Psychopharmacology
... • It has been proposed that a portion of the cognitive decline that is seen in aging may be due to dysfunction of the BFCS • Perhaps Alzheimer’s disease as well. – There is severe damage to the BFCS in Alzheimer’s disease. • As well as other cortical regions and the hippocampus ...
... • It has been proposed that a portion of the cognitive decline that is seen in aging may be due to dysfunction of the BFCS • Perhaps Alzheimer’s disease as well. – There is severe damage to the BFCS in Alzheimer’s disease. • As well as other cortical regions and the hippocampus ...
Intro to the Biological Perspective
... brain. Because of this fact, the process of synaptic transmission in a particular portion of the brain can be altered through the use of drugs. Drugs that chemically affect the function of one of these neurotransmitters can influence behaviour and experience in specific ways. Thus our emerging knowl ...
... brain. Because of this fact, the process of synaptic transmission in a particular portion of the brain can be altered through the use of drugs. Drugs that chemically affect the function of one of these neurotransmitters can influence behaviour and experience in specific ways. Thus our emerging knowl ...
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
... This information is sent to processing centers in the brain or in ganglia, which integrate the sensory input, interpreting it in context. o The vast majority of neurons in the brain are interneurons, which make local connections. ...
... This information is sent to processing centers in the brain or in ganglia, which integrate the sensory input, interpreting it in context. o The vast majority of neurons in the brain are interneurons, which make local connections. ...
Intro to the Biological Perspective
... brain. Because of this fact, the process of synaptic transmission in a particular portion of the brain can be altered through the use of drugs. Drugs that chemically affect the function of one of these neurotransmitters can influence behaviour and experience in specific ways. Thus our emerging knowl ...
... brain. Because of this fact, the process of synaptic transmission in a particular portion of the brain can be altered through the use of drugs. Drugs that chemically affect the function of one of these neurotransmitters can influence behaviour and experience in specific ways. Thus our emerging knowl ...
The History and Scope of Psychology Module 1
... Parts of a Neuron Cell Body: Life support center of the neuron. Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches ...
... Parts of a Neuron Cell Body: Life support center of the neuron. Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM - Welcome to SBI4U with Ms. Taman!
... • Sympathetic nervous system also stimulates secretion of epinephrine and nor-epinephrine from the medulla of the adrenal glands • Prepares body for “flight or fight” response • “Epi-pen” given in allergic reactions as it relaxes constricted airways ...
... • Sympathetic nervous system also stimulates secretion of epinephrine and nor-epinephrine from the medulla of the adrenal glands • Prepares body for “flight or fight” response • “Epi-pen” given in allergic reactions as it relaxes constricted airways ...
THERIGHTBRAINPOWERPOINT
... The second language area to be discovered is called Wernicke's Area, after Carl Wernicke, a German neurologist. Wernicke had a patient who could speak quite well, but was unable to understand the speech of others. After the patient's death, Wernicke performed an autopsy and found damage to an area a ...
... The second language area to be discovered is called Wernicke's Area, after Carl Wernicke, a German neurologist. Wernicke had a patient who could speak quite well, but was unable to understand the speech of others. After the patient's death, Wernicke performed an autopsy and found damage to an area a ...
Functional Classification of the Peripheral Nervous System
... Axon terminals are separated from the next neuron by a gap Synaptic cleft – just the space between adjacent neurons Synapse – junction between neurons; including the membranes of both neurons & the space between them ...
... Axon terminals are separated from the next neuron by a gap Synaptic cleft – just the space between adjacent neurons Synapse – junction between neurons; including the membranes of both neurons & the space between them ...
Nervous System - wondersofscience
... • B) Characteristics of neurons – Neurons can be stimulated – They are conductive – Consumes a great deal of oxygen and glucose – Can live more than 100 years – Cannot reproduce itself ...
... • B) Characteristics of neurons – Neurons can be stimulated – They are conductive – Consumes a great deal of oxygen and glucose – Can live more than 100 years – Cannot reproduce itself ...
PsychScich03
... • Neurons receive chemical signals from nearby neurons – Excitatory signals depolarize the cell membrane (i.e., reduce polarization), increasing the likelihood that the neuron will fire – Inhibitory signals hyperpolarize the cell (i.e., increase polarization), decreasing the likelihood that the neur ...
... • Neurons receive chemical signals from nearby neurons – Excitatory signals depolarize the cell membrane (i.e., reduce polarization), increasing the likelihood that the neuron will fire – Inhibitory signals hyperpolarize the cell (i.e., increase polarization), decreasing the likelihood that the neur ...
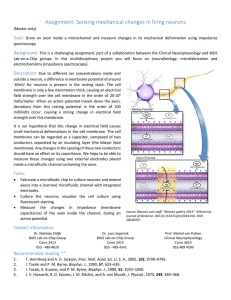
Assignment: Sensing mechanical changes in firing neurons
... membrane is only a few nanometers thick, causing an electrical field strength over the cell membrane in the order of 20∙106 Volts/meter. When an action potential travels down the axon, deviations from this resting potential in the order of 100 milliVolts occur, causing a strong change in electrical ...
... membrane is only a few nanometers thick, causing an electrical field strength over the cell membrane in the order of 20∙106 Volts/meter. When an action potential travels down the axon, deviations from this resting potential in the order of 100 milliVolts occur, causing a strong change in electrical ...
Heart
... - free transport of small non-polar molecules across membrane Membrane channel - transmembrane protein - transport is possible without additional energy - cell can regulate whether it is open or not (deactivated) - channel is specific for particular molecule Osmosis -solvent molecules go through sem ...
... - free transport of small non-polar molecules across membrane Membrane channel - transmembrane protein - transport is possible without additional energy - cell can regulate whether it is open or not (deactivated) - channel is specific for particular molecule Osmosis -solvent molecules go through sem ...
Nervous System
... out from the cell body; receive and carry impulses to the cell body 3. axon- long, fibrous part of neuron; conducts nerve impulses away from cell body 4. at the end of the axon, the impulse travels across the synapse, a tiny gap separating the axon of one neuron from the dendrite of another ...
... out from the cell body; receive and carry impulses to the cell body 3. axon- long, fibrous part of neuron; conducts nerve impulses away from cell body 4. at the end of the axon, the impulse travels across the synapse, a tiny gap separating the axon of one neuron from the dendrite of another ...
Biology Option Review Section E
... birth and successful survival until reproduction can occur, able to instinctively remember the beach they were born on, known as natal beaches, and travel immense distances when the time comes to lay their eggs, back to the beaches where they were born as they were able to survive themselves, thus t ...
... birth and successful survival until reproduction can occur, able to instinctively remember the beach they were born on, known as natal beaches, and travel immense distances when the time comes to lay their eggs, back to the beaches where they were born as they were able to survive themselves, thus t ...
1 Absolute refractory period a. Time during which a second
... WHERE DOES THE SPINAL L2 CORD END? produce myelin sheath around axons of PNS neurons. ...
... WHERE DOES THE SPINAL L2 CORD END? produce myelin sheath around axons of PNS neurons. ...
Example of completed specification
... historically been categorised and labelled using a variety of terms. This learning activity will help you to explore how such terms have developed and changed and to identify terminology currently in use within the UK and internationally. ...
... historically been categorised and labelled using a variety of terms. This learning activity will help you to explore how such terms have developed and changed and to identify terminology currently in use within the UK and internationally. ...
Biology of the Mind
... neurons called the synapse. After these molecules traverse the tiny synaptic gap between neurons, they combine with receptor sites of the neighboring neurons, thus passing on their excitatory or inhibitory messages. Different neurotransmitters have different effects on behavior and emotion. For ...
... neurons called the synapse. After these molecules traverse the tiny synaptic gap between neurons, they combine with receptor sites of the neighboring neurons, thus passing on their excitatory or inhibitory messages. Different neurotransmitters have different effects on behavior and emotion. For ...
Chapter 12 – Introduction to the Nervous System
... 3. What happens at the peak of an action potential? 4. What maintains the RMP after an action potential? 5. True or false: the magnitude of a stimulus directly affects the magnitude of an action potential. **Suggested reading for action potentials: (p. 355358) ...
... 3. What happens at the peak of an action potential? 4. What maintains the RMP after an action potential? 5. True or false: the magnitude of a stimulus directly affects the magnitude of an action potential. **Suggested reading for action potentials: (p. 355358) ...
chapter 11-nerve tissue
... a. These allow for rapid and very coordinated impulse conduction. These are responsible for carrying impulses to cardiac and smooth muscle. 2. Chemical Synapses-depend on neurotransmitters to carry impulses to effectors. a. In these synapses, the neurons are separated from the effector by a synaptic ...
... a. These allow for rapid and very coordinated impulse conduction. These are responsible for carrying impulses to cardiac and smooth muscle. 2. Chemical Synapses-depend on neurotransmitters to carry impulses to effectors. a. In these synapses, the neurons are separated from the effector by a synaptic ...
Nerve Cells and Nerve Impulses
... Terms associated with Neurons Motor neuron-receives excitation from other neurons and conducts impulses from its soma in the spinal cord to muscle of gland cells Sensory neuron-specialized at one end to be highly sensitive to a particular type of stimulation Local neuron-small neuron with no axon or ...
... Terms associated with Neurons Motor neuron-receives excitation from other neurons and conducts impulses from its soma in the spinal cord to muscle of gland cells Sensory neuron-specialized at one end to be highly sensitive to a particular type of stimulation Local neuron-small neuron with no axon or ...
structure of the brain (cont.)
... – if an action potential starts at the beginning of the axon, the action potential will continue at the same speed segment to segment to the very end of the axon • Nerve impulse – nerve impulse is made up of 6 action potentials, with the first occurring at the beginning of the axon ...
... – if an action potential starts at the beginning of the axon, the action potential will continue at the same speed segment to segment to the very end of the axon • Nerve impulse – nerve impulse is made up of 6 action potentials, with the first occurring at the beginning of the axon ...