total variable cost
... Costs in the Short Run Fixed Costs Variable Costs Total Costs Short-Run Costs: A Review Output Decisions: Revenues, Costs, and Profit Maximization Total Revenue (TR) and Marginal ...
... Costs in the Short Run Fixed Costs Variable Costs Total Costs Short-Run Costs: A Review Output Decisions: Revenues, Costs, and Profit Maximization Total Revenue (TR) and Marginal ...
The Prisoners` Dilemma
... attempts to prevent monopoly behavior. When monopolies are “created” rather than natural, governments should act to prevent them from forming and break up existing ones. The government policies used to prevent or eliminate monopolies are known as antitrust policy. ...
... attempts to prevent monopoly behavior. When monopolies are “created” rather than natural, governments should act to prevent them from forming and break up existing ones. The government policies used to prevent or eliminate monopolies are known as antitrust policy. ...
Chapter 3
... D schedule, D curve, movement along D curve, law of D Factors affecting D, shift of D curve Individual and market D Types of goods (normal, inferior, substitutes, complements) S schedule, S curve, movement along S curve, law of S Factors affecting S, shift of S curve Individual and market S ...
... D schedule, D curve, movement along D curve, law of D Factors affecting D, shift of D curve Individual and market D Types of goods (normal, inferior, substitutes, complements) S schedule, S curve, movement along S curve, law of S Factors affecting S, shift of S curve Individual and market S ...
Practice_Questions_Midterm_Economics_651
... away from CleanAir Camping. Pollutex employs an obsolete production process, dumping scum in the lake. The camp has experienced a steady decline in the number of attendees since Pollutex moved nearby. In particular, the owners forecast that CleanAir Camping will generate a profit of only $50,000 a y ...
... away from CleanAir Camping. Pollutex employs an obsolete production process, dumping scum in the lake. The camp has experienced a steady decline in the number of attendees since Pollutex moved nearby. In particular, the owners forecast that CleanAir Camping will generate a profit of only $50,000 a y ...
Managerial Decisions for Firms with Market Power
... e. Consumer lock-in. For some products or services, consumers may find it costly to switch to another brand, which makes previous consumption decisions costly to change. Potential rivals can be deterred from entering if they believe high switching costs will make it difficult for them to induce many ...
... e. Consumer lock-in. For some products or services, consumers may find it costly to switch to another brand, which makes previous consumption decisions costly to change. Potential rivals can be deterred from entering if they believe high switching costs will make it difficult for them to induce many ...
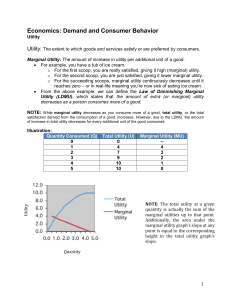
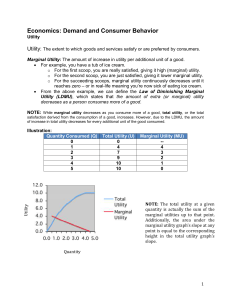
Economics: Demand and Consumer Behavior Utility Utility: The
... o On the other hand, since there are so few diamonds in the world, the marginal utility of the LAST diamond relative to that of the last glass of water is extremely high, since the amount of diamonds relative to water is extremely small; thus the water-diamond paradox.
...
... o On the other hand, since there are so few diamonds in the world, the marginal utility of the LAST diamond relative to that of the last glass of water is extremely high, since the amount of diamonds relative to water is extremely small; thus the water-diamond paradox.
ConsumerChoice - Molson`s Practical Econ
... potential customer is willing to pay, then total revenues (the price of a good times the quantity sold in a given time period) would go up and consumer surplus would go to zero. ...
... potential customer is willing to pay, then total revenues (the price of a good times the quantity sold in a given time period) would go up and consumer surplus would go to zero. ...
Oligopolistic Competition
... suppose firm 1 believes that firm 2 would choose a price p2 above the monopoly’s price, then the best response of firm 1 is to price at the monopoly’s price since at that point, its profit is maximized. And firm 2 would be driven out of the market. Therefore no firm would ever price above the monopo ...
... suppose firm 1 believes that firm 2 would choose a price p2 above the monopoly’s price, then the best response of firm 1 is to price at the monopoly’s price since at that point, its profit is maximized. And firm 2 would be driven out of the market. Therefore no firm would ever price above the monopo ...
Profits, Goals of Firms, and Key Prices File
... ***Idea that no ONE goal (including profits) is dominant in a firm ***instead, compromises happen where many different objectives are pursued at a satisfactory, rather than a maximum level ...
... ***Idea that no ONE goal (including profits) is dominant in a firm ***instead, compromises happen where many different objectives are pursued at a satisfactory, rather than a maximum level ...
Consumers, Producers, and the Efficiency of Markets
... affect the market price. transactions have side effects, called externalities, that affect bystanders. (example: pollution) ...
... affect the market price. transactions have side effects, called externalities, that affect bystanders. (example: pollution) ...
Document
... affect the market price. transactions have side effects, called externalities, that affect bystanders. (example: pollution) ...
... affect the market price. transactions have side effects, called externalities, that affect bystanders. (example: pollution) ...
Slide 1
... affect the market price. transactions have side effects, called externalities, that affect bystanders. (example: pollution) ...
... affect the market price. transactions have side effects, called externalities, that affect bystanders. (example: pollution) ...
Taxes
... receive more on each ton sold—the price of $30 a ton plus the subsidy of $20 a ton, which is $50 a ton. © 2012 Pearson Education ...
... receive more on each ton sold—the price of $30 a ton plus the subsidy of $20 a ton, which is $50 a ton. © 2012 Pearson Education ...
Untitled - Cengage
... goods and services. Taxes impair the operation of the economy by inducing individuals to make choices based not only on the benefits and costs of their actions but also on the tax advantages or disadvantages of their decisions. The distortion in resource use and loss in output that results from the ...
... goods and services. Taxes impair the operation of the economy by inducing individuals to make choices based not only on the benefits and costs of their actions but also on the tax advantages or disadvantages of their decisions. The distortion in resource use and loss in output that results from the ...
Principles of Economics
... Zero-Profit Point Total cost includes all the opportunity costs of the firm. In the zero-profit equilibrium, the firm’s revenue compensates the owners for the time and money they expend to keep the ...
... Zero-Profit Point Total cost includes all the opportunity costs of the firm. In the zero-profit equilibrium, the firm’s revenue compensates the owners for the time and money they expend to keep the ...
Tcheque
... there instances where an above costs abuse was identified in your jurisdiction? Please describe In the Czech Republic, I have not identified any case dealing with this issue. There is no praxis, yet. The outcome of the replicability assessment depends also on the definition of the sales of the domin ...
... there instances where an above costs abuse was identified in your jurisdiction? Please describe In the Czech Republic, I have not identified any case dealing with this issue. There is no praxis, yet. The outcome of the replicability assessment depends also on the definition of the sales of the domin ...
Perfectly Competitive Markets
... • The additional supply of produce, though, has forced down prices and many farmers have found that the profits they earn from selling in farmers’ markets is no longer higher than what they earn selling to supermarkets. • Throughout the economy, entrepreneurs are continually introducing new products ...
... • The additional supply of produce, though, has forced down prices and many farmers have found that the profits they earn from selling in farmers’ markets is no longer higher than what they earn selling to supermarkets. • Throughout the economy, entrepreneurs are continually introducing new products ...
Externality

In economics, an externality is the cost or benefit that affects a party who did not choose to incur that cost or benefit.For example, manufacturing activities that cause air pollution impose health and clean-up costs on the whole society, whereas the neighbors of an individual who chooses to fire-proof his home may benefit from a reduced risk of a fire spreading to their own houses. If external costs exist, such as pollution, the producer may choose to produce more of the product than would be produced if the producer were required to pay all associated environmental costs. Because responsibility or consequence for self-directed action lies partly outside the self, an element of externalization is involved. If there are external benefits, such as in public safety, less of the good may be produced than would be the case if the producer were to receive payment for the external benefits to others. For the purpose of these statements, overall cost and benefit to society is defined as the sum of the imputed monetary value of benefits and costs to all parties involved. Thus, unregulated markets in goods or services with significant externalities generate prices that do not reflect the full social cost or benefit of their transactions; such markets are therefore inefficient.