COMP25111: Operating Systems - Lecture 4: Operating System
... Process: a program in execution (not a program on the disk) Address Space: all memory locations the process can use Thread: “of execution” – sequence of instructions obeyed Multi-threading: multiple threads within the same process ...
... Process: a program in execution (not a program on the disk) Address Space: all memory locations the process can use Thread: “of execution” – sequence of instructions obeyed Multi-threading: multiple threads within the same process ...
Computer Software - Welcome to the UNC Department of
... control programs for I/O devices. Painful! • Today, O.S. reads from and writes to the I/O devices: mouse, keyboard, printer, monitor… • About half the instructions in today’s OS are to manage input and output operations. ...
... control programs for I/O devices. Painful! • Today, O.S. reads from and writes to the I/O devices: mouse, keyboard, printer, monitor… • About half the instructions in today’s OS are to manage input and output operations. ...
Abstract View of System Components
... • Stack Pointer (SP): points to the top of the current stack in memory. The stack contains one frame for each procedure that has been entered but not yet exited. • Program Status Word (PSW): contains the condition code bits and various other control bits. ...
... • Stack Pointer (SP): points to the top of the current stack in memory. The stack contains one frame for each procedure that has been entered but not yet exited. • Program Status Word (PSW): contains the condition code bits and various other control bits. ...
Chapter 1 - Introduction
... switches jobs so frequently that users can interact with each job while it is running, creating interactive computing ...
... switches jobs so frequently that users can interact with each job while it is running, creating interactive computing ...
Chap 01 - Introduction
... hardware, operating system, software) Information in use copied from slower to faster storage temporarily Faster storage (cache) checked first to determine if information is ...
... hardware, operating system, software) Information in use copied from slower to faster storage temporarily Faster storage (cache) checked first to determine if information is ...
CS533 Concepts of Operating Systems
... Linux implemented as a single Linux server in a μ-kernel task μ-kernel tasks used for Linux user processes A single L4 thread in the Linux server handles system calls and page faults. This thread is multiplexed (treated as a virtual CPU) On booting, the Linux server requests memory from its pager, w ...
... Linux implemented as a single Linux server in a μ-kernel task μ-kernel tasks used for Linux user processes A single L4 thread in the Linux server handles system calls and page faults. This thread is multiplexed (treated as a virtual CPU) On booting, the Linux server requests memory from its pager, w ...
Chapter 4
... Different varieties of operating systems. Show as many different operating systems as you can, focusing on the user interface. For example, compare the DOS and Linux command line, and the Mac, Windows 95, and Windows XP GUIs. Show how to perform a typical task in a command-line OS and how to perform ...
... Different varieties of operating systems. Show as many different operating systems as you can, focusing on the user interface. For example, compare the DOS and Linux command line, and the Mac, Windows 95, and Windows XP GUIs. Show how to perform a typical task in a command-line OS and how to perform ...
What is an Operating System?
... • Maximize throughput, minimize response time, and accommodate as many users as possible ...
... • Maximize throughput, minimize response time, and accommodate as many users as possible ...
Protected, User-Level DMA for the SHRIMP Network Interface
... addresses of the user programs must be translated to physical addresses before being loaded into the address registers. Virtual-to-physical address translation is performed by the operating system kernel. Finally, the physical memory pages used for DMA data transfers must be pinned to prevent the vi ...
... addresses of the user programs must be translated to physical addresses before being loaded into the address registers. Virtual-to-physical address translation is performed by the operating system kernel. Finally, the physical memory pages used for DMA data transfers must be pinned to prevent the vi ...
... interact with each program while it is running. The CPU is multiplexed among several jobs that are kept in memory and on disk (the CPU is allocated to a job only if the job is in memory). A job is swapped in and out of memory to the disk. On-line communication between the user and the system is prov ...
CS 571 Operating Systems - GMU Computer Science
... • Stack Pointer (SP): points to the top of the current stack in memory. The stack contains one frame for each procedure that has been entered but not yet exited.! • Program Status Word (PSW): contains the condition code bits and various other control bits. ! When time multiplexing the CPU, the ...
... • Stack Pointer (SP): points to the top of the current stack in memory. The stack contains one frame for each procedure that has been entered but not yet exited.! • Program Status Word (PSW): contains the condition code bits and various other control bits. ! When time multiplexing the CPU, the ...
Towards a Flexible, Lightweight Virtualization Alternative,
... on a single host will bear great similarity, because they implement the same application interface, and thus can share programs, libraries, and data, both in memory and on disk. The abstractions should make sharing of such resources a natural result rather than an afterthought, but with copyon-write ...
... on a single host will bear great similarity, because they implement the same application interface, and thus can share programs, libraries, and data, both in memory and on disk. The abstractions should make sharing of such resources a natural result rather than an afterthought, but with copyon-write ...
Chapter 1: Introduction
... One job selected and run via job scheduling When it has to wait (for I/O for example), OS switches to another job ...
... One job selected and run via job scheduling When it has to wait (for I/O for example), OS switches to another job ...
, Frameworks and Refinement* Choices H.
... subframeworks refine the general operating system framework, as it applies to a specific subsystem. The framework for the qystem provides generalized components and constraints to which the specialized subframeworks must conform. The subframeworks introduce additional components and constraints and ...
... subframeworks refine the general operating system framework, as it applies to a specific subsystem. The framework for the qystem provides generalized components and constraints to which the specialized subframeworks must conform. The subframeworks introduce additional components and constraints and ...
lec-3 - WordPress.com
... instructions until it either encounters an input/output operation or the time allocated for that program has expired Then, it saves the address of the memory location where the last instruction was executed and moves to the next program. The same procedure is repeated with the second program After a ...
... instructions until it either encounters an input/output operation or the time allocated for that program has expired Then, it saves the address of the memory location where the last instruction was executed and moves to the next program. The same procedure is repeated with the second program After a ...
ppt
... L4Linux will use a single-server approach. A single Linux server will run on top of L4, multiplexing a single thread for system calls and page faults. The Linux server maps physical memory into its address space, and acts as the pager for any user processes it creates. The Server cannot directly acc ...
... L4Linux will use a single-server approach. A single Linux server will run on top of L4, multiplexing a single thread for system calls and page faults. The Linux server maps physical memory into its address space, and acts as the pager for any user processes it creates. The Server cannot directly acc ...
Memory - UNL CSE
... instructions executed by VMM, speed to emulate – ISA is virtualizable if can execute VM directly on real machine while letting VMM retain ultimate control of CPU: “direct execution” – Since VMs have been considered for desktop/PC server apps only recently, most ISAs were created ignoring virtualizat ...
... instructions executed by VMM, speed to emulate – ISA is virtualizable if can execute VM directly on real machine while letting VMM retain ultimate control of CPU: “direct execution” – Since VMs have been considered for desktop/PC server apps only recently, most ISAs were created ignoring virtualizat ...
the internal operating system
... Some monitors can even reconfigure and reassign resources dynamically to optimize performance, particularly in clustered systems. These roles are handled by other operating system components in some systems. To increase security, many operating systems construct these programs as a hierarchy in whic ...
... Some monitors can even reconfigure and reassign resources dynamically to optimize performance, particularly in clustered systems. These roles are handled by other operating system components in some systems. To increase security, many operating systems construct these programs as a hierarchy in whic ...
slides
... • Since main memory (primary storage) is volatile and too small to accommodate all data and programs permanently, the computer system must provide secondary storage to back up main memory. • Most modern computer systems use disks as the principal on-line storage medium, for both programs and data. • ...
... • Since main memory (primary storage) is volatile and too small to accommodate all data and programs permanently, the computer system must provide secondary storage to back up main memory. • Most modern computer systems use disks as the principal on-line storage medium, for both programs and data. • ...
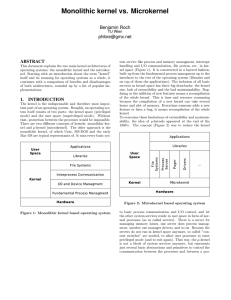
Monolithic kernel vs. Microkernel
... Monolithic kernels (and most of the first generation µ-kernels) run device drivers inside the kernel space. Hardware interrupts are directly handled by kernel processes. To add or change features provided by the hardware, all layers above the changed layer in the monolithic kernel also have to be ch ...
... Monolithic kernels (and most of the first generation µ-kernels) run device drivers inside the kernel space. Hardware interrupts are directly handled by kernel processes. To add or change features provided by the hardware, all layers above the changed layer in the monolithic kernel also have to be ch ...
ppt
... and one or more group IDs that determine the process’s rights to access system resources and files Personality - Not traditionally found on UNIX systems, but under Linux each process has an associated personality identifier that can slightly modify the semantics of certain system calls Used prim ...
... and one or more group IDs that determine the process’s rights to access system resources and files Personality - Not traditionally found on UNIX systems, but under Linux each process has an associated personality identifier that can slightly modify the semantics of certain system calls Used prim ...
Operating Systems for Embedded Computers
... Benu is a collection of increments that uses step by step presentation of core operating system operations, data structures and algorithms, where each new increment brings only a few new subjects. Other educational operating systems, while presenting single topic still use complete system, highlight ...
... Benu is a collection of increments that uses step by step presentation of core operating system operations, data structures and algorithms, where each new increment brings only a few new subjects. Other educational operating systems, while presenting single topic still use complete system, highlight ...
Operating-System - Jyoti Computer Centre
... 69) Segmentation is a method for both……………….and …………………… . It also eases the control of …………and……….. a) Memory management, Virtual memory, Sharing, Protection. b) File management, Resource, Sharing, Protection. c) Both a) & b). d) None of the above. 70) The FIFO (………) policy treats the allocated to ...
... 69) Segmentation is a method for both……………….and …………………… . It also eases the control of …………and……….. a) Memory management, Virtual memory, Sharing, Protection. b) File management, Resource, Sharing, Protection. c) Both a) & b). d) None of the above. 70) The FIFO (………) policy treats the allocated to ...