Firms decision making
... • Every firm would love to decrease costs as much as possible but there is limit for doing so • Given production technology determines the different combinations of inputs the firm can use to produce its output. • Firms must pay prices for each of the inputs that it used ...
... • Every firm would love to decrease costs as much as possible but there is limit for doing so • Given production technology determines the different combinations of inputs the firm can use to produce its output. • Firms must pay prices for each of the inputs that it used ...
Household Behavior and Consumer Choice
... The Substitution Effect of a Price Change: • When the price of a product falls, that product becomes more attractive relative to potential substitutes. • When the price of a product rises, that product becomes less attractive relative to potential substitutes. ...
... The Substitution Effect of a Price Change: • When the price of a product falls, that product becomes more attractive relative to potential substitutes. • When the price of a product rises, that product becomes less attractive relative to potential substitutes. ...
Chapter 4: Demand
... e. Expectations – future price of a product can also affect the supply curve. f. Government Regulations – new regulations or repeal of regulations can change costs and affect supply. g. Number of Sellers – a change in the number of suppliers causes the market supply curve to shift to the right or le ...
... e. Expectations – future price of a product can also affect the supply curve. f. Government Regulations – new regulations or repeal of regulations can change costs and affect supply. g. Number of Sellers – a change in the number of suppliers causes the market supply curve to shift to the right or le ...
Tourism Economics
... products and services, since they can have an impact on their total revenues (TRs of sellers in a market are equal to the price (P) of the good or service times the total quantity sold Q ) – If the price elasticity is known, a tourism product supplier can increase total revenues by making an appropr ...
... products and services, since they can have an impact on their total revenues (TRs of sellers in a market are equal to the price (P) of the good or service times the total quantity sold Q ) – If the price elasticity is known, a tourism product supplier can increase total revenues by making an appropr ...
Supply vs. Demand Worksheet
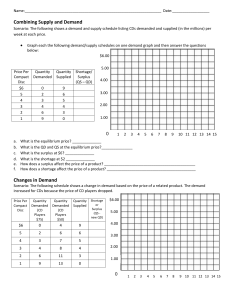
... What happened to the original supply curve? ___________________________________________________ How was the equilibrium point affected? ______________________________________________________ What is the surplus at $6.00? ___________ Why is there no longer a shortage at $2.00? _______________________ ...
... What happened to the original supply curve? ___________________________________________________ How was the equilibrium point affected? ______________________________________________________ What is the surplus at $6.00? ___________ Why is there no longer a shortage at $2.00? _______________________ ...
Tourism Economics
... products and services, since they can have an impact on their total revenues (TRs of sellers in a market are equal to the price (P) of the good or service times the total quantity sold Q ) – If the price elasticity is known, a tourism product supplier can increase total revenues by making an appropr ...
... products and services, since they can have an impact on their total revenues (TRs of sellers in a market are equal to the price (P) of the good or service times the total quantity sold Q ) – If the price elasticity is known, a tourism product supplier can increase total revenues by making an appropr ...
Review of chapters 1-4
... Opportunity cost, scarcity, “no free lunch” Opportunity cost examples ...
... Opportunity cost, scarcity, “no free lunch” Opportunity cost examples ...
Name - Cherry Creek Academy
... What happened to the original supply curve? ___________________________________________________ How was the equilibrium point affected? ______________________________________________________ What is the surplus at $6.00? ___________ Why is there no longer a shortage at $2.00? _______________________ ...
... What happened to the original supply curve? ___________________________________________________ How was the equilibrium point affected? ______________________________________________________ What is the surplus at $6.00? ___________ Why is there no longer a shortage at $2.00? _______________________ ...
Demand - Cloudfront.net
... Diminishing Marginal Utility? A law of economics stating that as a person increases consumption of a product - while keeping consumption of other products constant - there is a decline in the marginal utility (satisfaction) that person derives from consuming each additional unit of that product. It ...
... Diminishing Marginal Utility? A law of economics stating that as a person increases consumption of a product - while keeping consumption of other products constant - there is a decline in the marginal utility (satisfaction) that person derives from consuming each additional unit of that product. It ...
Slide 1
... – Arises because a single firm can supply a good or service to an entire market • At a smaller cost than could two or more firms ...
... – Arises because a single firm can supply a good or service to an entire market • At a smaller cost than could two or more firms ...
Chapter 6 - Pegasus @ UCF
... would be upward-sloping. Generally ignore Giffen Goods since – they are rare – Even if possible for an individual, no evidence it could happen for the demand of group of individuals ...
... would be upward-sloping. Generally ignore Giffen Goods since – they are rare – Even if possible for an individual, no evidence it could happen for the demand of group of individuals ...
Document
... If some units of K are better suited to x than other units of K, then MCx would increase as x increases (as more costly K was used to produce x) and MCy would decrease as y decreased (less costly K to produce y) and vice versa. For example, if a farmer increases cotton production and decreases corn ...
... If some units of K are better suited to x than other units of K, then MCx would increase as x increases (as more costly K was used to produce x) and MCy would decrease as y decreased (less costly K to produce y) and vice versa. For example, if a farmer increases cotton production and decreases corn ...
Chapter Fifteen
... wedge between the consumer’s willingness to pay (D) and the producer’s cost of production (MC) . • This outcome is inefficient compared to perfect competition. • Units not produced and consumed that could benefit society. Copyright © 2004 South-Western ...
... wedge between the consumer’s willingness to pay (D) and the producer’s cost of production (MC) . • This outcome is inefficient compared to perfect competition. • Units not produced and consumed that could benefit society. Copyright © 2004 South-Western ...
University of Wisconsin Milwaukee
... The use of cell phones is not allowed in my class. You may not use your cell phone as a clock or as a calculator or for any other reason during class or during quizzes or exams. You will need to turn your cell phone off or to silent before the beginning of class and leave your cell phone in your pur ...
... The use of cell phones is not allowed in my class. You may not use your cell phone as a clock or as a calculator or for any other reason during class or during quizzes or exams. You will need to turn your cell phone off or to silent before the beginning of class and leave your cell phone in your pur ...
PROBLEMS
... Profit is maximized where MR=MC which occurs at the output level of 4. The MR is equal to $7 at 4 units of output. Price, the maximum price consumers are willing and able to pay, at 4 units of output is $10. If output is increased beyond 4 units of output, MC>MR. This will cause total profits to fal ...
... Profit is maximized where MR=MC which occurs at the output level of 4. The MR is equal to $7 at 4 units of output. Price, the maximum price consumers are willing and able to pay, at 4 units of output is $10. If output is increased beyond 4 units of output, MC>MR. This will cause total profits to fal ...
prices
... Supply is a relationship between price and quantity supplied Qs = f (P) – Quantity supplied is a function of price – quantity supplied is determined by price The Law of Supply: Qs and P are positively related Supply Curve: upward sloping Market supply: the sum of individual supply ...
... Supply is a relationship between price and quantity supplied Qs = f (P) – Quantity supplied is a function of price – quantity supplied is determined by price The Law of Supply: Qs and P are positively related Supply Curve: upward sloping Market supply: the sum of individual supply ...
9-Name and explain the 7 factors that determine whether supplies
... 2-Productivity-increases whenever more output is produced using the same amount of input [cost of resources] •Happy, motivated workers: increase in supply [rightward shift] •Unhappy, unmotivated workers: decrease in supply [left] ...
... 2-Productivity-increases whenever more output is produced using the same amount of input [cost of resources] •Happy, motivated workers: increase in supply [rightward shift] •Unhappy, unmotivated workers: decrease in supply [left] ...
ECONOMICS
... A new entrant able to sell only S automobiles would incur a much higher average cost of ca at point a. If automobile prices are below ca, a new entrant would suffer a loss. At point b, an existing firm can produce M or more automobiles at an average cost of cb. b ...
... A new entrant able to sell only S automobiles would incur a much higher average cost of ca at point a. If automobile prices are below ca, a new entrant would suffer a loss. At point b, an existing firm can produce M or more automobiles at an average cost of cb. b ...
Externality

In economics, an externality is the cost or benefit that affects a party who did not choose to incur that cost or benefit.For example, manufacturing activities that cause air pollution impose health and clean-up costs on the whole society, whereas the neighbors of an individual who chooses to fire-proof his home may benefit from a reduced risk of a fire spreading to their own houses. If external costs exist, such as pollution, the producer may choose to produce more of the product than would be produced if the producer were required to pay all associated environmental costs. Because responsibility or consequence for self-directed action lies partly outside the self, an element of externalization is involved. If there are external benefits, such as in public safety, less of the good may be produced than would be the case if the producer were to receive payment for the external benefits to others. For the purpose of these statements, overall cost and benefit to society is defined as the sum of the imputed monetary value of benefits and costs to all parties involved. Thus, unregulated markets in goods or services with significant externalities generate prices that do not reflect the full social cost or benefit of their transactions; such markets are therefore inefficient.