exercisesch12
... much greater than the quantity demanded of 250,000 at $11.60. Price would fall, so $11.60 can’t be the market price. If price were to equal $7.50, people would be willing to buy about 375,000 cassettes, but each firm would only be willing to produce a little less than 300 or 300,000 in total. Quant ...
... much greater than the quantity demanded of 250,000 at $11.60. Price would fall, so $11.60 can’t be the market price. If price were to equal $7.50, people would be willing to buy about 375,000 cassettes, but each firm would only be willing to produce a little less than 300 or 300,000 in total. Quant ...
1 - Economics By
... the way a homemaker should divide money among several commodities. that if more money is spent on one good, the breadwinner must work all the harder to maintain a satisfactory level of living. ...
... the way a homemaker should divide money among several commodities. that if more money is spent on one good, the breadwinner must work all the harder to maintain a satisfactory level of living. ...
10. monopooly - WordPress.com
... form of higher profit, a practice that requires some departure from marginal-cost pricing. ...
... form of higher profit, a practice that requires some departure from marginal-cost pricing. ...
Ch7
... the last apartment rented is greater than its marginal benefit C. inefficient because the marginal cost of the last apartment rented is greater than its marginal benefit D. inefficient because the marginal benefit from the last apartment rented is greater than its marginal cost. © 2013 Pearson ...
... the last apartment rented is greater than its marginal benefit C. inefficient because the marginal cost of the last apartment rented is greater than its marginal benefit D. inefficient because the marginal benefit from the last apartment rented is greater than its marginal cost. © 2013 Pearson ...
ESSENTIALS OF MICROECONOMICS ECON 201
... • Salary usually tied into production • Called Residual Claimant – Person who shares in the profits of the firm – More shirkers?? Less Production…so less pay for monitor ...
... • Salary usually tied into production • Called Residual Claimant – Person who shares in the profits of the firm – More shirkers?? Less Production…so less pay for monitor ...
Handout for lecture 11
... • Here with competition high priced production and low scale • Monopoly allows economies of scale to be exploited and hence a lower cost of production. • There may be supernormal profits, but ...
... • Here with competition high priced production and low scale • Monopoly allows economies of scale to be exploited and hence a lower cost of production. • There may be supernormal profits, but ...
Econ 384 Chapter13b
... Both Coke and Pepsi make profits of 2005.55 when they produce 63.3 each at a price of ...
... Both Coke and Pepsi make profits of 2005.55 when they produce 63.3 each at a price of ...
File
... demanded of a good or service, is functionally related to the selling price P. Inequality asserts that quantity demanded and price are inversely related. This relationship is illustrated in Figure. The downward-sloping demand curve illustrates the inverse relationship between the quantity demanded o ...
... demanded of a good or service, is functionally related to the selling price P. Inequality asserts that quantity demanded and price are inversely related. This relationship is illustrated in Figure. The downward-sloping demand curve illustrates the inverse relationship between the quantity demanded o ...
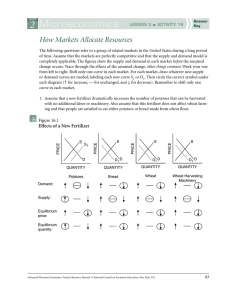
How Markets Allocate Resources
... The following questions refer to a group of related markets in the United States during a long period of time. Assume that the markets are perfectly competitive and that the supply and demand model is completely applicable. The figures show the supply and demand in each market before the assumed cha ...
... The following questions refer to a group of related markets in the United States during a long period of time. Assume that the markets are perfectly competitive and that the supply and demand model is completely applicable. The figures show the supply and demand in each market before the assumed cha ...
Chapter 07 Key Question Solutions
... (b) Disagree. The marginal utility of a unit beyond the first may be sufficiently great (relative to product price) to make it a worthwhile purchase. Consumers are interested in maximizing total utility, not marginal utility. (c) Agree. This product’s price could be so high relative to the first uni ...
... (b) Disagree. The marginal utility of a unit beyond the first may be sufficiently great (relative to product price) to make it a worthwhile purchase. Consumers are interested in maximizing total utility, not marginal utility. (c) Agree. This product’s price could be so high relative to the first uni ...
Answers to Final Exam - Summer 2007
... newer buses, the marginal cost of reducing this pollution is different for these two companies. For Firm #1, the marginal cost of abatement is given by MCA1 = 200 – 2Q1. For the company with the newer buses (Firm #2), the marginal cost of abatement is given by MCA2 = 50 – 0.5Q2. In each case, MCA is ...
... newer buses, the marginal cost of reducing this pollution is different for these two companies. For Firm #1, the marginal cost of abatement is given by MCA1 = 200 – 2Q1. For the company with the newer buses (Firm #2), the marginal cost of abatement is given by MCA2 = 50 – 0.5Q2. In each case, MCA is ...
Document
... 6. What are the conditions of consumer’s equilibrium under the indifference curve approach? What changes will take place if the conditions are not fulfilled to reach equilibrium? 7. Explain the three properties of indifference curve. 8. With the help of numerical example measure price elasticity of ...
... 6. What are the conditions of consumer’s equilibrium under the indifference curve approach? What changes will take place if the conditions are not fulfilled to reach equilibrium? 7. Explain the three properties of indifference curve. 8. With the help of numerical example measure price elasticity of ...
Externality

In economics, an externality is the cost or benefit that affects a party who did not choose to incur that cost or benefit.For example, manufacturing activities that cause air pollution impose health and clean-up costs on the whole society, whereas the neighbors of an individual who chooses to fire-proof his home may benefit from a reduced risk of a fire spreading to their own houses. If external costs exist, such as pollution, the producer may choose to produce more of the product than would be produced if the producer were required to pay all associated environmental costs. Because responsibility or consequence for self-directed action lies partly outside the self, an element of externalization is involved. If there are external benefits, such as in public safety, less of the good may be produced than would be the case if the producer were to receive payment for the external benefits to others. For the purpose of these statements, overall cost and benefit to society is defined as the sum of the imputed monetary value of benefits and costs to all parties involved. Thus, unregulated markets in goods or services with significant externalities generate prices that do not reflect the full social cost or benefit of their transactions; such markets are therefore inefficient.