Monitoring heart failure hemodynamics with an implanted
... progress has been made in the management as well as diagnosis. Physicians measure BNP when they suspect a significant change in a patient’s status; therefore, its use for monitoring the course of HF is sporadic and influenced by clinical bias. Parameters that can be accessed any time during the clin ...
... progress has been made in the management as well as diagnosis. Physicians measure BNP when they suspect a significant change in a patient’s status; therefore, its use for monitoring the course of HF is sporadic and influenced by clinical bias. Parameters that can be accessed any time during the clin ...
Cryptogenic Ventricular Arrhythmias and Sudden Death by Fabry
... walls, valvular pattern, and left ventricular ejection fraction (68%), and tissue Doppler imaging registered reduced relaxation and contraction velocities, suggesting some myocardial abnormality. Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging failed to show areas of thickened or dysfunctional cardiac wall as we ...
... walls, valvular pattern, and left ventricular ejection fraction (68%), and tissue Doppler imaging registered reduced relaxation and contraction velocities, suggesting some myocardial abnormality. Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging failed to show areas of thickened or dysfunctional cardiac wall as we ...
l-Transposition of the Great Arteries
... inverted ventricles, this lesion is also called “congenitally corrected TGA.” Some children may also have ventricular septal defects, obstruction to flow into the pulmonary artery, or leakage of the valve tricuspid valve. What causes it? The cause is unknown, but genetic factors may contribute to it ...
... inverted ventricles, this lesion is also called “congenitally corrected TGA.” Some children may also have ventricular septal defects, obstruction to flow into the pulmonary artery, or leakage of the valve tricuspid valve. What causes it? The cause is unknown, but genetic factors may contribute to it ...
Cardiac Tamponade - Jefferson EM Ultrasound
... Progressively worse as pericardial pressure becomes higher than ventricular diastolic pressures. ...
... Progressively worse as pericardial pressure becomes higher than ventricular diastolic pressures. ...
Diastolic Dysfunction - Annals of Internal Medicine
... Older than 45 years. High blood pressure. Aortic stenosis (narrowing of the aortic heart valve). Atherosclerosis (clogged arteries). Diabetes. More common in women. ...
... Older than 45 years. High blood pressure. Aortic stenosis (narrowing of the aortic heart valve). Atherosclerosis (clogged arteries). Diabetes. More common in women. ...
Enlarged Heart (Cardiomegaly)
... Cardiomegaly is a general term used to describe any condition that results in an enlarged heart. There are two types of cardiomegaly: 1. Dilative- The heart can become enlarged due to dilation of the myocardium. An example is Dilated Cardiomyopathy (DCM), which is the most common form of non-ischemi ...
... Cardiomegaly is a general term used to describe any condition that results in an enlarged heart. There are two types of cardiomegaly: 1. Dilative- The heart can become enlarged due to dilation of the myocardium. An example is Dilated Cardiomyopathy (DCM), which is the most common form of non-ischemi ...
Valvular Heart Disease - Home
... Palpation: Systolic thrill may be present at apex depending on turbulence. Auscultation: S1 soft or absent; S3 gallop if significant MR; Systolic Murmur is hallmark - Gr. II-IV/VI holosystolic in most cases -radiates to axilla (exception is MVP); murmur is high pitched and blowing. ...
... Palpation: Systolic thrill may be present at apex depending on turbulence. Auscultation: S1 soft or absent; S3 gallop if significant MR; Systolic Murmur is hallmark - Gr. II-IV/VI holosystolic in most cases -radiates to axilla (exception is MVP); murmur is high pitched and blowing. ...
Cardiogenic Shock Due to Dynamic Left Ventricular Outflow Tract
... severe LV dysfunction, an intra-aortic counterpulsation balloon was inserted and catecholamines were administered. Still, the patient's condition did not improve. Transesophageal echocardiography was performed to exclude a mechanical complication, which confirmed a moderate MI and no evidence of a v ...
... severe LV dysfunction, an intra-aortic counterpulsation balloon was inserted and catecholamines were administered. Still, the patient's condition did not improve. Transesophageal echocardiography was performed to exclude a mechanical complication, which confirmed a moderate MI and no evidence of a v ...
Heart Failure 2013
... • Inability of the ventricle to fully relax • Increased pressure & volume in ventricle • Pressures back up to pulmonary veins pulmonary congestion • Stroke volume reduced • Echo: normal EF?, left atrial enlargement, pulmonary hypertension, heart wall abnormalities, right ventricular dilation ...
... • Inability of the ventricle to fully relax • Increased pressure & volume in ventricle • Pressures back up to pulmonary veins pulmonary congestion • Stroke volume reduced • Echo: normal EF?, left atrial enlargement, pulmonary hypertension, heart wall abnormalities, right ventricular dilation ...
10 .Congenitally corrected TGA- A case diagnosed incidentally
... course of conduction tissue, there is an increased risk of spontaneous complete AV block. CCTGA is commonly associated with other cardiac defects and its isolated occurrence is rare. SCD is still the leading cause of death in patients with CHD. CCTGA has the highest mortality among all CHD patients ...
... course of conduction tissue, there is an increased risk of spontaneous complete AV block. CCTGA is commonly associated with other cardiac defects and its isolated occurrence is rare. SCD is still the leading cause of death in patients with CHD. CCTGA has the highest mortality among all CHD patients ...
The Cardiovascular System: The Heart
... with closing of heart valves – First sound occurs as AV valves close and signifies beginning of systole – Second sound occurs when SL valves close at the beginning of ventricular diastole ...
... with closing of heart valves – First sound occurs as AV valves close and signifies beginning of systole – Second sound occurs when SL valves close at the beginning of ventricular diastole ...
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in 12 dogs (2004
... is available in literature published abroad on HCM dogs, there is a dearth in India. The present paper is the first of its kind in India to record retrospectively the manifestations, diagnosis and therapeutic management of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in dogs. Materials and methods The present invest ...
... is available in literature published abroad on HCM dogs, there is a dearth in India. The present paper is the first of its kind in India to record retrospectively the manifestations, diagnosis and therapeutic management of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in dogs. Materials and methods The present invest ...
Cardiac Disease and Anesthesia Anesthetic management of
... The use of inhalant gases for induction by mask or chamber is not recommended for patients with cardiovascular disease due to associated stress, respiratory depression and potential for hypotension. Prop ...
... The use of inhalant gases for induction by mask or chamber is not recommended for patients with cardiovascular disease due to associated stress, respiratory depression and potential for hypotension. Prop ...
Cardiothoracic Surgery - University of Pennsylvania
... 26 y/o male drug abuser admitted with fevers and sudden onset congestive heart failure. On PE he has a new loud diastolic murmur at the 3rd ICS along lower left ...
... 26 y/o male drug abuser admitted with fevers and sudden onset congestive heart failure. On PE he has a new loud diastolic murmur at the 3rd ICS along lower left ...
Early Postoperative Care of the Bypass Patient
... 26 y/o male drug abuser admitted with fevers and sudden onset congestive heart failure. On PE he has a new loud diastolic murmur at the 3rd ICS along lower left ...
... 26 y/o male drug abuser admitted with fevers and sudden onset congestive heart failure. On PE he has a new loud diastolic murmur at the 3rd ICS along lower left ...
Diastolic Mitral Regurgitation Secondary to Acute Aortic Regurgitation
... precardiopulmonary bypass TEE confirmed the diagnosis of severe AI. On evaluation of the mitral valve with CFD, systolic and diastolic MR jets were noted. This was confirmed by transmitral continuous wave Doppler and CFD M-mode. The decision was made to replace the aortic valve with a mechanical aor ...
... precardiopulmonary bypass TEE confirmed the diagnosis of severe AI. On evaluation of the mitral valve with CFD, systolic and diastolic MR jets were noted. This was confirmed by transmitral continuous wave Doppler and CFD M-mode. The decision was made to replace the aortic valve with a mechanical aor ...
cardiomyopathies - howMed Lectures
... (DCM) Prognosis: • 50% death- 2 years • 25% death- 5 years • Some improvement with therapy • Transplantation frequently done ...
... (DCM) Prognosis: • 50% death- 2 years • 25% death- 5 years • Some improvement with therapy • Transplantation frequently done ...
Feline Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
... concentration to distinguish between cats with cardiac and non-cardiac causes of respiratory distress. Connolly DJ, et al. J Vet Cardiol, 2009 Dec;11(2):71-8 • “Serum cTnI concentrations were different in RD+CHF compared to RD-NC cats. However the overlap in cTnI concentrations between the 2 groups ...
... concentration to distinguish between cats with cardiac and non-cardiac causes of respiratory distress. Connolly DJ, et al. J Vet Cardiol, 2009 Dec;11(2):71-8 • “Serum cTnI concentrations were different in RD+CHF compared to RD-NC cats. However the overlap in cTnI concentrations between the 2 groups ...
Glossary of Cardiology Terms
... Holter Monitoring: a technique for the continuous recording of electrocardiographic (ECG) signals, usually over 24 hours, to detect and diagnose heart rhythm problems (also called ambulatory monitoring). ...
... Holter Monitoring: a technique for the continuous recording of electrocardiographic (ECG) signals, usually over 24 hours, to detect and diagnose heart rhythm problems (also called ambulatory monitoring). ...
Supravalvular Aortic Stenosis - Massachusetts General Hospital
... Cardiac CT was performed for anatomic survey and quantitative assessment of biventricular function. The exam found residual post-surgical supravalvular aortic stenosis with collaterals (Figure 1), post-surgical stenosis of the pulmonic trunk (Figure 2), non-obstructive coronary artery disease (CAD) ...
... Cardiac CT was performed for anatomic survey and quantitative assessment of biventricular function. The exam found residual post-surgical supravalvular aortic stenosis with collaterals (Figure 1), post-surgical stenosis of the pulmonic trunk (Figure 2), non-obstructive coronary artery disease (CAD) ...
BIOL242 Lab30
... membrane. These membranes form the tricuspid valve between the right atrium and the right ventricle. The membranes are connected to flaps of muscle called the papillary muscles by tendons called the chordae tendinae or "heartstrings." Next, insert your probe into the pulmonary artery and see it come ...
... membrane. These membranes form the tricuspid valve between the right atrium and the right ventricle. The membranes are connected to flaps of muscle called the papillary muscles by tendons called the chordae tendinae or "heartstrings." Next, insert your probe into the pulmonary artery and see it come ...
Haron Kirikiru Wk 4 discussion Atrial fibrillation They are
... Blood tends to stagnate in the incompletely emptied atria and is therefore more likely to clot. When clot moves to the left ventricle, they may be embolized to the brain causing stroke. Symptoms Common symptoms includes palpitations, which are sensations of a racing, uncomfortable, irregular heart b ...
... Blood tends to stagnate in the incompletely emptied atria and is therefore more likely to clot. When clot moves to the left ventricle, they may be embolized to the brain causing stroke. Symptoms Common symptoms includes palpitations, which are sensations of a racing, uncomfortable, irregular heart b ...
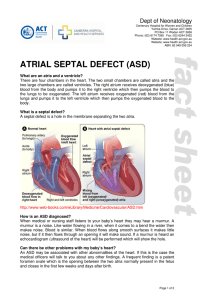
atrial septal defect (asd)
... In most children ASDs will rarely cause a problem. However, if the defect is large it may cause heart failure. Symptoms of heart failure include fast breathing, fast heart rate and poor growth. These symptoms are often controlled with medications until the hole decreases in size or closes. The major ...
... In most children ASDs will rarely cause a problem. However, if the defect is large it may cause heart failure. Symptoms of heart failure include fast breathing, fast heart rate and poor growth. These symptoms are often controlled with medications until the hole decreases in size or closes. The major ...
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy

Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a primary disease of the myocardium (the muscle of the heart) in which a portion of the myocardium is hypertrophied (thickened) without any obvious cause, creating functional impairment of the cardiac muscle. It is a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young athletes.The occurrence of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a significant cause of sudden unexpected cardiac death in any age group and as a cause of disabling cardiac symptoms. Younger people are likely to have a more severe form of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.HCM is frequently asymptomatic until sudden cardiac death, and for this reason some suggest routinely screening certain populations for this disease.A cardiomyopathy is a disease that affects the muscle of the heart. With HCM, the myocytes (cardiac contractile cells) in the heart increase in size, which results in the thickening of the heart muscle. In addition, the normal alignment of muscle cells is disrupted, a phenomenon known as myocardial disarray. HCM also causes disruptions of the electrical functions of the heart. HCM is most commonly due to a mutation in one of nine sarcomeric genes that results in a mutated protein in the sarcomere, the primary component of the myocyte (the muscle cell of the heart). These are predominantly single-point missense mutations in the genes for beta-myosin heavy chain (MHC), myosin-binding protein C, cardiac troponinT, or tropomyosin. These mutations cause myofibril and myocyte structural abnormalities and possible deficiencies in force generation. Not to be confused with dilated cardiomyopathy or any other cardiomyopathy.While most literature so far focuses on European, American, and Japanese populations, HCM appears in all ethnic groups. The prevalence of HCM is about 0.2% to 0.5% of the general population.