Neurons and Glia Three basic neurons: ∼ Multipolar: Neurons by
... Autapse: Neuron synapses on itself; a negative feedback mechanism. ...
... Autapse: Neuron synapses on itself; a negative feedback mechanism. ...
Document
... Best understood limbic center is the AMYGDALA AMYGDALA is required for experiencing both fearful and pleasurable responses and is required for generating memories associated with emotional experiences ...
... Best understood limbic center is the AMYGDALA AMYGDALA is required for experiencing both fearful and pleasurable responses and is required for generating memories associated with emotional experiences ...
Neurons
... An action potential is self-regenerating because it spreads to adjacent membrane regions. ...
... An action potential is self-regenerating because it spreads to adjacent membrane regions. ...
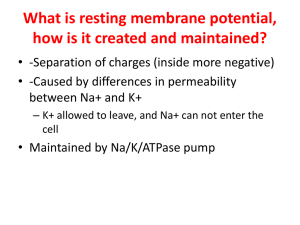
What is resting membrane potential, how is it created and maintained?
... open = rapid depolarization • 2. Action potential ends; K+ channels open leading to hyperpolarization ...
... open = rapid depolarization • 2. Action potential ends; K+ channels open leading to hyperpolarization ...
kumc 05 nervous system review student
... Have receptors for neurotransmitters. Conduct local potentials. ...
... Have receptors for neurotransmitters. Conduct local potentials. ...
Chapter 48 Reading Guide and Key Terms
... Under what circumstances could ions flow through ion channels from regions of low ion concentration to regions of high ion concentration? ...
... Under what circumstances could ions flow through ion channels from regions of low ion concentration to regions of high ion concentration? ...
CHAPTER 10
... For a very short time following passage of a nerve impulse, a threshold stimulus will not trigger another impulse on an axon. This brief period is known as the _______________________________ period. See table 10.3 for the steps involved in impulse conduction (page 373). ...
... For a very short time following passage of a nerve impulse, a threshold stimulus will not trigger another impulse on an axon. This brief period is known as the _______________________________ period. See table 10.3 for the steps involved in impulse conduction (page 373). ...
Neurons: What They`re Made Of and How They
... This space is known as the "synaptic cleft." Once the chemicals cross the synaptic cleft, they bind to special receptors on the dendrites. When bound, these receptors open channels in the cell membrane that allow positively charged particles (called ions) to enter the cell, changing the internal ch ...
... This space is known as the "synaptic cleft." Once the chemicals cross the synaptic cleft, they bind to special receptors on the dendrites. When bound, these receptors open channels in the cell membrane that allow positively charged particles (called ions) to enter the cell, changing the internal ch ...
9-18-04 Nervous System Peripheral No1
... – All ganglionic transmission is cholinergic (acetylcholine) • Drugs that block ganglionic transmission block either parasympathetic or sympathetic depending on which is active • This is a paradox many have a problem grasping ...
... – All ganglionic transmission is cholinergic (acetylcholine) • Drugs that block ganglionic transmission block either parasympathetic or sympathetic depending on which is active • This is a paradox many have a problem grasping ...
Locandina Slater.cdr - univr dsnm - Università degli Studi di Verona
... this structure of fundamental importance for our movements but it also represents a classic model synapse in which basic properties of the communications between nerve cells are investigated. In particular it is a model of chemical communication (as opposed to electrical) where particular molecules, ...
... this structure of fundamental importance for our movements but it also represents a classic model synapse in which basic properties of the communications between nerve cells are investigated. In particular it is a model of chemical communication (as opposed to electrical) where particular molecules, ...
Exercise 17 - Harford Community College
... specialized cells that conduct messages in the form of electrical impulses throughout the body ...
... specialized cells that conduct messages in the form of electrical impulses throughout the body ...
ANATOMICAL ORGANIZATION of the NERVOUS SYSTEM
... Branches off the cell body that carry information to the cell body. Usually several to many. Relatively short. Often branched. Have receptors for neurotransmitters. Conduct local potentials. ...
... Branches off the cell body that carry information to the cell body. Usually several to many. Relatively short. Often branched. Have receptors for neurotransmitters. Conduct local potentials. ...
Developmental plasticity: Pruning
... temporally correlates with postmortem findings of increased synaptic pruning during adolescence and early adulthood. The primary cause for loss of GM density is unknown. It may be driven at least partially by the process of synaptic pruning, together with trophic glial and vascular changes and or ce ...
... temporally correlates with postmortem findings of increased synaptic pruning during adolescence and early adulthood. The primary cause for loss of GM density is unknown. It may be driven at least partially by the process of synaptic pruning, together with trophic glial and vascular changes and or ce ...
Central nervous system
... • Net postsynaptic potentials in the trigger zone – whether neuron fires depends on net input of other cells (EPSPs > IPSPs? Or IPSP’s>EPSPs?) • typical EPSP has a voltage of 0.5 mV & lasts 20 msec ...
... • Net postsynaptic potentials in the trigger zone – whether neuron fires depends on net input of other cells (EPSPs > IPSPs? Or IPSP’s>EPSPs?) • typical EPSP has a voltage of 0.5 mV & lasts 20 msec ...
The synapse.
... chemical synapses • 1) Conduction velocities are far to quick for ordinary metabolic activity (against). • Loew’s study with the two hearts ...
... chemical synapses • 1) Conduction velocities are far to quick for ordinary metabolic activity (against). • Loew’s study with the two hearts ...
Neurons, Neurons, Neurons!
... as sclerosis, plaques, or lesions, can slow down or completely prevent the transmission of signals between nerve cells. Messages from the brain and spinal cord cannot reach other parts of the body. Damage, or scarring, occurs in many places throughout the central nervous system, hence the term "Mult ...
... as sclerosis, plaques, or lesions, can slow down or completely prevent the transmission of signals between nerve cells. Messages from the brain and spinal cord cannot reach other parts of the body. Damage, or scarring, occurs in many places throughout the central nervous system, hence the term "Mult ...
Neuron Function 2
... Two general types Fast 250 to 400 mm/day; typically involves preassembly of components into membrane bound organelle or vesicle Slow 50 mm/day; cytoskeletal and cytoplasmic elements (non-membrane bound) ...
... Two general types Fast 250 to 400 mm/day; typically involves preassembly of components into membrane bound organelle or vesicle Slow 50 mm/day; cytoskeletal and cytoplasmic elements (non-membrane bound) ...
Synapses and neurotransmitters
... • Allows flow of ions from one neuron to another • Bi directional • Used when you need very fast reaction, say for defensive beahviour, that sort of thing • No receptor or binding site, but a connexon ...
... • Allows flow of ions from one neuron to another • Bi directional • Used when you need very fast reaction, say for defensive beahviour, that sort of thing • No receptor or binding site, but a connexon ...
Synaptogenesis
... express α,β,γ,δ and ε subunits; all other nuclei re-express the fetal subunit pattern of α2βγδ. Embryonic AChRs are found all over the surface of the myofiber, producing denervation supersensitivity. The adult form of the receptor is restricted to the end plate region. D: If denervated muscles are s ...
... express α,β,γ,δ and ε subunits; all other nuclei re-express the fetal subunit pattern of α2βγδ. Embryonic AChRs are found all over the surface of the myofiber, producing denervation supersensitivity. The adult form of the receptor is restricted to the end plate region. D: If denervated muscles are s ...
Neurons - Jordan High School
... Action Potential (Nerve Impulse) All-or-none principle Action potential begins between -60 & -55 mV (threshold) Stimulus triggers action potential, or not at all if doesn’t meet threshold ...
... Action Potential (Nerve Impulse) All-or-none principle Action potential begins between -60 & -55 mV (threshold) Stimulus triggers action potential, or not at all if doesn’t meet threshold ...