Constellations
... interpretation of stars and planets based on the premise that there is a relationship between astronomical phenomena and events in the human world. ...
... interpretation of stars and planets based on the premise that there is a relationship between astronomical phenomena and events in the human world. ...
History of Astronomy
... 4th through 12th centuries These were the Dark Ages when scientific studies ...
... 4th through 12th centuries These were the Dark Ages when scientific studies ...
Early history of astronomy
... • The motion of a body, such as a planet or moon, along a path around some point in space • Earth's orbit is elliptical • Earth is closest to the Sun (perihelion) in January • Earth is farthest from the Sun (aphelion) in July • The plane of the ecliptic is an imaginary plane that connects Earth's or ...
... • The motion of a body, such as a planet or moon, along a path around some point in space • Earth's orbit is elliptical • Earth is closest to the Sun (perihelion) in January • Earth is farthest from the Sun (aphelion) in July • The plane of the ecliptic is an imaginary plane that connects Earth's or ...
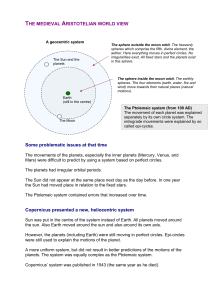
THE MEDIEVAL ARISTOTELIAN WORLD VIEW Some
... The movement of each planet was explained separately by its own circle system. The retrograde movements were explained by so called epi-cycles. ...
... The movement of each planet was explained separately by its own circle system. The retrograde movements were explained by so called epi-cycles. ...
Eratosthenes of Cyrene (c.276-c.196 BC)
... http://www.daviddarling.info/encyclopedia/G/Greek_astronomy.html ...
... http://www.daviddarling.info/encyclopedia/G/Greek_astronomy.html ...
The History of Astronomy
... Early Chinese, Central American, and North European cultures show evidence of studying astronomy ...
... Early Chinese, Central American, and North European cultures show evidence of studying astronomy ...
Early Astronomy
... • 1 extra day in every 4 years (leap year) is too much! • Leap year at the close of the century omitted, unless year a multiple of 400! i.e : 1600, 2000 leap years 1700, 1800, 1900 not leap years ...
... • 1 extra day in every 4 years (leap year) is too much! • Leap year at the close of the century omitted, unless year a multiple of 400! i.e : 1600, 2000 leap years 1700, 1800, 1900 not leap years ...
Astronomy - Earth Systems A
... Invented the first telescope Discovered moons around Jupiter and the Saturn's rings Mapped the moon ...
... Invented the first telescope Discovered moons around Jupiter and the Saturn's rings Mapped the moon ...
Saraswati River - Ancient Greece
... The Babylonians believed that the sun, moon, planets and stars were placed there by the gods. They observed that the stars travelled in a certain band of sky – which they divided into 12, recognizable patterns or constellations – now known as the zodiac. They named the constellations after animals / ...
... The Babylonians believed that the sun, moon, planets and stars were placed there by the gods. They observed that the stars travelled in a certain band of sky – which they divided into 12, recognizable patterns or constellations – now known as the zodiac. They named the constellations after animals / ...
Adobe Acrobat - Ancient Greece
... The Babylonians believed that the sun, moon, planets and stars were placed there by the gods. They observed that the stars travelled in a certain band of sky – which they divided into 12, recognizable patterns or constellations – now known as the zodiac. They named the constellations after animals / ...
... The Babylonians believed that the sun, moon, planets and stars were placed there by the gods. They observed that the stars travelled in a certain band of sky – which they divided into 12, recognizable patterns or constellations – now known as the zodiac. They named the constellations after animals / ...
Document
... across the sky. Messenger of the gods. • Venus (Aphrodite), the morning and evening star, very bright but variable, goddess of love. • Mars (Ares), the red planet, god of war. • Jupiter (Zeus), very bright, king of the gods. • Saturn (Kronos), bright and pale yellow, first of the Titan’s, father of ...
... across the sky. Messenger of the gods. • Venus (Aphrodite), the morning and evening star, very bright but variable, goddess of love. • Mars (Ares), the red planet, god of war. • Jupiter (Zeus), very bright, king of the gods. • Saturn (Kronos), bright and pale yellow, first of the Titan’s, father of ...
History_of_Astronomy
... noon, the Sun cast no shadow in Syene, but in Alexandria a shadow was visible. Using a gnomon (a vertical stick), Eratosthenes measured the shadow's angle to be about one-fiftieth of a circle. Calculated earth radius at 4212 miles vs the 3963 Calculated moon radius at 1478 vs. 1080 miles ...
... noon, the Sun cast no shadow in Syene, but in Alexandria a shadow was visible. Using a gnomon (a vertical stick), Eratosthenes measured the shadow's angle to be about one-fiftieth of a circle. Calculated earth radius at 4212 miles vs the 3963 Calculated moon radius at 1478 vs. 1080 miles ...
History of Astronomy Ancient to 200 A.D.
... noon, the Sun cast no shadow in Syene, but in Alexandria a shadow was visible. Using a gnomon (a vertical stick), Eratosthenes measured the shadow's angle to be about one-fiftieth of a circle. Calculated earth radius at 4212 miles vs the 3963 Calculated moon radius at 1478 vs. 1080 miles ...
... noon, the Sun cast no shadow in Syene, but in Alexandria a shadow was visible. Using a gnomon (a vertical stick), Eratosthenes measured the shadow's angle to be about one-fiftieth of a circle. Calculated earth radius at 4212 miles vs the 3963 Calculated moon radius at 1478 vs. 1080 miles ...
History of Astronomy Ancient to 200 AD
... noon, the Sun cast no shadow in Syene, but in Alexandria a shadow was visible. Using a gnomon (a vertical stick), Eratosthenes measured the shadow's angle to be about one-fiftieth of a circle. Calculated earth radius at 4212 miles vs the 3963 Calculated moon radius at 1478 vs. 1080 miles ...
... noon, the Sun cast no shadow in Syene, but in Alexandria a shadow was visible. Using a gnomon (a vertical stick), Eratosthenes measured the shadow's angle to be about one-fiftieth of a circle. Calculated earth radius at 4212 miles vs the 3963 Calculated moon radius at 1478 vs. 1080 miles ...
Astronomy Miscellaneous Items Test
... Answer the following questions. Answer in complete sentences, but answer succinctly. Remember: You must pass with 80% to receive credit for this section. This test is worth 3 points 1. What calendar do we use now, on a day-to-day basis? 2. The keeping of time accurately is very important to astronom ...
... Answer the following questions. Answer in complete sentences, but answer succinctly. Remember: You must pass with 80% to receive credit for this section. This test is worth 3 points 1. What calendar do we use now, on a day-to-day basis? 2. The keeping of time accurately is very important to astronom ...
planet - Groups
... but one that results in specific predictions, which we can test and confirm or refute. It has become a commonly used word as a result of the success of Thomas Kuhn's 1962 book The Structure of Scientific Revolutions. Examples of scientific paradigms are: 1) the Earth is just one of a number of plane ...
... but one that results in specific predictions, which we can test and confirm or refute. It has become a commonly used word as a result of the success of Thomas Kuhn's 1962 book The Structure of Scientific Revolutions. Examples of scientific paradigms are: 1) the Earth is just one of a number of plane ...
Greek and Hellenistic astronomy
... concentric spheres, whose circular motions combined to carry the planets around the earth. This basic cosmological model prevailed, in various forms, until the Sixteenth century. One of the earliest accepted models of the universe is credited to the Greek philosopher Aristotle, who lived in the 4th ...
... concentric spheres, whose circular motions combined to carry the planets around the earth. This basic cosmological model prevailed, in various forms, until the Sixteenth century. One of the earliest accepted models of the universe is credited to the Greek philosopher Aristotle, who lived in the 4th ...
Astronomy from the ancients to the Renaissance
... but one that results in specific predictions, which we can test and confirm or refute. It has become a commonly used word as a result of the success of Thomas Kuhn's 1962 book The Structure of Scientific Revolutions. Examples of scientific paradigms are: 1) the Earth is just one of a number of plane ...
... but one that results in specific predictions, which we can test and confirm or refute. It has become a commonly used word as a result of the success of Thomas Kuhn's 1962 book The Structure of Scientific Revolutions. Examples of scientific paradigms are: 1) the Earth is just one of a number of plane ...
And let there be light!
... astronomy for religious and societal purposes— when to plant crops, harvest them, when to offer sacrifice, etc. Mesoamerican tribes, the Anasazi, the Babylonians, and other ancient civilizations also developed calendars based on relatively sophisticated astronomical observations. •The history of sci ...
... astronomy for religious and societal purposes— when to plant crops, harvest them, when to offer sacrifice, etc. Mesoamerican tribes, the Anasazi, the Babylonians, and other ancient civilizations also developed calendars based on relatively sophisticated astronomical observations. •The history of sci ...
proposed another geocentric _ _ _ _ _.
... Copernicus (1473-1543) proposed that the sun is stationary near the _ _ _ _ _ _ of the universe. His _ _ _ _ _ _ proposed that the Earth _ _ _ _ _ _ _ on its _ _ _ _ once daily and _ _ _ _ _ _ _ around the sun once a year. He suggested that the _ _ _ _ _ _ _ the radius of a planet’s _ _ _ _ _ , the ...
... Copernicus (1473-1543) proposed that the sun is stationary near the _ _ _ _ _ _ of the universe. His _ _ _ _ _ _ proposed that the Earth _ _ _ _ _ _ _ on its _ _ _ _ once daily and _ _ _ _ _ _ _ around the sun once a year. He suggested that the _ _ _ _ _ _ _ the radius of a planet’s _ _ _ _ _ , the ...
Timekeeping - UC Berkeley Astronomy Department
... using the day when the Sun shines right down a well at the solstice ...
... using the day when the Sun shines right down a well at the solstice ...
Ancient Greek astronomy

Greek astronomy is astronomy written in the Greek language in classical antiquity. Greek astronomy is understood to include the ancient Greek, Hellenistic, Greco-Roman, and Late Antiquity eras. It is not limited geographically to Greece or to ethnic Greeks, as the Greek language had become the language of scholarship throughout the Hellenistic world following the conquests of Alexander. This phase of Greek astronomy is also known as Hellenistic astronomy, while the pre-Hellenistic phase is known as Classical Greek astronomy. During the Hellenistic and Roman periods, much of the Greek and non-Greek astronomers working in the Greek tradition studied at the Musaeum and the Library of Alexandria in Ptolemaic Egypt.The development of astronomy by the Greek and Hellenistic astronomers is considered by historians to be a major phase in the history of astronomy. Greek astronomy is characterized from the start by seeking a rational, physical explanation for celestial phenomena. Most of the constellations of the northern hemisphere derive from Greek astronomy, as are the names of many stars, asteroids, and planets. It was influenced by Egyptian and especially Babylonian astronomy; in turn, it influenced Indian, Arabic-Islamic and Western European astronomy.