must have enough memory in which to execute, and it can neither run into the memory space of another process nor be run into by another process. ...
Virtual memory
... • I/O devices very slow. • When one program is waiting for I/O, another can use the CPU. ...
... • I/O devices very slow. • When one program is waiting for I/O, another can use the CPU. ...
83-381 Syllabus English
... First Semester 2016/17 Weekly hours: 2 lecture + 1 training 1) Course objectives: An operating system is a set of subsystems/programs that manage a computer system composed of hardware and software resources, providing common services/utilities needed to run system and user applications. All compute ...
... First Semester 2016/17 Weekly hours: 2 lecture + 1 training 1) Course objectives: An operating system is a set of subsystems/programs that manage a computer system composed of hardware and software resources, providing common services/utilities needed to run system and user applications. All compute ...
OSTEP Chapter 2 - eecis.udel.edu
... • DRAM is volatile – when power goes away or system crashes, data in memory is lost; need hardware and software to store data persistently – I/I devices: disk (hard drive) and solid-state drive (SSD) – File system (the part of OS that manages disk/SSD and files) ...
... • DRAM is volatile – when power goes away or system crashes, data in memory is lost; need hardware and software to store data persistently – I/I devices: disk (hard drive) and solid-state drive (SSD) – File system (the part of OS that manages disk/SSD and files) ...
LINUX System (English
... The one program running at all times on the computer is the kernel. Everything else is either a system program (shipped with OS) or an application program ...
... The one program running at all times on the computer is the kernel. Everything else is either a system program (shipped with OS) or an application program ...
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture
... • Allows programs to be altered and recompiled independently, without re-linking and re-loading • Lends itself to sharing among processes • Lends itself to protection • Some systems combine segmentation with ...
... • Allows programs to be altered and recompiled independently, without re-linking and re-loading • Lends itself to sharing among processes • Lends itself to protection • Some systems combine segmentation with ...
tutorial-02-with
... Q 11) List five services provided by an operating system, and explain how each creates convenience for users. In which cases would it be impossible for user-level programs to provide these services? Explain your answer. The five services are: a) Program execution. The operating system loads the cont ...
... Q 11) List five services provided by an operating system, and explain how each creates convenience for users. In which cases would it be impossible for user-level programs to provide these services? Explain your answer. The five services are: a) Program execution. The operating system loads the cont ...
08-OS-Support
... • Determines which programs are submitted for processing • i.e. controls the degree of multiprogramming • Once submitted, a job becomes a process for the short term scheduler • (or it becomes a swapped out job for the medium term scheduler) ...
... • Determines which programs are submitted for processing • i.e. controls the degree of multiprogramming • Once submitted, a job becomes a process for the short term scheduler • (or it becomes a swapped out job for the medium term scheduler) ...
Overview and History
... specialized management tasks 2. system libraries define standard set of functions through which apps interact with the kernel 3. kernel is responsible for maintaining the important abstractions of the OS • executes in unrestricted kernel mode • all kernel code & data in one address space ...
... specialized management tasks 2. system libraries define standard set of functions through which apps interact with the kernel 3. kernel is responsible for maintaining the important abstractions of the OS • executes in unrestricted kernel mode • all kernel code & data in one address space ...
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture
... • Allows programs to be altered and recompiled independently, without re-linking and re-loading • Lends itself to sharing among processes • Lends itself to protection • Some systems combine segmentation with ...
... • Allows programs to be altered and recompiled independently, without re-linking and re-loading • Lends itself to sharing among processes • Lends itself to protection • Some systems combine segmentation with ...
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture
... • Allows programs to be altered and recompiled independently, without re-linking and re-loading • Lends itself to sharing among processes • Lends itself to protection • Some systems combine segmentation with ...
... • Allows programs to be altered and recompiled independently, without re-linking and re-loading • Lends itself to sharing among processes • Lends itself to protection • Some systems combine segmentation with ...
Operating System Principle (DKT 221) Tutorial 1 1. Describe how
... a. How does the CPU interface with the device to coordinate the transfer? b. How does the CPU know when the memory operations are complete? c. The CPU is allowed to execute other programs while the DMA controller is transferring data. Does this process interfere with the execution of the user progra ...
... a. How does the CPU interface with the device to coordinate the transfer? b. How does the CPU know when the memory operations are complete? c. The CPU is allowed to execute other programs while the DMA controller is transferring data. Does this process interfere with the execution of the user progra ...
08_Operating System Support
... • Determines which programs are submitted for processing • i.e. controls the degree of multiprogramming • Once submitted, a job becomes a process for the short term scheduler • (or it becomes a swapped out job for the medium term scheduler) ...
... • Determines which programs are submitted for processing • i.e. controls the degree of multiprogramming • Once submitted, a job becomes a process for the short term scheduler • (or it becomes a swapped out job for the medium term scheduler) ...
Section 10: Intro to I/O and File Systems
... • Asynchronous I/O For I/O operations, we can have the requesting process sleep until the operation is complete, or have the call return immediately and have the process continue execution and later notify the process when the operation is complete. • Memory-Mapped File A memory-mapped file is a seg ...
... • Asynchronous I/O For I/O operations, we can have the requesting process sleep until the operation is complete, or have the call return immediately and have the process continue execution and later notify the process when the operation is complete. • Memory-Mapped File A memory-mapped file is a seg ...
Overview and History
... specialized management tasks 2. system libraries define standard set of functions through which apps interact with the kernel 3. kernel is responsible for maintaining the important abstractions of the OS • executes in unrestricted kernel mode • all kernel code & data in one address space ...
... specialized management tasks 2. system libraries define standard set of functions through which apps interact with the kernel 3. kernel is responsible for maintaining the important abstractions of the OS • executes in unrestricted kernel mode • all kernel code & data in one address space ...