physio unit 9 [4-20
... Characteristic of corticospinal pathway, which controls skeletal muscles Divergence into multiple tracts Occurs in information transmitted by dorsal column-medial lemniscal system Labelled line principle Only one modality of sensation is transmitted by a nerve fiber Accommodation of Receptors Lessen ...
... Characteristic of corticospinal pathway, which controls skeletal muscles Divergence into multiple tracts Occurs in information transmitted by dorsal column-medial lemniscal system Labelled line principle Only one modality of sensation is transmitted by a nerve fiber Accommodation of Receptors Lessen ...
CHAPTER 11 Nervous Tissue - Austin Community College
... system is the master controlling system of the body. It is designed to constantly and rapidly adjust and respond to stimuli the body receives. It includes the brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, and associated peripheral nerves. Divisions of the nervous sytem: ...
... system is the master controlling system of the body. It is designed to constantly and rapidly adjust and respond to stimuli the body receives. It includes the brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, and associated peripheral nerves. Divisions of the nervous sytem: ...
2016-2017_1stSemester_Exam1_050117_final_solution
... The neural regulation of different organs in the human body is accomplished by the…autonomic nervous…………… system. Conservation of energy is achieved via the ……parasympathetic………… ………… wing of the system whose central regulatory units are situated in the …brainstem…... and the caudal part of the ……sp ...
... The neural regulation of different organs in the human body is accomplished by the…autonomic nervous…………… system. Conservation of energy is achieved via the ……parasympathetic………… ………… wing of the system whose central regulatory units are situated in the …brainstem…... and the caudal part of the ……sp ...
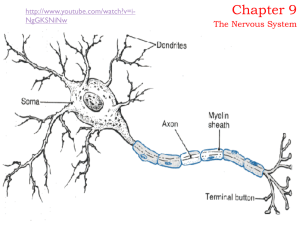
1. Cell body
... neurons, called the synaptic cleft. 5. Neurotransmitters bind to receptors on dendrites of the next neuron thereby passing on the signal. ...
... neurons, called the synaptic cleft. 5. Neurotransmitters bind to receptors on dendrites of the next neuron thereby passing on the signal. ...
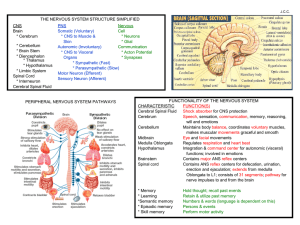
CNS Brain * Cerebrum * Cerebellum * Brain Stem * Diencephalon
... Maintains body balance, coordinates voluntary muscles, makes muscular movements graceful and smooth Midbrain Eye and facial movements Medulla Oblongata Regulates respiration and heart beat Hypothalamus Integration & command center for autonomic (visceral) functions; involved in emotions Brainstem Co ...
... Maintains body balance, coordinates voluntary muscles, makes muscular movements graceful and smooth Midbrain Eye and facial movements Medulla Oblongata Regulates respiration and heart beat Hypothalamus Integration & command center for autonomic (visceral) functions; involved in emotions Brainstem Co ...
file - Athens Academy
... hammer taps the patellar ligament to the knee jerk response? 1) The leg extends at the knee. 2) Sensory neurons conduct the action potentials to the spinal cord. 3) Motor neurons are stimulated and generate an action potential. 4) Sensory neurons synapse with motor neurons in the spinal cord. 5) The ...
... hammer taps the patellar ligament to the knee jerk response? 1) The leg extends at the knee. 2) Sensory neurons conduct the action potentials to the spinal cord. 3) Motor neurons are stimulated and generate an action potential. 4) Sensory neurons synapse with motor neurons in the spinal cord. 5) The ...
I) Mark right or false beside each sentence and correct the wrong
... 1- Cardiac muscle of atria or ventricle acts as motor unit and the skeletal muscle as a whole acts as a single motor unit. ( bi ) 2- Oligodendroglia cells form myelin sheath outside CNS while Schwann cells form myelin sheath inside CNS. ( اﻋ)ﻛس 3- The stimulus must be strong enough to depolarize t ...
... 1- Cardiac muscle of atria or ventricle acts as motor unit and the skeletal muscle as a whole acts as a single motor unit. ( bi ) 2- Oligodendroglia cells form myelin sheath outside CNS while Schwann cells form myelin sheath inside CNS. ( اﻋ)ﻛس 3- The stimulus must be strong enough to depolarize t ...
electrochemical impulse - Glebe
... o E.g. warm water = low frequency, hot water = high frequency 2. Different neurons have different thresholds o E.g. water at 40°C will cause one neuron to reach threshold level, but water at 60°C may cause two or more o Brain distinguishes between neural impulses Synaptic Transmission Neurons can ...
... o E.g. warm water = low frequency, hot water = high frequency 2. Different neurons have different thresholds o E.g. water at 40°C will cause one neuron to reach threshold level, but water at 60°C may cause two or more o Brain distinguishes between neural impulses Synaptic Transmission Neurons can ...
Development of glutamatergic and GABAergic synapses
... The main types of glutamate synapses in the cerebellum are those established by mossy fibers (MFs), parallel fibers (PFs) and climbing fibers (CFs). In rodents, MFs invade the gray matter at P3-P5 and start establishing the first synapses onto granule cells at the end of the first postnatal week. H ...
... The main types of glutamate synapses in the cerebellum are those established by mossy fibers (MFs), parallel fibers (PFs) and climbing fibers (CFs). In rodents, MFs invade the gray matter at P3-P5 and start establishing the first synapses onto granule cells at the end of the first postnatal week. H ...
Nerves and nervous impulses File
... concentrations of certain ions across their cell membranes. Neurons pump out positively charged _ sodium ___ ions. In addition, they pump in positively charged __ potassium _ ions . Thus there is a high concentration of sodium ions present _ outside _ the neuron, and a high concentration of potassiu ...
... concentrations of certain ions across their cell membranes. Neurons pump out positively charged _ sodium ___ ions. In addition, they pump in positively charged __ potassium _ ions . Thus there is a high concentration of sodium ions present _ outside _ the neuron, and a high concentration of potassiu ...
Neurons - MrsMcFadin
... • An impulse begins when a neuron is stimulated by another neuron or by the environment. • A neuron remains in its resting state until it receives a stimulus to its dendrites large enough to start a nerve impulse from the cell body • Once it begins, the impulse travels quickly down the axon away fro ...
... • An impulse begins when a neuron is stimulated by another neuron or by the environment. • A neuron remains in its resting state until it receives a stimulus to its dendrites large enough to start a nerve impulse from the cell body • Once it begins, the impulse travels quickly down the axon away fro ...
Action Potential Web Quest
... 5. There are about ______________ neurons in the brain as well as ______________ of support cells called _____________________. 6. There are 3 major types of glial cells. Name each of the 3 and explain their function: ...
... 5. There are about ______________ neurons in the brain as well as ______________ of support cells called _____________________. 6. There are 3 major types of glial cells. Name each of the 3 and explain their function: ...
CS 256: Neural Computation Lecture Notes
... Let us assume then that the persistence or repetition of a reverberatory activity (or “trace”) tends to induce lasting cellular changes that add to its stability. The assumption can be precisely stated as follows: When an axon of cell A is near enough to excite a cell B and repeatedly or persistentl ...
... Let us assume then that the persistence or repetition of a reverberatory activity (or “trace”) tends to induce lasting cellular changes that add to its stability. The assumption can be precisely stated as follows: When an axon of cell A is near enough to excite a cell B and repeatedly or persistentl ...
Chapter 7: Structure of Nervous System
... Chapter 7: Structure of Nervous System Is divided into: Central nervous system (CNS) = brain and spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) = cranial and spinal nerves Consists of 2 kinds of cells: Neurons and supporting cells (glial cells). Neurons are ______________________ units of N ...
... Chapter 7: Structure of Nervous System Is divided into: Central nervous system (CNS) = brain and spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) = cranial and spinal nerves Consists of 2 kinds of cells: Neurons and supporting cells (glial cells). Neurons are ______________________ units of N ...
Synapse
... •It results mainly from depletion of the neurotransmitter stores the in the synaptic knobs→ because in intensive stimulation the resynthesis and reuptake mechanisms that fill these stores are unable to provide all the demands for the transmitter ...
... •It results mainly from depletion of the neurotransmitter stores the in the synaptic knobs→ because in intensive stimulation the resynthesis and reuptake mechanisms that fill these stores are unable to provide all the demands for the transmitter ...
Terms being described
... 27. It’s a neurological disease that progressively destroys myelin sheaths of neurons in multiple areas of the central nervous system. 29. An action potential is this kind of event as it occurs only in the tiny stimulated region of the axon membrane and not in the rest of the axon. 31. It’s the cond ...
... 27. It’s a neurological disease that progressively destroys myelin sheaths of neurons in multiple areas of the central nervous system. 29. An action potential is this kind of event as it occurs only in the tiny stimulated region of the axon membrane and not in the rest of the axon. 31. It’s the cond ...
Local Cortical Circuits
... 7 Transmission of Information by Coincidence . . 7.1 The Single Neuron as a Coincidence Detector 7.2 Existence of Chains of Neuronal Sets with Appropriate Connections 7.3 Some Properties of Synfire Chains 8 Organization of Generators of the ECoG 8.1 The Generation of the ECoG 8.2 Population Statist ...
... 7 Transmission of Information by Coincidence . . 7.1 The Single Neuron as a Coincidence Detector 7.2 Existence of Chains of Neuronal Sets with Appropriate Connections 7.3 Some Properties of Synfire Chains 8 Organization of Generators of the ECoG 8.1 The Generation of the ECoG 8.2 Population Statist ...
The Brain and Its Disorders
... The Neuron • Soma (cell body) – contains nucleus, cytoplasm, organelles • Dendrites – receive info • Axon – transmits info • Myelin sheath – covers the axon to increase transmission speed (cause of sensory and motor disturbances in multiple sclerosis) ...
... The Neuron • Soma (cell body) – contains nucleus, cytoplasm, organelles • Dendrites – receive info • Axon – transmits info • Myelin sheath – covers the axon to increase transmission speed (cause of sensory and motor disturbances in multiple sclerosis) ...
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
... the autonomic nervous system such as smooth muscle around blood vessels. • Proceeds without conscious intention but can be influenced by volition. ...
... the autonomic nervous system such as smooth muscle around blood vessels. • Proceeds without conscious intention but can be influenced by volition. ...
ppt
... 1) synthesized and released by neurons 2) released at the nerve terminal in a 'chemically identifiable' form 3) the chemical should reproduce the activity of the presynaptic neuron 4) can be blocked by competitive antagonist based on concentration 5) active mechanisms to stop the function of the neu ...
... 1) synthesized and released by neurons 2) released at the nerve terminal in a 'chemically identifiable' form 3) the chemical should reproduce the activity of the presynaptic neuron 4) can be blocked by competitive antagonist based on concentration 5) active mechanisms to stop the function of the neu ...
Nervous System Student Notes
... i. Action potential (electrical signal reaches axon ______________________ ii. Vesicle fuses with membrane and ruptures releasing ________________________ into synaptic cleft iii. NT (chemical signal) diffuses across cleft and binds to ______________________ iv. Action potential (electrical signal) ...
... i. Action potential (electrical signal reaches axon ______________________ ii. Vesicle fuses with membrane and ruptures releasing ________________________ into synaptic cleft iii. NT (chemical signal) diffuses across cleft and binds to ______________________ iv. Action potential (electrical signal) ...
Nervous System
... neurotransmitter, which diffuses across the junction and stimulates the muscle fiber. Action potential: Electrical changes that occurs along the sarcolemma. 1. Membrane Depolarization – Na+ entering the cell. 2. Action potential is propagated as the move of depolarization spreads. 3. Repolarization ...
... neurotransmitter, which diffuses across the junction and stimulates the muscle fiber. Action potential: Electrical changes that occurs along the sarcolemma. 1. Membrane Depolarization – Na+ entering the cell. 2. Action potential is propagated as the move of depolarization spreads. 3. Repolarization ...
Week 2 Lecture Notes
... contains a salt solution resembling the fluid normally found within the cell, is lowered to the cell membrane where a tight seal is formed. When a little suction is applied to the pipette, the "patch" of membrane within the pipette ruptures, permitting access to the whole cell. The electrode, which ...
... contains a salt solution resembling the fluid normally found within the cell, is lowered to the cell membrane where a tight seal is formed. When a little suction is applied to the pipette, the "patch" of membrane within the pipette ruptures, permitting access to the whole cell. The electrode, which ...