document
... memory. Recurrent networks can have connections between nodes in any layer, which enables them to store data – a memory. Recurrent networks can be used to solve problems where the solution depends on previous inputs as well as current inputs ...
... memory. Recurrent networks can have connections between nodes in any layer, which enables them to store data – a memory. Recurrent networks can be used to solve problems where the solution depends on previous inputs as well as current inputs ...
notes as
... that dies when you poke it around • To understand a new style of computation – Inspired by neurons and their adaptive connections – Very different style from sequential computation • should be good for things that brains are good at (e.g. vision) • Should be bad for things that brains are bad at (e. ...
... that dies when you poke it around • To understand a new style of computation – Inspired by neurons and their adaptive connections – Very different style from sequential computation • should be good for things that brains are good at (e.g. vision) • Should be bad for things that brains are bad at (e. ...
AND Network
... a 7X36 range finder. Output units represent “drive straight”, “turn left” or “turn right”. After training about 40 times on 1200 road images, the car drove around CMU campus at 5 km/h (using a small workstation on the car). This was almost twice the speed of any other non-NN algorithm at the time. ...
... a 7X36 range finder. Output units represent “drive straight”, “turn left” or “turn right”. After training about 40 times on 1200 road images, the car drove around CMU campus at 5 km/h (using a small workstation on the car). This was almost twice the speed of any other non-NN algorithm at the time. ...
Preface
... Artificial intelligence (AI) researchers continue to face large challenges in their quest to develop truly intelligent systems. e recent developments in the area of neural-symbolic integration bring an opportunity to combine symbolic AI with robust neural computation to tackle some of these challen ...
... Artificial intelligence (AI) researchers continue to face large challenges in their quest to develop truly intelligent systems. e recent developments in the area of neural-symbolic integration bring an opportunity to combine symbolic AI with robust neural computation to tackle some of these challen ...
Application of ART neural networks in Wireless sensor networks
... ART neural networks are surprisingly stable in real world environments, and allow for high accuracy pattern recognition, even in constantly changing environments Their nature as neural networks makes them energy efficient. This makes them very suitable for application in wireless sensor networks ...
... ART neural networks are surprisingly stable in real world environments, and allow for high accuracy pattern recognition, even in constantly changing environments Their nature as neural networks makes them energy efficient. This makes them very suitable for application in wireless sensor networks ...
1 - AGH
... Here, with same color, are marked fragments with microscopically examined similar connections, whereas different colors corresponds to substantial differences. This map, with rather historical meaning, was called Brodmann’s areas. Brodmann divided the cortex into 52 regions. Currently we treat brain ...
... Here, with same color, are marked fragments with microscopically examined similar connections, whereas different colors corresponds to substantial differences. This map, with rather historical meaning, was called Brodmann’s areas. Brodmann divided the cortex into 52 regions. Currently we treat brain ...
عرض تقديمي من PowerPoint
... a 7X36 range finder. Output units represent “drive straight”, “turn left” or “turn right”. After training about 40 times on 1200 road images, the car drove around CMU campus at 5 km/h (using a small workstation on the car). This was almost twice the speed of any other non-NN algorithm at the time. ...
... a 7X36 range finder. Output units represent “drive straight”, “turn left” or “turn right”. After training about 40 times on 1200 road images, the car drove around CMU campus at 5 km/h (using a small workstation on the car). This was almost twice the speed of any other non-NN algorithm at the time. ...
Document
... Recall that orientation selective cells in V1 could be explained by receiving input from proper constellation of center surround LGN cells. However, this ignores lateral connectivity in V1, which is more prominent than feed-forward connectivity. Same as prev. model with h(q)=A(1-e+e cos(2q) and glob ...
... Recall that orientation selective cells in V1 could be explained by receiving input from proper constellation of center surround LGN cells. However, this ignores lateral connectivity in V1, which is more prominent than feed-forward connectivity. Same as prev. model with h(q)=A(1-e+e cos(2q) and glob ...
(Early Period) - Connectionism
... Connectionism is a movement in cognitive science that seeks to explain intellectual abilities using artificial neural networks. Neural networks are simplified models of the brain composed of large numbers of units (the analogs of neurons) together with weights that measure the strength of connection ...
... Connectionism is a movement in cognitive science that seeks to explain intellectual abilities using artificial neural networks. Neural networks are simplified models of the brain composed of large numbers of units (the analogs of neurons) together with weights that measure the strength of connection ...
sheets DA 7
... Recall that orientation selective cells in V1 could be explained by receiving input from proper constellation of center surround LGN cells. However, this ignores lateral connectivity in V1, which is more prominent than feed-forward connectivity. Same as prev. model with h(q)=A(1-e+e cos(2q)) and glo ...
... Recall that orientation selective cells in V1 could be explained by receiving input from proper constellation of center surround LGN cells. However, this ignores lateral connectivity in V1, which is more prominent than feed-forward connectivity. Same as prev. model with h(q)=A(1-e+e cos(2q)) and glo ...
Lecture 02 – Single Layer Neural Network
... However, we can also use one neuron to classify only one class. The neuron decides whether the input belongs to its class or not This configuration has the disadvantage that the network ...
... However, we can also use one neuron to classify only one class. The neuron decides whether the input belongs to its class or not This configuration has the disadvantage that the network ...
Theoretical Neuroscience - Neural Dynamics and Computation Lab
... All higher level cognitive functions, like perception, attention, learning, decision making, and memory, emerge from networks of neurons coupled to each other through synapses. Although we understand a great deal now about how single neurons transform inputs to outputs, and how single plastic synaps ...
... All higher level cognitive functions, like perception, attention, learning, decision making, and memory, emerge from networks of neurons coupled to each other through synapses. Although we understand a great deal now about how single neurons transform inputs to outputs, and how single plastic synaps ...
Introduction to Neural Networks
... J. J. Hopfield (1982), “Neural networks and physical systems with emergent collective computational ability,” Proc. of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, vol. 79, pp. 2554-2558. J. J. Hopfield and D. W. Tank (1985), “Neural computation of decisions in optimisationproblems,” Biological Cybernetic ...
... J. J. Hopfield (1982), “Neural networks and physical systems with emergent collective computational ability,” Proc. of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, vol. 79, pp. 2554-2558. J. J. Hopfield and D. W. Tank (1985), “Neural computation of decisions in optimisationproblems,” Biological Cybernetic ...
... The continued development of computational tools offers the possibility to execute processes with the ability to carry out activities more efficiently, exact-ness and precision. Between these tools there is the neural architecture, Deep Belief Network (DBN), designed to collaborate in the developmen ...
Neural Networks
... state. Recurrent networks are cyclic: links can feed back into themselves. Thus, the activation levels of the network form a dynamic system, and can exhibit either stable, oscillatory or even chaotic behaviour. A recurrent network’s response will depend on its initial state, which depends on prior i ...
... state. Recurrent networks are cyclic: links can feed back into themselves. Thus, the activation levels of the network form a dynamic system, and can exhibit either stable, oscillatory or even chaotic behaviour. A recurrent network’s response will depend on its initial state, which depends on prior i ...
Slide 1
... Network (FFNN) is sufficient for realizing a broad class of input/output non-linear maps (Kolmogorov’s theorem) Disadvantages: • number of neurons in the hidden layer cannot be determined • number of neurons can be large implying expensive calculation Fainan May 2006 ...
... Network (FFNN) is sufficient for realizing a broad class of input/output non-linear maps (Kolmogorov’s theorem) Disadvantages: • number of neurons in the hidden layer cannot be determined • number of neurons can be large implying expensive calculation Fainan May 2006 ...
Mathematical model
... simulate, in a gross manner, the networks of nerve cell (neurons) of the biological central nervous system. ANNs are an attempt to create machines that work in a similar way to the human brain by building these machines using components that behave like biological neurons, called artificial neurons. ...
... simulate, in a gross manner, the networks of nerve cell (neurons) of the biological central nervous system. ANNs are an attempt to create machines that work in a similar way to the human brain by building these machines using components that behave like biological neurons, called artificial neurons. ...
Slide ()
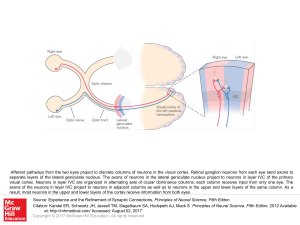
... separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the primary visual cortex. Neurons in layer IVC are organized in alternating sets of ocular dominance columns; each column receives input from only one eye. Th ...
... separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the primary visual cortex. Neurons in layer IVC are organized in alternating sets of ocular dominance columns; each column receives input from only one eye. Th ...
lecture notes - The College of Saint Rose
... Combine linearly separable functions of neurons 3 and 4: ...
... Combine linearly separable functions of neurons 3 and 4: ...
Methods S2.
... previous layer and provide inputs to the neurons of the next layer. The connections among neurons are represented by weighted “synapses”: each synapse connects the output of a neuron in a layer to an input of another neuron in the next layer. A schematic representation of a MLP is reported in Figure ...
... previous layer and provide inputs to the neurons of the next layer. The connections among neurons are represented by weighted “synapses”: each synapse connects the output of a neuron in a layer to an input of another neuron in the next layer. A schematic representation of a MLP is reported in Figure ...
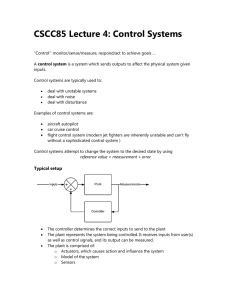
CSCC85 Lecture 4: Control Systems
... Examples of f: sigmoid(), tanh(), etc. Single Layer: multiple neurons ...
... Examples of f: sigmoid(), tanh(), etc. Single Layer: multiple neurons ...
Biological Inspiration for Artificial Neural Networks
... Biological Inspiration for Artificial Neural Networks Nick Mascola ...
... Biological Inspiration for Artificial Neural Networks Nick Mascola ...
Lecture 2: Basics and definitions - Homepages | The University of
... wi weight, (synaptic strength) measuring the strength of the interaction between neurons. ...
... wi weight, (synaptic strength) measuring the strength of the interaction between neurons. ...