The Action Potential, Synaptic Transmission, and Maintenance of
... and voltage-gated (Fig. 3.3). Nongated ion channels are always open. They are responsible for the influx of Na⫹ and efflux of K⫹ when the neuron is in its resting state. Ligandgated ion channels are directly or indirectly activated by chemical neurotransmitters binding to membrane receptors. In this ...
... and voltage-gated (Fig. 3.3). Nongated ion channels are always open. They are responsible for the influx of Na⫹ and efflux of K⫹ when the neuron is in its resting state. Ligandgated ion channels are directly or indirectly activated by chemical neurotransmitters binding to membrane receptors. In this ...
10.4. What follows from the fact that some neurons we consider
... “share” the function of recognizing these signals, so that each subset of signals will have its “guardian angel” in the form of neuron, which will detect and recognize all signals from one sub-area, another will detect signals from another sub-area, etc. Fig. 10.17 illustrates this. ...
... “share” the function of recognizing these signals, so that each subset of signals will have its “guardian angel” in the form of neuron, which will detect and recognize all signals from one sub-area, another will detect signals from another sub-area, etc. Fig. 10.17 illustrates this. ...
Neurons - Noba Project
... pressure work collectively to facilitate electrochemical communication. 3. Define resting membrane potential, excitatory postsynaptic potentials, inhibitory postsynaptic potentials, and action potentials. 4. Explain the features of axonal and synaptic communication in neurons. ...
... pressure work collectively to facilitate electrochemical communication. 3. Define resting membrane potential, excitatory postsynaptic potentials, inhibitory postsynaptic potentials, and action potentials. 4. Explain the features of axonal and synaptic communication in neurons. ...
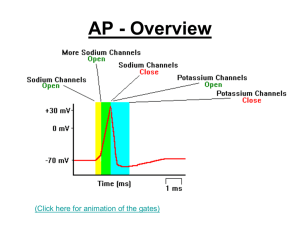
AP – All or nothing
... • There is a time after depolarisation where no new AP can start – called the refractory period. – Time is needed to restore the proteins of voltage sensitive ion channels to their original resting conditions. – Na+ channels cannot be opened, as it can’t be depolarised again. WHY? – AP travel in one ...
... • There is a time after depolarisation where no new AP can start – called the refractory period. – Time is needed to restore the proteins of voltage sensitive ion channels to their original resting conditions. – Na+ channels cannot be opened, as it can’t be depolarised again. WHY? – AP travel in one ...
Design principles of sensory receptors
... of the organism is reported by a variety of internal receptors including those for gases, temperature, or pH. According to the activating stimulus sensory receptors can be classified into electromagnetic receptors (photoreceptor, thermoreceptor), mechanoreceptors (hearing, touch, balance, osmorecept ...
... of the organism is reported by a variety of internal receptors including those for gases, temperature, or pH. According to the activating stimulus sensory receptors can be classified into electromagnetic receptors (photoreceptor, thermoreceptor), mechanoreceptors (hearing, touch, balance, osmorecept ...
The vocabulary of nerve cells
... • Since all external signals must be transduced into voltage in order for the brain to perceive them, and • Since all changes in electrical signals in the nervous system are the result of changes in membrane proteins, then • For any signal (stimulus) to be perceived by a cell there must be one or mo ...
... • Since all external signals must be transduced into voltage in order for the brain to perceive them, and • Since all changes in electrical signals in the nervous system are the result of changes in membrane proteins, then • For any signal (stimulus) to be perceived by a cell there must be one or mo ...
Amsterdam Brn Adapt View P3
... [kittens?] (M. Friedlander). It should be noted that these effects are not limited to cerebellar cortex. Kleim et al. (papers and absts) have described synaptogenesis and changes in synapse morphology in association with the same AC motor learning procedure in the somatosensory-somatomotor forelimb ...
... [kittens?] (M. Friedlander). It should be noted that these effects are not limited to cerebellar cortex. Kleim et al. (papers and absts) have described synaptogenesis and changes in synapse morphology in association with the same AC motor learning procedure in the somatosensory-somatomotor forelimb ...
Ch 15 Notes: The Autonomic Nervous System 2012
... Somatic motor neurons innervate skeletal muscle to produce conscious, voluntary movements and the effect of a motor neuron is always excitation. Autonomic: The autonomic nervous system contains both autonomic sensory and motor neurons. Autonomic sensory neurons are associated with interoceptors. Aut ...
... Somatic motor neurons innervate skeletal muscle to produce conscious, voluntary movements and the effect of a motor neuron is always excitation. Autonomic: The autonomic nervous system contains both autonomic sensory and motor neurons. Autonomic sensory neurons are associated with interoceptors. Aut ...
Class X: Control and Coordination Some movements are in fact the
... Some movements are in fact the result of growth, . eg) seed germinates Some movements, as in many animals and some plants, are not connected with growth.eg) cat running, children playing on swings. These visible movements are as a response to a change in the environment of the organism. Eg) The cat ...
... Some movements are in fact the result of growth, . eg) seed germinates Some movements, as in many animals and some plants, are not connected with growth.eg) cat running, children playing on swings. These visible movements are as a response to a change in the environment of the organism. Eg) The cat ...
ChapTer 3 - Physicians for Social Responsibility
... by increasing brain levels of acetylcholine. Thus, it is not surprising that the loss of a neurotransmitter so intimately involved in learning, memory, and cognition would be a common finding in dementia. Loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra is a cardinal feature of Parkinson’s ...
... by increasing brain levels of acetylcholine. Thus, it is not surprising that the loss of a neurotransmitter so intimately involved in learning, memory, and cognition would be a common finding in dementia. Loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra is a cardinal feature of Parkinson’s ...
Neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine and Dopamine
... concentrate increase the amount of dopamine that is released in the brain • People with Schizophrenia will be given drugs to inhibit dopamine production, however, as a side effect, this makes it hard for the person to concentrate, reduce feelings of pleasure, and reduce motor function ...
... concentrate increase the amount of dopamine that is released in the brain • People with Schizophrenia will be given drugs to inhibit dopamine production, however, as a side effect, this makes it hard for the person to concentrate, reduce feelings of pleasure, and reduce motor function ...
F: Acronyms and Glossary of Terms
... Lymphatic drainage: The movement of fluids, molecules, foreign particles, and cells from various tissues in the body through the lymph system to the immune system; a means by which grafted cells reach the host’s immune system and trigger rejection. MAO-B, monoamine oxidase B: An enzyme that breaks d ...
... Lymphatic drainage: The movement of fluids, molecules, foreign particles, and cells from various tissues in the body through the lymph system to the immune system; a means by which grafted cells reach the host’s immune system and trigger rejection. MAO-B, monoamine oxidase B: An enzyme that breaks d ...
Somatic Sensations
... determined the signal recognition by the brain • It must convey the intensity of the stimulus the stronger the signals, the more frequent will be the ...
... determined the signal recognition by the brain • It must convey the intensity of the stimulus the stronger the signals, the more frequent will be the ...
Nervous System
... system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones. The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors ...
... system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones. The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors ...
Action Potentials & Nerve Conduction
... •A graded potential depolarization is called excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP). A graded potential hyperpolarization is called an inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSP). •They occur in the cell body and dendrites of the neuron. •The wave of depolarization or hyperpolarization which moves ...
... •A graded potential depolarization is called excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP). A graded potential hyperpolarization is called an inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSP). •They occur in the cell body and dendrites of the neuron. •The wave of depolarization or hyperpolarization which moves ...
Action Potential - Angelo State University
... There are 2 Basic Forms of Electrochemical Signals: Graded Potentials & Action Potentials 1. Graded Potentials are short-lived local changes in membrane potential that occur in varying degrees of magnitude: -70 to -60mV or -70 to -65 mV. a) These changes cause local flow of current that decrease wit ...
... There are 2 Basic Forms of Electrochemical Signals: Graded Potentials & Action Potentials 1. Graded Potentials are short-lived local changes in membrane potential that occur in varying degrees of magnitude: -70 to -60mV or -70 to -65 mV. a) These changes cause local flow of current that decrease wit ...
Lecture notes for Chapter 13
... above schema separate from Special sensory and Visceral sensory) Receives inputs from Exteroceptors, proprioceptors, and interoceptors Input relayed toward head, but processed along way ...
... above schema separate from Special sensory and Visceral sensory) Receives inputs from Exteroceptors, proprioceptors, and interoceptors Input relayed toward head, but processed along way ...
Document
... • Warns of actual or impending tissue damage • Stimuli include extreme pressure and temperature, histamine, K+, ATP, acids, and bradykinin • Impulses travel on fibers that release neurotransmitters glutamate and substance P • Some pain impulses are blocked by inhibitory endogenous opioids ...
... • Warns of actual or impending tissue damage • Stimuli include extreme pressure and temperature, histamine, K+, ATP, acids, and bradykinin • Impulses travel on fibers that release neurotransmitters glutamate and substance P • Some pain impulses are blocked by inhibitory endogenous opioids ...
1. A unicellular protest may use a contractile vacuole to expel
... 22. Which of the following is incorrectly paired with its embryonic germ layer? a. Muscles – mesoderm b. Central nervous system – ectoderm c. Liver and pancreas – endoderm d. Heart – endoderm e. All of the above are correctly paired with their embryonic germ layers. 23. Somites are a. Blocks of meso ...
... 22. Which of the following is incorrectly paired with its embryonic germ layer? a. Muscles – mesoderm b. Central nervous system – ectoderm c. Liver and pancreas – endoderm d. Heart – endoderm e. All of the above are correctly paired with their embryonic germ layers. 23. Somites are a. Blocks of meso ...
The Loss of Glutamate-GABA Harmony in Anxiety Disorders
... transmembrane ion channels that open or close in response to the binding of a ligand. These receptors convert the chemical signal of a presynaptically released neurotransmitter directly and very quickly into a postsynaptic electrical signal (Olsen & Sieghart, 2008), inducing the inhibitory postsynap ...
... transmembrane ion channels that open or close in response to the binding of a ligand. These receptors convert the chemical signal of a presynaptically released neurotransmitter directly and very quickly into a postsynaptic electrical signal (Olsen & Sieghart, 2008), inducing the inhibitory postsynap ...
Hormones of the Gut
... 2. May be a low molecular weight CCK-releasing factor. 3. Release is inhibited by somatostatin. ...
... 2. May be a low molecular weight CCK-releasing factor. 3. Release is inhibited by somatostatin. ...
Ch48(2) - ISpatula
... 38) Functionally, this cellular location is the neuronʹs ʺdecision-making siteʺ as to whether or not an action potential will be initiated: A) axonal membranes B) axon hillocks C) dendritic membranes D) mitochondrial membranes E) presynaptic membranes Answer: B Topic: Concept 48.4 Skill: Knowledge/ ...
... 38) Functionally, this cellular location is the neuronʹs ʺdecision-making siteʺ as to whether or not an action potential will be initiated: A) axonal membranes B) axon hillocks C) dendritic membranes D) mitochondrial membranes E) presynaptic membranes Answer: B Topic: Concept 48.4 Skill: Knowledge/ ...
Increased leak conductance alters ISI variability.
... CV = standard deviation of ISI distribution/mean ISI ...
... CV = standard deviation of ISI distribution/mean ISI ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... - the cell bodies of these neurons are in the lateral gray horns of the spinal cord Sympathetic Division - the preganglionic fibers arise from the spinal cord segments T1 through T12 and L1, L2, and L3 - for this reason they are called the Thoracolumbar Division - the fibers of this system are calle ...
... - the cell bodies of these neurons are in the lateral gray horns of the spinal cord Sympathetic Division - the preganglionic fibers arise from the spinal cord segments T1 through T12 and L1, L2, and L3 - for this reason they are called the Thoracolumbar Division - the fibers of this system are calle ...