The Peloponnesian War
... 2. Led by Athens, they use the League to create an Athenian empire 3. Sparta and her allies oppose Athenian expansion B. Athens constructed huge walls around the city and down to the sea C. The First Peloponnesian War 1. Allies of Sparta and Athens fight off and on from 460-446 B.C. D. Uneasy Peace ...
... 2. Led by Athens, they use the League to create an Athenian empire 3. Sparta and her allies oppose Athenian expansion B. Athens constructed huge walls around the city and down to the sea C. The First Peloponnesian War 1. Allies of Sparta and Athens fight off and on from 460-446 B.C. D. Uneasy Peace ...
Chapter-7
... 5. Women of Athens: Women spent their days in the house secluded from society and could not vote. 6. Slavery: 33% of the population of Athens were slaves and were owned by someone else. 7. Lives of slaves: They had no political rights, nor citizenship. They had a chance to buy their freedom or be fr ...
... 5. Women of Athens: Women spent their days in the house secluded from society and could not vote. 6. Slavery: 33% of the population of Athens were slaves and were owned by someone else. 7. Lives of slaves: They had no political rights, nor citizenship. They had a chance to buy their freedom or be fr ...
Delian League
... o Got paid for their service which came from the tribute Symbiotic relationship occurs between the rowers and political leaders, particularly Perecles whose policy rests on supporting everything for the naval empire o Political leaders needed votes to keep them in power and the rowers wanted to ke ...
... o Got paid for their service which came from the tribute Symbiotic relationship occurs between the rowers and political leaders, particularly Perecles whose policy rests on supporting everything for the naval empire o Political leaders needed votes to keep them in power and the rowers wanted to ke ...
File - Mrs. Mueller`s World!
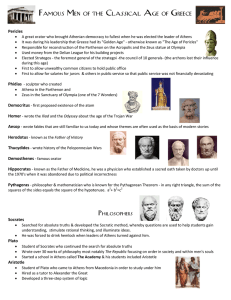
... A great orator who brought Athenian democracy to fullest when he was elected the leader of Athens It was during his leadership that Greece had its "Golden Age" - otherwise known as "The Age of Pericles" Responsible for reconstruction of the Parthenon on the Acropolis and the Zeus statue at Olympia U ...
... A great orator who brought Athenian democracy to fullest when he was elected the leader of Athens It was during his leadership that Greece had its "Golden Age" - otherwise known as "The Age of Pericles" Responsible for reconstruction of the Parthenon on the Acropolis and the Zeus statue at Olympia U ...
Notes on Movie
... -used wealth to gain power -was taught to be an aristocrat, which controlled everything that happened in his home town in Athens -most houses were mud brick no sewage at first it was more hard word and labor, while women weaved and cooked. There was no science and writing and reading was very rare l ...
... -used wealth to gain power -was taught to be an aristocrat, which controlled everything that happened in his home town in Athens -most houses were mud brick no sewage at first it was more hard word and labor, while women weaved and cooked. There was no science and writing and reading was very rare l ...
Background Essay Questions
... Directions: Answer the following using sentences when appropriate. 1. What two Mediterranean societies are being compared? During what approximate time period? ...
... Directions: Answer the following using sentences when appropriate. 1. What two Mediterranean societies are being compared? During what approximate time period? ...
PowerPoint on Greece - Henry County Schools
... at the trial in which he is charged with not recognizing the gods recognized by the state, inventing new deities, and corrupting the youth of Athens. Socrates' speech, however, is by no means an "apology" in our modern understanding of the word. The name of the dialogue derives from the Greek "apolo ...
... at the trial in which he is charged with not recognizing the gods recognized by the state, inventing new deities, and corrupting the youth of Athens. Socrates' speech, however, is by no means an "apology" in our modern understanding of the word. The name of the dialogue derives from the Greek "apolo ...
Chapter 5 Notes
... Solon – reversed the Draconian laws, outlawed debt-slavery, encourage trade, instituted a limited democracy where all men could serve in the assembly, but only the wealthy could run for and hold office – somewhat effective Cleisthenes – broke up noble families, created 10 tribes for basis of ele ...
... Solon – reversed the Draconian laws, outlawed debt-slavery, encourage trade, instituted a limited democracy where all men could serve in the assembly, but only the wealthy could run for and hold office – somewhat effective Cleisthenes – broke up noble families, created 10 tribes for basis of ele ...
Greek Achievements
... decisive in the history of the West. Had the Greeks been defeated, the cultural and political vitality we associate and inherit from the Greeks would never have evolved. • The confidence and pride from these victories propelled Greece and Athens, in particular, to its “Golden Age.” ...
... decisive in the history of the West. Had the Greeks been defeated, the cultural and political vitality we associate and inherit from the Greeks would never have evolved. • The confidence and pride from these victories propelled Greece and Athens, in particular, to its “Golden Age.” ...
Sovereignty - No country (or Gov`t) has the legal right to tell another
... iii. Money for navy used to beautify Athens Peloponnesian War a. Sparta and allies i. Allies were the Peloponnesian League ii. will fight Athens to free all Greek City States b. Sparta Defeats Athens i. Athens must surrender unconditionally 1. Must do whatever Sparta wants a. No walls b. No Navy c. ...
... iii. Money for navy used to beautify Athens Peloponnesian War a. Sparta and allies i. Allies were the Peloponnesian League ii. will fight Athens to free all Greek City States b. Sparta Defeats Athens i. Athens must surrender unconditionally 1. Must do whatever Sparta wants a. No walls b. No Navy c. ...
Where is Greece?
... (members of rich and powerful families). • Many Athenians also thought this type of government was unfair. ...
... (members of rich and powerful families). • Many Athenians also thought this type of government was unfair. ...
Notes for teachers Key Stage 2: The Persian wars
... KS2 History – ancient Greece KS2 Citizenship – preparing to play an active role as citizens ...
... KS2 History – ancient Greece KS2 Citizenship – preparing to play an active role as citizens ...
ancient greece - Mesa Public Schools
... Women were not allowed to become citizens, however, women were allowed to own land and businesses, which gave them more freedom than other Greek city-states. ...
... Women were not allowed to become citizens, however, women were allowed to own land and businesses, which gave them more freedom than other Greek city-states. ...
Worksheet - WordPress.com
... In Greece there were three main forms of government. These were used in different states at different times. Tyranny In the Sixth Century, many states in Greece were governed by a single ruler or tyrant (king). Most tyrants were very harsh. Some like Polycrates of Samos and Peisistratus of Athens im ...
... In Greece there were three main forms of government. These were used in different states at different times. Tyranny In the Sixth Century, many states in Greece were governed by a single ruler or tyrant (king). Most tyrants were very harsh. Some like Polycrates of Samos and Peisistratus of Athens im ...
The Effects of the Persian and Pelopponesian Wars PowerPoint
... Post Persian War ◦ Athens is the leader of the Delian League, whose goal was to be a mutual defense group in case of invasion ◦ Other city-states pay money to help fund Athens’ navy and army ◦ Athens is the premier city-state of Greece at this point in time ◦ Sparta began the Peloponnesian League ( ...
... Post Persian War ◦ Athens is the leader of the Delian League, whose goal was to be a mutual defense group in case of invasion ◦ Other city-states pay money to help fund Athens’ navy and army ◦ Athens is the premier city-state of Greece at this point in time ◦ Sparta began the Peloponnesian League ( ...
Classical Greece, 2000 BC*300 BC
... 3. Harsh rule leads to Messenian revolt; Spartans build stronger state ...
... 3. Harsh rule leads to Messenian revolt; Spartans build stronger state ...
Chapter 5 Ancient Greece (1750 B
... Slowly, power shifted to a class of noble landowners. At first, the nobles defended the king, but in time, they won power for themselves. A government ruled by a landholding elite is called an aristocracy. As trade expanded, a new class of wealthy merchants, farmers, and artisans came to dominate so ...
... Slowly, power shifted to a class of noble landowners. At first, the nobles defended the king, but in time, they won power for themselves. A government ruled by a landholding elite is called an aristocracy. As trade expanded, a new class of wealthy merchants, farmers, and artisans came to dominate so ...
PHIL 310 Prelude to Socrates Lesher
... excellence as a person and citizen --“If you come study with me, after the first day you will be better than you were before, and the same will be true for every day you stay with me’. Enjoyed a wide circle of admirers but worried some Athenians because he seemed to be departing from the old ways of ...
... excellence as a person and citizen --“If you come study with me, after the first day you will be better than you were before, and the same will be true for every day you stay with me’. Enjoyed a wide circle of admirers but worried some Athenians because he seemed to be departing from the old ways of ...
Name: Period: Date: Freedom In Sparta and Athens Which Persian
... 4. Which Spartan warrior remarked, “We shall have our fight in the shade”? 5. Which Greek city-state took the lead in commerce, industry, diplomacy, the arts, and the sciences? 6. Which ruler reformed Sparta into a military state? ...
... 4. Which Spartan warrior remarked, “We shall have our fight in the shade”? 5. Which Greek city-state took the lead in commerce, industry, diplomacy, the arts, and the sciences? 6. Which ruler reformed Sparta into a military state? ...
to read an essay
... before long, “it was for motives of personal ambition that most of them were following the line that is most disastrous to oligarchies when they take over from democracies…every single man, not content with being the equal of others, regards himself as greatly superior to everyone else.” The result ...
... before long, “it was for motives of personal ambition that most of them were following the line that is most disastrous to oligarchies when they take over from democracies…every single man, not content with being the equal of others, regards himself as greatly superior to everyone else.” The result ...
Freedom In Sparta and Athe - morganhighhistoryacademy.org
... 4. Which Spartan warrior remarked, “We shall have our fight in the shade”? 5. Which Greek city-state took the lead in commerce, industry, diplomacy, the arts, and the sciences? 6. Which ruler reformed Sparta into a military state? ...
... 4. Which Spartan warrior remarked, “We shall have our fight in the shade”? 5. Which Greek city-state took the lead in commerce, industry, diplomacy, the arts, and the sciences? 6. Which ruler reformed Sparta into a military state? ...
File - Mr. Amiti`s History Class
... Trade and wealth were looked down upon in Spartan life They forbade their citizens from travel and had little use for news ideas or the arts Their military was highly admired but their lifestyle was not imitated by other Greeks “Spartans are willing to die for their city, because they have no reason ...
... Trade and wealth were looked down upon in Spartan life They forbade their citizens from travel and had little use for news ideas or the arts Their military was highly admired but their lifestyle was not imitated by other Greeks “Spartans are willing to die for their city, because they have no reason ...
File
... plotting for one’s own security was thought a reasonable excuse for delaying action. A man who started a quarrel was always to be trusted, while one who opposed him was under suspicion” (3:82). Violence was becoming the answer to all problems in Athens and their ethos continued to change drastical ...
... plotting for one’s own security was thought a reasonable excuse for delaying action. A man who started a quarrel was always to be trusted, while one who opposed him was under suspicion” (3:82). Violence was becoming the answer to all problems in Athens and their ethos continued to change drastical ...
Athenian democracy

Athenian democracy developed around the fifth century BC in the Greek city-state (known as a polis) of Athens, comprising the city of Athens and the surrounding territory of Attica and is the first known democracy in the world. Other Greek cities set up democracies, most following the Athenian model, but none are as well documented as Athens.It was a system of direct democracy, in which participating citizens voted directly on legislation and executive bills. Participation was not open to all residents: to vote one had to be an adult, male citizen, and the number of these ""varied between 30,000 and 50,000 out of a total population of around 250,000 to 300,000.""The longest-lasting democratic leader was Pericles. After his death, Athenian democracy was twice briefly interrupted by oligarchic revolutions towards the end of the Peloponnesian War. It was modified somewhat after it was restored under Eucleides; and the most detailed accounts of the system are of this fourth-century modification rather than the Periclean system. Democracy was suppressed by the Macedonians in 322 BC. The Athenian institutions were later revived, but how close they were to a real democracy is debatable. Solon (594 BC), Cleisthenes (508/7 BC), an aristocrat, and Ephialtes (462 BC) contributed to the development of Athenian democracy.