NS Outline
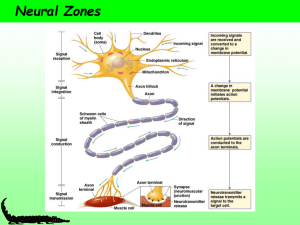
... iiii. Gray matter: concentration of cell bodies & unmyelinated fibers. (in PNS=ganglia; in CNS=nuclei). {Neurolemmacytes are most active during the first year of life, and spiral around an axon to leave a covering called the neurolemma. This covering will also aid in repair. Oligodendrocytes myelina ...
... iiii. Gray matter: concentration of cell bodies & unmyelinated fibers. (in PNS=ganglia; in CNS=nuclei). {Neurolemmacytes are most active during the first year of life, and spiral around an axon to leave a covering called the neurolemma. This covering will also aid in repair. Oligodendrocytes myelina ...
15-1 Section Summary
... he nervous system receives information about what is happening both inside and outside your body. It also directs the way in which your body responds to this information. In addition, the nervous system helps in maintaining stable internal conditions. A stimulus is any change or signal in the enviro ...
... he nervous system receives information about what is happening both inside and outside your body. It also directs the way in which your body responds to this information. In addition, the nervous system helps in maintaining stable internal conditions. A stimulus is any change or signal in the enviro ...
Open Document - Clinton Community College
... ◦ E.) Terminal Buttons- Axon ends with a cluster of these small knobs secreting chemicals known as neurotransmitters. ◦ F.) Synapse – A “Gap” or junction where information is transmitted from one neuron to another. ...
... ◦ E.) Terminal Buttons- Axon ends with a cluster of these small knobs secreting chemicals known as neurotransmitters. ◦ F.) Synapse – A “Gap” or junction where information is transmitted from one neuron to another. ...
Chapter 33
... Sensory (afferent) neurons carry impulses from sensory receptors to the CNS. Motor (efferent) neurons carry impulses away from the CNS to effectors (muscles and glands). Interneurons connect neurons together. ...
... Sensory (afferent) neurons carry impulses from sensory receptors to the CNS. Motor (efferent) neurons carry impulses away from the CNS to effectors (muscles and glands). Interneurons connect neurons together. ...
Mind, Brain & Behavior
... Axons have terminals (synapses) and no ribosomes. Dendrites have spines (punching bags). Don’t be fooled by the branches – both have them. ...
... Axons have terminals (synapses) and no ribosomes. Dendrites have spines (punching bags). Don’t be fooled by the branches – both have them. ...
Chapter 34
... Neurotransmitter: type of signaling molecule that is synthesized in neurons only Plasma membrane has many gated channels for calcium ions In between action potentials, more calcium ions outside than inside (gate are shut) ...
... Neurotransmitter: type of signaling molecule that is synthesized in neurons only Plasma membrane has many gated channels for calcium ions In between action potentials, more calcium ions outside than inside (gate are shut) ...
Biology 3B Exam 3 Stuff – Here`s a quick list of items for the next
... Know the accessory and digestive organs discussed along with their functions Know the GI hormones and enzymes discussed (where found and function), target site(s), stimulus for release Where and how nutrients are absorbed and enter general circulation Chapter 48 – neurons, synapses and signali ...
... Know the accessory and digestive organs discussed along with their functions Know the GI hormones and enzymes discussed (where found and function), target site(s), stimulus for release Where and how nutrients are absorbed and enter general circulation Chapter 48 – neurons, synapses and signali ...
Synapses - UBC Zoology
... - change in membrane potential (e.g. muscle contraction in the case of a motorneuron at a neuromuscular junction) 9. Neurotransmitter is removed from the cleft by two mechanisms i) transmitter is destroyed by an enzyme such as acetylcholine ...
... - change in membrane potential (e.g. muscle contraction in the case of a motorneuron at a neuromuscular junction) 9. Neurotransmitter is removed from the cleft by two mechanisms i) transmitter is destroyed by an enzyme such as acetylcholine ...
Nervous System
... • Nervous tissue is composed of neurons and neuroglial cells. • Neuroglial cells provide support, insulation, and nutrients to neurons • Neurons consist of a cell body and extensions called dendrites and axons • Axons send information in the form of nerve impulses; each neuron ...
... • Nervous tissue is composed of neurons and neuroglial cells. • Neuroglial cells provide support, insulation, and nutrients to neurons • Neurons consist of a cell body and extensions called dendrites and axons • Axons send information in the form of nerve impulses; each neuron ...
General Neurophysiology
... Reduced the animal to a head and the floor of the thorax and the thoracic nerve cord Elecrodes on the stumps of the nerves that had innervated the ...
... Reduced the animal to a head and the floor of the thorax and the thoracic nerve cord Elecrodes on the stumps of the nerves that had innervated the ...
Norepinephrine as a neurotransmitter
... • They have effects similar to that of THC • Short fatty acids produced in the dendrites and cell bodies and released directly from the plasma membrane (no vesicle) ...
... • They have effects similar to that of THC • Short fatty acids produced in the dendrites and cell bodies and released directly from the plasma membrane (no vesicle) ...
Madison Pejsa Pd.4
... Neurotransmitters is how are information is carried it plays a role in our sleep, feelings, and how we learn and behave. It influences the next neuron to grab the information coming from the synapse to grab the information with their dendrites and to be processed through the neuron to the next. IPSP ...
... Neurotransmitters is how are information is carried it plays a role in our sleep, feelings, and how we learn and behave. It influences the next neuron to grab the information coming from the synapse to grab the information with their dendrites and to be processed through the neuron to the next. IPSP ...
Biology 4 Study Guide
... internal & external ____________ and is gathered by ____________ receptors; 2) ________________ is the __________________ of that sensory input gathered by the receptors; and 3) It provides a ____________ output by way of the activation of _____________ organs (____________, glands, etc.)…ultimately ...
... internal & external ____________ and is gathered by ____________ receptors; 2) ________________ is the __________________ of that sensory input gathered by the receptors; and 3) It provides a ____________ output by way of the activation of _____________ organs (____________, glands, etc.)…ultimately ...
Neuron Anatomy
... • Diameter remains relatively constant over its length. • Shape is maintained by the cytoskeleton. • Carries nerve impulses (information) to the soma ...
... • Diameter remains relatively constant over its length. • Shape is maintained by the cytoskeleton. • Carries nerve impulses (information) to the soma ...
Nervous and Endocrine System
... Axon Terminals release neurotransmitters into the synapse Nerve impulses travel from the dendrite through the cell to the axon terminal (one direction only) Nerve impulses travel through the cell as electrical signals ...
... Axon Terminals release neurotransmitters into the synapse Nerve impulses travel from the dendrite through the cell to the axon terminal (one direction only) Nerve impulses travel through the cell as electrical signals ...
Modeling the brain
... Nonlinearly weighted sums of incoming data Information storage – still enigmatic Short term maybe clear, chemical changes in synapses Long term requires changes in CSN structure ...
... Nonlinearly weighted sums of incoming data Information storage – still enigmatic Short term maybe clear, chemical changes in synapses Long term requires changes in CSN structure ...
What is the Nervous System?
... Complex communication network – how your body/brain communicate ...
... Complex communication network – how your body/brain communicate ...
Slide 1 - AccessPhysiotherapy
... dendrites and also on its cell body, the soma. The soma of this type of cell integrates the electrical information and also provides metabolic support for the cell as a whole. The place where the axon comes out of the soma is called the axon hillock, and this is where the information is encoded into ...
... dendrites and also on its cell body, the soma. The soma of this type of cell integrates the electrical information and also provides metabolic support for the cell as a whole. The place where the axon comes out of the soma is called the axon hillock, and this is where the information is encoded into ...
Ch 3 Review
... Millions of neurons must send messages at the same time to produce a single thought. ...
... Millions of neurons must send messages at the same time to produce a single thought. ...
Motor Proteins
... Moving components to and from the synapse Complete Part 2 on your worksheet. Match the process with the number in the picture. 3. Vesicles are filled with neurotransmitter and then the action potential makes the vesicles release their neurotransmitter into the synapse ...
... Moving components to and from the synapse Complete Part 2 on your worksheet. Match the process with the number in the picture. 3. Vesicles are filled with neurotransmitter and then the action potential makes the vesicles release their neurotransmitter into the synapse ...
The Nervous System
... The cells that transmit the electrical signals of the nervous system are called neurons Sensory neurons carry information (impulses) from the sense organs to the central nervous system (CNS). Motor neurons carry information (impulses) from the central nervous system (CNS) to the muscles and glands. ...
... The cells that transmit the electrical signals of the nervous system are called neurons Sensory neurons carry information (impulses) from the sense organs to the central nervous system (CNS). Motor neurons carry information (impulses) from the central nervous system (CNS) to the muscles and glands. ...
Chapter 3: The Biological Bases of Behavior
... Parental investment and mating: increased survival in offspring where there is more parental investment “The effects of chronic social stress in juvenile hamsters makes sense because if they were permanently fearful of conspecifics, they would not be able to mate and have ...
... Parental investment and mating: increased survival in offspring where there is more parental investment “The effects of chronic social stress in juvenile hamsters makes sense because if they were permanently fearful of conspecifics, they would not be able to mate and have ...