Drugs
... An acute viral infection, that can cause a small illness but eventually destroy ventral horns of the spinal cord (spinal polio) It is highly contagious and sometimes fatal disease that affects the nerves, and can cause paralysis. Can be caught by swallowing something with the virus on it. As the inf ...
... An acute viral infection, that can cause a small illness but eventually destroy ventral horns of the spinal cord (spinal polio) It is highly contagious and sometimes fatal disease that affects the nerves, and can cause paralysis. Can be caught by swallowing something with the virus on it. As the inf ...
Sensory pathways
... Sensory pathways • Sensory systems allow us to detect, analyze and respond to our environment • “ascending pathways” • Carry information from sensory receptors to the brain • Conscious: reach cerebral cortex • Unconscious: do not reach cerebral ...
... Sensory pathways • Sensory systems allow us to detect, analyze and respond to our environment • “ascending pathways” • Carry information from sensory receptors to the brain • Conscious: reach cerebral cortex • Unconscious: do not reach cerebral ...
Slide ()
... Internal capsule (A) and MRIs through internal capsule (B) and midbrain (C). The locations of the descending axons in the internal capsule and basis pedunculi are shown on the MRIs. The letters "FATL" abbreviate Face, Arm, Trunk, and Leg. In the midbrain, the descending cortical fibers (filled middl ...
... Internal capsule (A) and MRIs through internal capsule (B) and midbrain (C). The locations of the descending axons in the internal capsule and basis pedunculi are shown on the MRIs. The letters "FATL" abbreviate Face, Arm, Trunk, and Leg. In the midbrain, the descending cortical fibers (filled middl ...
The Nervous System - Canton Local Schools
... neurons that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body. Two parts: 1. Autonomatic (ANS): controls the glands and muscles of the internal organs. AUTOMATIC 2. Somatic (SNS): controls the body skeletal muscles ...
... neurons that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body. Two parts: 1. Autonomatic (ANS): controls the glands and muscles of the internal organs. AUTOMATIC 2. Somatic (SNS): controls the body skeletal muscles ...
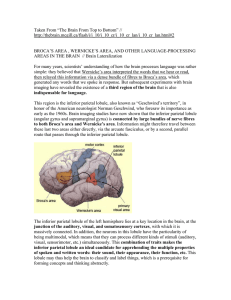
Language Processing in the Brain
... otherwise be needed to connect regions on opposite sides of the brain. Also, when two symmetrical areas on opposite sides of the brain perform two different functions, the brain’s cognitive capacities are in a sense doubled. Handedness and language are two highly lateralized functions. Though there ...
... otherwise be needed to connect regions on opposite sides of the brain. Also, when two symmetrical areas on opposite sides of the brain perform two different functions, the brain’s cognitive capacities are in a sense doubled. Handedness and language are two highly lateralized functions. Though there ...
the biology of brain and glandular system in the
... shall also see that information is passed from one neuron to another by chemical known as neurotransmitters. ( Morgan, 1986) Nerve cells, or neurons, are the information carriers of the nervous system. Each has a cell body that contains the machinery to keep neuron alive, and each has two types of f ...
... shall also see that information is passed from one neuron to another by chemical known as neurotransmitters. ( Morgan, 1986) Nerve cells, or neurons, are the information carriers of the nervous system. Each has a cell body that contains the machinery to keep neuron alive, and each has two types of f ...
cogsci200
... Each region encompasses a cortical surface area of roughly 2 mm2 and possesses a total of about 200,000 neurons. ...
... Each region encompasses a cortical surface area of roughly 2 mm2 and possesses a total of about 200,000 neurons. ...
Chapter 3
... • Depth and Distance Perception – where it is • Depth perception – ability to perceive the world in 3D – Binocular cues- cues to depth or distance; 2 eyes; 50 ft • Binocular disparity –difference in images between both eyes ...
... • Depth and Distance Perception – where it is • Depth perception – ability to perceive the world in 3D – Binocular cues- cues to depth or distance; 2 eyes; 50 ft • Binocular disparity –difference in images between both eyes ...
PPT
... • Symbolic AI is well-suited for representing explicit knowledge that can be appropriately formalized. • However, learning in biological systems is mostly implicit – it is an adaptation process based on uncertain information and reasoning. • ANNs are inherently parallel and work extremely efficientl ...
... • Symbolic AI is well-suited for representing explicit knowledge that can be appropriately formalized. • However, learning in biological systems is mostly implicit – it is an adaptation process based on uncertain information and reasoning. • ANNs are inherently parallel and work extremely efficientl ...
Chapter 13 - Integration
... E.g. muscles in thumb, fingers, lips, tongue, and vocal cords have large representations, while the trunk has a much smaller representation. o By comparing the somatosensory cortex (Fig. 10-10) and the primary motor cortex (Fig. 13-12 ), you can see that somatosensory and motor representations are ...
... E.g. muscles in thumb, fingers, lips, tongue, and vocal cords have large representations, while the trunk has a much smaller representation. o By comparing the somatosensory cortex (Fig. 10-10) and the primary motor cortex (Fig. 13-12 ), you can see that somatosensory and motor representations are ...
Unit 7 PowerPoint (PDF file)
... Characterized by slurred speech, loss of or blurred vision, dizziness, weakness, paralysis of a limb or hemiplegia, coma, and death Ischemic CVA - due to lack of blood supply to a particular area of the brain Hemorrhagic CVA - due to the rupture of a blood vessel in the brain ...
... Characterized by slurred speech, loss of or blurred vision, dizziness, weakness, paralysis of a limb or hemiplegia, coma, and death Ischemic CVA - due to lack of blood supply to a particular area of the brain Hemorrhagic CVA - due to the rupture of a blood vessel in the brain ...
Unit 6 Powerpoint
... Characterized by slurred speech, loss of or blurred vision, dizziness, weakness, paralysis of a limb or hemiplegia, coma, and death Ischemic CVA - due to lack of blood supply to a particular area of the brain Hemorrhagic CVA - due to the rupture of a blood vessel in the brain ...
... Characterized by slurred speech, loss of or blurred vision, dizziness, weakness, paralysis of a limb or hemiplegia, coma, and death Ischemic CVA - due to lack of blood supply to a particular area of the brain Hemorrhagic CVA - due to the rupture of a blood vessel in the brain ...
Nervous Systems
... • Peripheral nervous system (PNS) – network of nerves extending into different parts of the body – carries sensory input to the CNS and motor output away from the CNS ...
... • Peripheral nervous system (PNS) – network of nerves extending into different parts of the body – carries sensory input to the CNS and motor output away from the CNS ...
Chemistry of Psychology - Point Loma High School
... Used by more neurons than any other Lots in Cerebral Cortex and Hippocampus Too much Glutamate = causes neurons to die Plays a role in allowing and supporting synaptic connections allows messages to cross synapse efficiently Important for learning & memory (p98) Peptides= Endorphins Hund ...
... Used by more neurons than any other Lots in Cerebral Cortex and Hippocampus Too much Glutamate = causes neurons to die Plays a role in allowing and supporting synaptic connections allows messages to cross synapse efficiently Important for learning & memory (p98) Peptides= Endorphins Hund ...
Artificial Neural Network using for climate extreme in La
... Sailor et al., (2000) – ANN approach to local downscaling of GCMs outputs. Olsson et al., (2001) – Statistical atmospheric downscaling of short-term extreme rainfall. Boulanger et al., (2006/2007) – Projection of Future climate change in South America. ...
... Sailor et al., (2000) – ANN approach to local downscaling of GCMs outputs. Olsson et al., (2001) – Statistical atmospheric downscaling of short-term extreme rainfall. Boulanger et al., (2006/2007) – Projection of Future climate change in South America. ...
local - Ruhr-Universität Bochum
... cortical areas for about 30 attribute dimensions could be anatomically located in the monkey (Felleman & van Essen, 1991). In contrast, the correlates of substance concepts, we assume, are highly distributed neural states. Substance concepts are thus not expected to be realized by single cells – so- ...
... cortical areas for about 30 attribute dimensions could be anatomically located in the monkey (Felleman & van Essen, 1991). In contrast, the correlates of substance concepts, we assume, are highly distributed neural states. Substance concepts are thus not expected to be realized by single cells – so- ...
Neuron highlight
... savings in the GNG task that makes the discrimination and response easier. The mechanisms may involve some of the areas that are connected in feedforward or feedback arrangements with the olfactory bulb or cortex (Shipley and Adamek, 1984; Sobel et al., 1998). For most of the mice in the Rinberg et ...
... savings in the GNG task that makes the discrimination and response easier. The mechanisms may involve some of the areas that are connected in feedforward or feedback arrangements with the olfactory bulb or cortex (Shipley and Adamek, 1984; Sobel et al., 1998). For most of the mice in the Rinberg et ...
Epilepsy and Seizure Disorders
... Twin studies Study with 199 twins Concordance rates were 4 times higher in MZ twins than DZ twins 20% of affected twin pairs had an epileptic firstdegree relative Concordance high for generalized epilepsies compared to partial/focal epilepsies ...
... Twin studies Study with 199 twins Concordance rates were 4 times higher in MZ twins than DZ twins 20% of affected twin pairs had an epileptic firstdegree relative Concordance high for generalized epilepsies compared to partial/focal epilepsies ...
Frames, Coherency Chains and Hierarchical Binding: The Cortical Markus Werning (-duesseldorf.de)
... Frame theory provides us with a universal account not only for the psychology of categorization, but also for the decomposition of concepts. A frame is defined for a large domain of things and contains a fixed set of attribute dimensions each of which allows for a number of different attribute value ...
... Frame theory provides us with a universal account not only for the psychology of categorization, but also for the decomposition of concepts. A frame is defined for a large domain of things and contains a fixed set of attribute dimensions each of which allows for a number of different attribute value ...
12 The Central Nervous System Part A Central Nervous System
... Major parts and functions: Wernicke’s area – involved in sounding out unfamiliar words Broca’s area – speech preparation and production Lateral prefrontal cortex – language comprehension and word analysis Lateral and ventral temporal lobe – coordinate auditory and visual aspects of language General ...
... Major parts and functions: Wernicke’s area – involved in sounding out unfamiliar words Broca’s area – speech preparation and production Lateral prefrontal cortex – language comprehension and word analysis Lateral and ventral temporal lobe – coordinate auditory and visual aspects of language General ...
Slide () - Anesthesiology - American Society of Anesthesiologists
... Myelinating oligodendrocytes at a midrostrocaudal level: All panels are stained immunochemically with antibodies to myelin basic protein (MBP). A presents an overview showing different stages of myelination at a midrostrocaudal level of a control brain. In the cerebrocortical mantel, and in the tran ...
... Myelinating oligodendrocytes at a midrostrocaudal level: All panels are stained immunochemically with antibodies to myelin basic protein (MBP). A presents an overview showing different stages of myelination at a midrostrocaudal level of a control brain. In the cerebrocortical mantel, and in the tran ...
CONSCIOUSNESS FROM NEURONS 1 Abstract. Consciousness
... read out informs a n external observer when "red" occurs. However, no such external integrative mechanism is known for brain, and this is the heart of the problem: either to invent one, as in the dualist conception of a n external soul that supernaturally scans and manipulates neurons, or to discove ...
... read out informs a n external observer when "red" occurs. However, no such external integrative mechanism is known for brain, and this is the heart of the problem: either to invent one, as in the dualist conception of a n external soul that supernaturally scans and manipulates neurons, or to discove ...
Gray matters: How neuroscience can inform economics
... Although fMRI is increasingly becoming the method of choice, each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. EEG has excellent temporal resolution (on the order of 1 millisecond) and is the only method used with humans that directly monitors neural activity, as opposed to, e.g., blood flow. Bu ...
... Although fMRI is increasingly becoming the method of choice, each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. EEG has excellent temporal resolution (on the order of 1 millisecond) and is the only method used with humans that directly monitors neural activity, as opposed to, e.g., blood flow. Bu ...