Cardiac Auscultation The Ohio State University
... closure of the aortic and pulmonic valves. These sounds may be abnormal in certain conditions. For example, pericardial disease, pleural effusion, or myocardial failure from dilated cardiomyopathy can decrease the intensity of the first heart sound. Arrhythmias typically lead to variable intensity h ...
... closure of the aortic and pulmonic valves. These sounds may be abnormal in certain conditions. For example, pericardial disease, pleural effusion, or myocardial failure from dilated cardiomyopathy can decrease the intensity of the first heart sound. Arrhythmias typically lead to variable intensity h ...
comparison of prognosis between patients with acute coronary
... Despite improvements in diagnosis and therapy over the last years, mortality among patients with acute coronary syndrome is still high. Cardiovascular diseases are the main global cause of death. An estimated 17.5 million people died from cardiovascular disease in 2012, representing 31% of all globa ...
... Despite improvements in diagnosis and therapy over the last years, mortality among patients with acute coronary syndrome is still high. Cardiovascular diseases are the main global cause of death. An estimated 17.5 million people died from cardiovascular disease in 2012, representing 31% of all globa ...
Heart Murmurs in Dogs - Kingsbrook Animal Hospital
... a few weeks time to track whether the murmur has decreased in intensity or disappeared, indicating that it was likely an innocent murmur. Similarly, if your adult dog appears to be extremely stressed at the time of a routine health examination and the murmur is of low intensity, your veterinarian ma ...
... a few weeks time to track whether the murmur has decreased in intensity or disappeared, indicating that it was likely an innocent murmur. Similarly, if your adult dog appears to be extremely stressed at the time of a routine health examination and the murmur is of low intensity, your veterinarian ma ...
PDF poster 347KB - University of Oxford
... Figure 3B. SNP significantly enhanced the response at 10Hz in WKY (n=7) but not SHR (n=6) preparations (p<0.05). SNP significantly increased baseline heart rate by a similar amount in both WKYs (+49±7, n=8) and SHRs (+43±6, n=6). SNP significantly enhanced the HR response to bath applied CCh (200 an ...
... Figure 3B. SNP significantly enhanced the response at 10Hz in WKY (n=7) but not SHR (n=6) preparations (p<0.05). SNP significantly increased baseline heart rate by a similar amount in both WKYs (+49±7, n=8) and SHRs (+43±6, n=6). SNP significantly enhanced the HR response to bath applied CCh (200 an ...
Remote Ischemic Conditioning Reduces Myocardial Infarct Size and
... treatment allocation and clinical details of each patient. Analysis of MI size and extent of myocardial edema was performed using an in-house macro written in ImageJ (National Institutes of Health, ...
... treatment allocation and clinical details of each patient. Analysis of MI size and extent of myocardial edema was performed using an in-house macro written in ImageJ (National Institutes of Health, ...
Ejection fraction determination without planimetry by two
... In method A, the left ventricular minor axis was measured in all 60 patients at the midventricular cavity level, and the left ventricular major axis was measured from the left ventricular apex to the base of the mitral valve in endsystole and end-diastole (Fig. 2). Then using formula (4), the ejecti ...
... In method A, the left ventricular minor axis was measured in all 60 patients at the midventricular cavity level, and the left ventricular major axis was measured from the left ventricular apex to the base of the mitral valve in endsystole and end-diastole (Fig. 2). Then using formula (4), the ejecti ...
Total heart volume variation throughout the cardiac cycle in humans
... Volumetric measurements. A ROI was drawn around the pericardial border (Image software; Scion Image, Scion) of the heart in each image of the cine-loop throughout the heart (Fig. 1, C and D). The ROI included all structures within the pericardium: the atria, ventricles, and the roots of the aorta an ...
... Volumetric measurements. A ROI was drawn around the pericardial border (Image software; Scion Image, Scion) of the heart in each image of the cine-loop throughout the heart (Fig. 1, C and D). The ROI included all structures within the pericardium: the atria, ventricles, and the roots of the aorta an ...
Transfer of Knowledge in the early History of Paediatric Cardiology
... b)Particularly P.C. in Germany was decisively influenced by the important incentives going out from GOSH and Gerald Graham. That way W-Germany P.C. was able to achieve the standards that apply throughout the USA und UK in the early 1950s. c)One of the most effective means of transfer of knowledge: t ...
... b)Particularly P.C. in Germany was decisively influenced by the important incentives going out from GOSH and Gerald Graham. That way W-Germany P.C. was able to achieve the standards that apply throughout the USA und UK in the early 1950s. c)One of the most effective means of transfer of knowledge: t ...
File
... 3. Rt posterolateral branch: Goes back of lt ventricle supply inferior aspect of interventricular septum 4. Atrial branches: Supply anterior and lateral surface of the right atrium. One branch supply posterior surface of both right and left atria. Artery of Sinuatrial Node (60%) ...
... 3. Rt posterolateral branch: Goes back of lt ventricle supply inferior aspect of interventricular septum 4. Atrial branches: Supply anterior and lateral surface of the right atrium. One branch supply posterior surface of both right and left atria. Artery of Sinuatrial Node (60%) ...
hypoplastic left heart syndrome
... is proposed, but not completely definite, as in each case many other individual factors may demand another approach. In this publication pathophysiologic, diagnostic and clinical aspects of the spectrum of HLHS will be systematically visualized and described, as there is no complete and uniform over ...
... is proposed, but not completely definite, as in each case many other individual factors may demand another approach. In this publication pathophysiologic, diagnostic and clinical aspects of the spectrum of HLHS will be systematically visualized and described, as there is no complete and uniform over ...
Fetal cardiac abnormalities identified prior to 14 weeks` gestation
... (C7). The four-chamber view and outflow tracts were identified on cross-sectional imaging with color flow mapping used as an adjunct to confirm identification. Pulsed wave Doppler traces of both atrioventricular and arterial valves were obtained where possible. Images were stored digitally and on vi ...
... (C7). The four-chamber view and outflow tracts were identified on cross-sectional imaging with color flow mapping used as an adjunct to confirm identification. Pulsed wave Doppler traces of both atrioventricular and arterial valves were obtained where possible. Images were stored digitally and on vi ...
File
... 3. Rt posterolateral branch: Goes back of lt ventricle supply inferior aspect of interventricular septum 4. Atrial branches: Supply anterior and lateral surface of the right atrium. One branch supply posterior surface of both right and left atria. Artery of Sinuatrial Node (60%) ...
... 3. Rt posterolateral branch: Goes back of lt ventricle supply inferior aspect of interventricular septum 4. Atrial branches: Supply anterior and lateral surface of the right atrium. One branch supply posterior surface of both right and left atria. Artery of Sinuatrial Node (60%) ...
Sudden cardiac death in children and adolescents: introduction and
... sudden cardiac death.’’ The true incidence, therefore, is likely to be greater than 15 per year (NCCSIR) but less than the 1166 per year as reported by Zheng et al [14]; a reasonable estimate is in the range of 500 episodes per year of unexplained SCD in children and adolescents in the United States ...
... sudden cardiac death.’’ The true incidence, therefore, is likely to be greater than 15 per year (NCCSIR) but less than the 1166 per year as reported by Zheng et al [14]; a reasonable estimate is in the range of 500 episodes per year of unexplained SCD in children and adolescents in the United States ...
Malignant Mitral Valve Prolapse - ORBi
... (Figure).3,16–20 Unexpectedly, no study assessed the morphofunctional abnormalities of the mitral valve complex as potential promoters of regional ventricular remodeling/alterations. As previously reported in their first study,3 Perazzolo Marra et al11 showed that LV fibrosis was mostly located clos ...
... (Figure).3,16–20 Unexpectedly, no study assessed the morphofunctional abnormalities of the mitral valve complex as potential promoters of regional ventricular remodeling/alterations. As previously reported in their first study,3 Perazzolo Marra et al11 showed that LV fibrosis was mostly located clos ...
Transcatheter Pulmonary Valve Implantation
... function following TPVI.6 Patients completed a standardized cardiopulmonary regimen 2 months before TPVI and 6 months after TPVI. Results of pre- and postexercise parameters were available for 94 to 114 patients, depending on the specific outcome. Numerous physiologic outcome measures were reported, ...
... function following TPVI.6 Patients completed a standardized cardiopulmonary regimen 2 months before TPVI and 6 months after TPVI. Results of pre- and postexercise parameters were available for 94 to 114 patients, depending on the specific outcome. Numerous physiologic outcome measures were reported, ...
letters to the editor
... these abnormalities are not apparent on examination alone but are only identified by specialized tests. Although all patients with congenital heart disease should be examined carefully for noncardiac features, infants with a 22q11 deletion are at risk for known anomalies that are best managed by ear ...
... these abnormalities are not apparent on examination alone but are only identified by specialized tests. Although all patients with congenital heart disease should be examined carefully for noncardiac features, infants with a 22q11 deletion are at risk for known anomalies that are best managed by ear ...
The evolutionary origin of cardiac chambers - IB-USP
... Difficulties in ascribing chamber identity to cardiac compartments arise because during vertebrate evolution, cardiac segments may have regressed, merged into others, or divided into left, right or more compartments. Besides, chambers can be defined on either morphological (Bourne, 1980; Fange, 1972 ...
... Difficulties in ascribing chamber identity to cardiac compartments arise because during vertebrate evolution, cardiac segments may have regressed, merged into others, or divided into left, right or more compartments. Besides, chambers can be defined on either morphological (Bourne, 1980; Fange, 1972 ...
Transplantation of the heart and both lungs
... neither his technique nor management differing in any crucial way from those of later workers. Durinig the,period of Demikhov's studies, other workers, notably Sinitsyn (1948) and Marcus, Wong, and Luisada (1951; 1953), were studying the effects of cervical implantation of the transplanted heart. Si ...
... neither his technique nor management differing in any crucial way from those of later workers. Durinig the,period of Demikhov's studies, other workers, notably Sinitsyn (1948) and Marcus, Wong, and Luisada (1951; 1953), were studying the effects of cervical implantation of the transplanted heart. Si ...
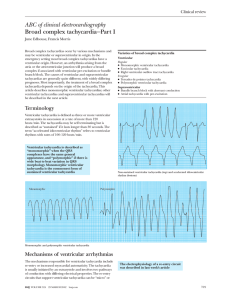
ABC of clinical electrocardiography Broad complex tachycardia—Part I
... originates close to the apex of the ventricle, with the wave of depolarisation moving upwards towards the base of the heart. Direct evidence of independent atrial activity In ventricular tachycardia, the sinus node continues to initiate atrial contraction. Since this atrial contraction is completely ...
... originates close to the apex of the ventricle, with the wave of depolarisation moving upwards towards the base of the heart. Direct evidence of independent atrial activity In ventricular tachycardia, the sinus node continues to initiate atrial contraction. Since this atrial contraction is completely ...
heart and neck vessel assessment
... and travel throughout the cardiac conduction circuit, can be detected on the surface of the skin. This electrical activity can be measured and recorded by electrocardiography (ECG, aka EKG), which records the depolarization and repolarization of the cardiac muscle. The phases of the ECG are known as ...
... and travel throughout the cardiac conduction circuit, can be detected on the surface of the skin. This electrical activity can be measured and recorded by electrocardiography (ECG, aka EKG), which records the depolarization and repolarization of the cardiac muscle. The phases of the ECG are known as ...
Cardiac contractility modulation
.jpg?width=300)
Cardiac contractility modulation (CCM) is a treatment for patients with moderate to severe left ventricular systolic heart failure (NYHA class II–IV). The short- and long-term use of this therapy enhances both the strength of ventricular contraction and the heart’s pumping capacity. The CCM mechanism is based on stimulation of the cardiac muscle by non-excitatory electrical signals (NES). CCM treatment is delivered by a pacemaker-like device that applies the NES, adjusted to and synchronized with the electrical action in the cardiac cycle.In CCM therapy, electrical stimulation is applied to the cardiac muscle during the absolute refractory period. In this phase of the cardiac cycle, electrical signals cannot trigger new cardiac muscle contractions, hence this type of stimulation is known as a non-excitatory stimulation. However, the electrical CCM signals increase the influx of calcium ions into the cardiac muscle cells (cardiomyocytes). In contrast to other electrical stimulation treatments for heart failure, such as pacemaker therapy or implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICD), CCM does not affect the cardiac rhythm directly. Rather, the aim is to enhance the heart’s natural contraction (the native cardiac contractility) sustainably over long periods of time. Furthermore, unlike most interventions that increase cardiac contractility, CCM is not associated with an unfavorable increase in oxygen demand by the heart (measured in terms of Myocardial Oxygen Consumption or MVO2). This may be explained by the beneficial effect CCM has in improving cardiac efficiency. A meta-analysis in 2014 and an overview of device-based treatment options in heart failure in 2013 concluded that CCM treatment is safe, that it is generally beneficial to patients and that CCM treatment increases the exercise tolerance (ET) and quality of life (QoL) of patients. Furthermore, preliminary long-term survival data shows that CCM is associated with lower long-term mortality in heart failure patients when compared with expected rates among similar patients not treated with CCM.