valve surgery
... The valves allow blood to pass through the atria and ventricles, ensuring that blood flows in the right direction. The coronary arteries are located on the surface of the heart, providing it with blood and oxygen. ...
... The valves allow blood to pass through the atria and ventricles, ensuring that blood flows in the right direction. The coronary arteries are located on the surface of the heart, providing it with blood and oxygen. ...
Sheep Heart Dissection Lab
... coronary artery supplies blood to the heart muscle tissue. The pointed bottom of the heart is called the apex. What do you think is the purpose of the coronary artery and what results if there is blockage in this vessel? ______________________________________________________________________________ ...
... coronary artery supplies blood to the heart muscle tissue. The pointed bottom of the heart is called the apex. What do you think is the purpose of the coronary artery and what results if there is blockage in this vessel? ______________________________________________________________________________ ...
right atrium right ventricle
... • Left to right shunt (according to pressure gradient) Addition of extra blood to normal pulmonary flow : • Increased PBF and increased pulmonary interstitial fluids up to oedema • Increased pulmonary venous return into LA • Increased LA volume, pressure & dilatation • LV hypertrophy • Finally biven ...
... • Left to right shunt (according to pressure gradient) Addition of extra blood to normal pulmonary flow : • Increased PBF and increased pulmonary interstitial fluids up to oedema • Increased pulmonary venous return into LA • Increased LA volume, pressure & dilatation • LV hypertrophy • Finally biven ...
Chapter 18
... – Tricuspid valve – 3 flaps of tissue – right side – Bicuspid valve (mitral valve) 2 flaps of tissue – left side – Chordae tendinae – connective tissue that attaches to valves and inferior muscle surface located in ventricles. – Blood flows into ventricles ventricles contract shoving flaps upward – ...
... – Tricuspid valve – 3 flaps of tissue – right side – Bicuspid valve (mitral valve) 2 flaps of tissue – left side – Chordae tendinae – connective tissue that attaches to valves and inferior muscle surface located in ventricles. – Blood flows into ventricles ventricles contract shoving flaps upward – ...
The Cardiovascular System: Part 1
... 1) Describe the structures of the heart that are responsible for regulating the movement of blood from one chamber to the next. 2) The pathway by which action potentials from the sinoatrial node travel through the heart is important for the normal function of the heart. Describe the conduction pathw ...
... 1) Describe the structures of the heart that are responsible for regulating the movement of blood from one chamber to the next. 2) The pathway by which action potentials from the sinoatrial node travel through the heart is important for the normal function of the heart. Describe the conduction pathw ...
Double outlet right ventricle
... A normal heart has two smaller upper chambers called the atria and two larger lower chambers called ventricles. It has four valves, one at the entrance to each chamber. They stop the blood flowing backwards and keep the blood moving forwards through the heart. The left side of the heart receives oxy ...
... A normal heart has two smaller upper chambers called the atria and two larger lower chambers called ventricles. It has four valves, one at the entrance to each chamber. They stop the blood flowing backwards and keep the blood moving forwards through the heart. The left side of the heart receives oxy ...
Cardiovascular System 1
... a. Atrioventricular (AV) valves - prevent backflow from ventricles to atria tricuspid valve - RA } RV bicuspid (mitral) valve - LA } LV chordae tendineae attached to papillary muscles prevent prolapse of AV valves b. Semilunar valves - prevent backflow from arteries to ventricles pulmonary valve - R ...
... a. Atrioventricular (AV) valves - prevent backflow from ventricles to atria tricuspid valve - RA } RV bicuspid (mitral) valve - LA } LV chordae tendineae attached to papillary muscles prevent prolapse of AV valves b. Semilunar valves - prevent backflow from arteries to ventricles pulmonary valve - R ...
299-1283-1-SP - International Cardiovascular Forum Journal
... A wide spectrum of cardiac manifestations have been described in the course of WG such as myocarditis, coronary vasculitis, valvular heart disease, pericarditis and/or rhythm disorders5. In the setting of WG cardiac masses are not common and can be presented as a tumour-like mass. These findings are ...
... A wide spectrum of cardiac manifestations have been described in the course of WG such as myocarditis, coronary vasculitis, valvular heart disease, pericarditis and/or rhythm disorders5. In the setting of WG cardiac masses are not common and can be presented as a tumour-like mass. These findings are ...
Making Heart better
... level for qualitative assessment of global and regional left ventricular function. MSCT image reconstructions showed previously unrecognised displacement of the posterior mitral valve leaflet into the left atrium during systole. An ...
... level for qualitative assessment of global and regional left ventricular function. MSCT image reconstructions showed previously unrecognised displacement of the posterior mitral valve leaflet into the left atrium during systole. An ...
The Heart
... *The walls around the ventricles have much thicker muscle, why? -The ventricles thrust blood out of heart to body, the atria just thrust it down to ventricles ...
... *The walls around the ventricles have much thicker muscle, why? -The ventricles thrust blood out of heart to body, the atria just thrust it down to ventricles ...
Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
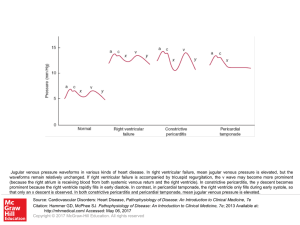
... Jugular venous pressure waveforms in various kinds of heart disease. In right ventricular failure, mean jugular venous pressure is elevated, but the waveforms remain relatively unchanged. If right ventricular failure is accompanied by tricuspid regurgitation, the v wave may become more prominent (be ...
... Jugular venous pressure waveforms in various kinds of heart disease. In right ventricular failure, mean jugular venous pressure is elevated, but the waveforms remain relatively unchanged. If right ventricular failure is accompanied by tricuspid regurgitation, the v wave may become more prominent (be ...
CVS Pathology Lecture Notes (L4)
... 3. occlusion of the branch vessels 4. rupture with hemorrhage a. usually results in death if aortic, due to high pressure blood loss Berry Aneurysm smell berry-like aneurysm circle of willis rupture subarachnoid haemorhage Aetiology ...
... 3. occlusion of the branch vessels 4. rupture with hemorrhage a. usually results in death if aortic, due to high pressure blood loss Berry Aneurysm smell berry-like aneurysm circle of willis rupture subarachnoid haemorhage Aetiology ...
Right Ventricle
... Purpose: stabilizes the position and the heart valves and physically isolates the atrial muscle from ventricular muscle tissue (important b/c it shows the timing of ventricular contraction is relative to atrial contraction can be controlled)” ...
... Purpose: stabilizes the position and the heart valves and physically isolates the atrial muscle from ventricular muscle tissue (important b/c it shows the timing of ventricular contraction is relative to atrial contraction can be controlled)” ...
- British Heart Valve Society
... 5. What are heart valves and what is valve disease? The heart valves stop blood moving in the wrong direction when the heart beats. The left ventricle pumps blood to the head and body. It receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the left atrium. The mitral valve is placed at the junction between ...
... 5. What are heart valves and what is valve disease? The heart valves stop blood moving in the wrong direction when the heart beats. The left ventricle pumps blood to the head and body. It receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the left atrium. The mitral valve is placed at the junction between ...
File
... 2 ________________________ chambers of heart; __________________________________________ Responsible for __________________________________ blood Right atrium receives __________________________________________________________ blood from the body through the ___________________________________ ...
... 2 ________________________ chambers of heart; __________________________________________ Responsible for __________________________________ blood Right atrium receives __________________________________________________________ blood from the body through the ___________________________________ ...
Angina - Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine
... The ventricles are the discharging chambers. The right ventricle pumps blood away from the heart to the lungs via the pulmonary arteries and the left ventricle pumps blood away from the heart to the body through the aorta. The ventricular chambers contain trabeculae carneae muscle. Ventricular chamb ...
... The ventricles are the discharging chambers. The right ventricle pumps blood away from the heart to the lungs via the pulmonary arteries and the left ventricle pumps blood away from the heart to the body through the aorta. The ventricular chambers contain trabeculae carneae muscle. Ventricular chamb ...
File
... The wall of the left because the left ventricle pumps blood all ventricle is thicker than around the body whereas the right ventricle the right pumps blood to the lungs Atrio ventricular valves prevent blood flow of blood from ventricles to atria ...
... The wall of the left because the left ventricle pumps blood all ventricle is thicker than around the body whereas the right ventricle the right pumps blood to the lungs Atrio ventricular valves prevent blood flow of blood from ventricles to atria ...
Rheumatic Fever 2010 1st yr2010-10-03 11:1464 KB
... Chronic Rheumatic Carditis: Clinical Manifestation after years or decades after the initial episode of rheumatic fever. Signs and symptoms depend on which involved valve(s): cardiac murmurs, hypertrophy, dilation, congestive heart failure, arrhythmia, thromboembolic complications and infective endoc ...
... Chronic Rheumatic Carditis: Clinical Manifestation after years or decades after the initial episode of rheumatic fever. Signs and symptoms depend on which involved valve(s): cardiac murmurs, hypertrophy, dilation, congestive heart failure, arrhythmia, thromboembolic complications and infective endoc ...
FREE Sample Here
... 10. T or F. The semilunar valves are the aortic and mitral valves. 11. T or F. The job of the heart valves is to prevent backflow of blood. 12. T or F. The vena cava is a large artery that carries blood from the right ventricle to the lungs. 13. T or F. The three main coronary arteries are the aorta ...
... 10. T or F. The semilunar valves are the aortic and mitral valves. 11. T or F. The job of the heart valves is to prevent backflow of blood. 12. T or F. The vena cava is a large artery that carries blood from the right ventricle to the lungs. 13. T or F. The three main coronary arteries are the aorta ...
Double Outlet Right Ventricle
... artery exit from the right ventricle. In the normal heart, the aorta leaves the left ventricle and the pulmonary artery leaves the right ventricle. In addition, there is a large ventricular septal defect (VSD), or hole in the muscle wall (septum) that separates the right and left ventricles. ...
... artery exit from the right ventricle. In the normal heart, the aorta leaves the left ventricle and the pulmonary artery leaves the right ventricle. In addition, there is a large ventricular septal defect (VSD), or hole in the muscle wall (septum) that separates the right and left ventricles. ...
4 valve Endocarditis Confirmed By Intraoperative
... sions using modern echocardiography, can greatly assist in making the correct diagnosis (2). In this context it is important to note that the transesophageal technique is save and more sensitive than transthoracic echocardiography for detecting vegetations (3). In the case presented here, the oscill ...
... sions using modern echocardiography, can greatly assist in making the correct diagnosis (2). In this context it is important to note that the transesophageal technique is save and more sensitive than transthoracic echocardiography for detecting vegetations (3). In the case presented here, the oscill ...
File
... • SV (ml/beat) X HR (beats/min) = CO(ml/min.) • 70 ml X 80 = 5600 ml /min. or 5.6 liters L/min ...
... • SV (ml/beat) X HR (beats/min) = CO(ml/min.) • 70 ml X 80 = 5600 ml /min. or 5.6 liters L/min ...
File
... • SV (ml/beat) X HR (beats/min) = CO(ml/min.) • 70 ml X 80 = 5600 ml /min. or 5.6 liters L/min ...
... • SV (ml/beat) X HR (beats/min) = CO(ml/min.) • 70 ml X 80 = 5600 ml /min. or 5.6 liters L/min ...
Mitral insufficiency

Mitral insufficiency (MI), mitral regurgitation or mitral incompetence is a disorder of the heart in which the mitral valve does not close properly when the heart pumps out blood. It is the abnormal leaking of blood backwards from the left ventricle, through the mitral valve, into the left atrium, when the left ventricle contracts, i.e. there is regurgitation of blood back into the left atrium. MI is the most common form of valvular heart disease.