Why Do We Sleep - The Dallas Philosophers Forum
... brain goes offline. We have wild escapades, violence, fighting, running. My wife says that I run in my sleep. I also get into fights and one time I actually hit her. That woke her and me up. So dreams are dreamlike because the prefrontal cortex is offline during REM sleep, allowing the limbic system ...
... brain goes offline. We have wild escapades, violence, fighting, running. My wife says that I run in my sleep. I also get into fights and one time I actually hit her. That woke her and me up. So dreams are dreamlike because the prefrontal cortex is offline during REM sleep, allowing the limbic system ...
research statement
... With raising awareness and deepening neurobiological knowledge of neural processes that take place in living creatures and the development of computational techniques, it is possible to build complex dynamic, reactive neural automatically reconfigurable associative systems for modeling real machine ...
... With raising awareness and deepening neurobiological knowledge of neural processes that take place in living creatures and the development of computational techniques, it is possible to build complex dynamic, reactive neural automatically reconfigurable associative systems for modeling real machine ...
schmid~4
... network is characterized by variants of the genome, epigenome, transcriptome, proteome, and metabolome. These molecular components, including receptors, transcription factors, and signaling molecules, represent viable target opportunities against which to develop countermeasures for the space enviro ...
... network is characterized by variants of the genome, epigenome, transcriptome, proteome, and metabolome. These molecular components, including receptors, transcription factors, and signaling molecules, represent viable target opportunities against which to develop countermeasures for the space enviro ...
Human nervous system_Final
... 7. Cerebral cortex: the outer layer of the cerebrum, composed of six cell layers of deeply folded and ridged gray matter. 8. Corpus callosum: a large bundle of nerve fibers that connect the two cerebral hemispheres. 9.Occiptial lobe: the region at the back of each cerebral hemisphere that contains t ...
... 7. Cerebral cortex: the outer layer of the cerebrum, composed of six cell layers of deeply folded and ridged gray matter. 8. Corpus callosum: a large bundle of nerve fibers that connect the two cerebral hemispheres. 9.Occiptial lobe: the region at the back of each cerebral hemisphere that contains t ...
Telemetric recording of neuronal activity
... potentiometer is milled down to a cross-section of 5 £ 3 mm (height 20 mm), so that only the spindle drive remains. The original slide is removed and replaced by a drop of acrylic cement embracing the worm. At the lower end of the potentiometer case, two stainless steel guiding tubes (outer diameter ...
... potentiometer is milled down to a cross-section of 5 £ 3 mm (height 20 mm), so that only the spindle drive remains. The original slide is removed and replaced by a drop of acrylic cement embracing the worm. At the lower end of the potentiometer case, two stainless steel guiding tubes (outer diameter ...
Neuron communication
... level of dopamine!) • Agonists: mimic neurotransmitters when you don’t have enough (ex: Depression is caused by low levels of serotonin.) ...
... level of dopamine!) • Agonists: mimic neurotransmitters when you don’t have enough (ex: Depression is caused by low levels of serotonin.) ...
A Small World of Neuronal Synchrony
... called ‘‘small-world’’ properties. A small-world network exhibits a connectivity that constitutes a compromise between random and nearest neighbor regimes resulting in a short average path length despite the predominance of local connections (Watts and Strogatz 1998; Sporns et al. 2004; Bassett and ...
... called ‘‘small-world’’ properties. A small-world network exhibits a connectivity that constitutes a compromise between random and nearest neighbor regimes resulting in a short average path length despite the predominance of local connections (Watts and Strogatz 1998; Sporns et al. 2004; Bassett and ...
Sparse coding in the primate cortex
... shapes, and fractal patterns, and the responses are usually not predictable from responses to simple stimuli. Cells responding to faces but not to a large collection of control stimuli could be considered, on the one hand, to be very tightly tuned cells in the space of all possible stimuli. On the o ...
... shapes, and fractal patterns, and the responses are usually not predictable from responses to simple stimuli. Cells responding to faces but not to a large collection of control stimuli could be considered, on the one hand, to be very tightly tuned cells in the space of all possible stimuli. On the o ...
Mircea Steriade
... esoteric arrows running from the motor cortex to basal ganglia and thalamus and back. These reciprocal projections that occurred to me right at the initiation in neuroscience anticipated the core of my entire research life, which is centered on the role of corticothalamic reciprocal loops in the gen ...
... esoteric arrows running from the motor cortex to basal ganglia and thalamus and back. These reciprocal projections that occurred to me right at the initiation in neuroscience anticipated the core of my entire research life, which is centered on the role of corticothalamic reciprocal loops in the gen ...
Neurotransmitters and Sleep
... a wide reaching and general effect when stimulated. As with ACh, both of these neurotransmitters, and the corresponding brain structures play an important role in cortical activation in general, though their specific effects are more complex. Experiments with lab animals have found that stimulation ...
... a wide reaching and general effect when stimulated. As with ACh, both of these neurotransmitters, and the corresponding brain structures play an important role in cortical activation in general, though their specific effects are more complex. Experiments with lab animals have found that stimulation ...
Our 5 Senses 2012 - teacher version no notes
... stimulus energy (signals i.e. light rays, sound waves etc.) into neural impulses • an action potential. • Each sense has its own process of transduction • Information goes from the senses to the thalamus , then to the various areas in the brain. • Example: Converting Light Rays into neural messages ...
... stimulus energy (signals i.e. light rays, sound waves etc.) into neural impulses • an action potential. • Each sense has its own process of transduction • Information goes from the senses to the thalamus , then to the various areas in the brain. • Example: Converting Light Rays into neural messages ...
McCulloch-Pitts Neuron
... The activation of a McCulloch Pitts neuron is binary. Neurons are connected by directed weighted paths. A connection path is excitatory if the weight on the path is positive else its inhibitory. All excitatory connections to a neuron have the same weights. Each neuron has a fixed threshold: f(n) = ...
... The activation of a McCulloch Pitts neuron is binary. Neurons are connected by directed weighted paths. A connection path is excitatory if the weight on the path is positive else its inhibitory. All excitatory connections to a neuron have the same weights. Each neuron has a fixed threshold: f(n) = ...
Monkey and humans exhibit similar motion
... motion directions inducing DAEs of opposite sign. However, the observed changes in the DAE density function cannot be explained solely in terms of a subtractive combination of opposing DAEs induced by the two directions. We had observers adapt to stimuli containing just the opposite-direction dots. ...
... motion directions inducing DAEs of opposite sign. However, the observed changes in the DAE density function cannot be explained solely in terms of a subtractive combination of opposing DAEs induced by the two directions. We had observers adapt to stimuli containing just the opposite-direction dots. ...
Motor Neuron - papbiobellaire
... 9. Motor end plate - (axon terminals) site where neurotransmitters (neurohumor) are stored and released into synapse or effector 10. Axon - carry impulses away from cell body to synapse or to effector ...
... 9. Motor end plate - (axon terminals) site where neurotransmitters (neurohumor) are stored and released into synapse or effector 10. Axon - carry impulses away from cell body to synapse or to effector ...
Guided Notes for the Nervous System-
... 16. Functional classification groups neurons according to the direction the nerve impulse is traveling relative to the CNS. Sensory neurons are neurons carrying impulses from sensory receptors to the CNS. They are also called afferent neurons. Sensory neurons keep us informed about what is happenin ...
... 16. Functional classification groups neurons according to the direction the nerve impulse is traveling relative to the CNS. Sensory neurons are neurons carrying impulses from sensory receptors to the CNS. They are also called afferent neurons. Sensory neurons keep us informed about what is happenin ...
Biology 2401 Anatomy and Physiology I notes
... makes membranes more permeable to Ca++ could be a stimulant. *What is the value of having two different neurotransmitter receptors at a synapse? * How can a neurotransmitter be excitatory in one place and inhibitory in another? ...
... makes membranes more permeable to Ca++ could be a stimulant. *What is the value of having two different neurotransmitter receptors at a synapse? * How can a neurotransmitter be excitatory in one place and inhibitory in another? ...
Are We Paying Attention Yet?
... Attention and eye movements are tightly related During saccade preparation, oculomotor system controls location selection even if attention is directed elsewhere Direction of attention is dissociable from eye position during fixations Findings are do not rule out interdependence or identity hypothes ...
... Attention and eye movements are tightly related During saccade preparation, oculomotor system controls location selection even if attention is directed elsewhere Direction of attention is dissociable from eye position during fixations Findings are do not rule out interdependence or identity hypothes ...
Associative memory with spatiotemporal chaos control
... Finally, the effects of the chaotic dynamics on the association in the present network are investigated by comparing the Lyapunov exponents with the success rate. The bifurcation diagram of the Lyapunov exponents versus the system parameters k(0) and a (0) have already been displayed in Fig. 2. Here ...
... Finally, the effects of the chaotic dynamics on the association in the present network are investigated by comparing the Lyapunov exponents with the success rate. The bifurcation diagram of the Lyapunov exponents versus the system parameters k(0) and a (0) have already been displayed in Fig. 2. Here ...
Rebuilding Brain Circuitry with Living Micro
... or delivered from exogenous sources.11–13 To date, benefits of stem cell therapies include secretion of neuroprotective factors, providing glia to remyelinate denuded axons, and in some cases providing new neurons to discrete regions.14–19 While cell replacement strategies have received great attent ...
... or delivered from exogenous sources.11–13 To date, benefits of stem cell therapies include secretion of neuroprotective factors, providing glia to remyelinate denuded axons, and in some cases providing new neurons to discrete regions.14–19 While cell replacement strategies have received great attent ...
middle ear
... Part of the brain which helps process information about touch: - Somatosensory cortex of parietal lobe - Info from touch receptors in head enters CNS through cranial nerves - Info from receptors below head enters spinal cord and travels through spinal nerves to brain ...
... Part of the brain which helps process information about touch: - Somatosensory cortex of parietal lobe - Info from touch receptors in head enters CNS through cranial nerves - Info from receptors below head enters spinal cord and travels through spinal nerves to brain ...
Depth perception - Bremerton School District
... perceived to be moving more slowly that smaller objects. The brain will also perceive continuous movement in a series of slightly varying images. The illusion of movement is also created using the phi phenomenon – when two adjacent stationary lights blink on and off in quick succession ...
... perceived to be moving more slowly that smaller objects. The brain will also perceive continuous movement in a series of slightly varying images. The illusion of movement is also created using the phi phenomenon – when two adjacent stationary lights blink on and off in quick succession ...
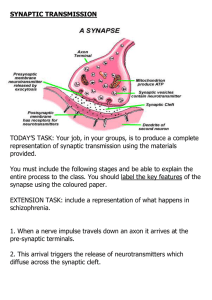
SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION
... serotonin. These can all influence the post-synaptic neuron to respond in an inhibitory way (decreases the firing of a cell) or an excitatory way (increases the firing of a cell). Schizophrenia, for example, is a mental disorder thought to be the result of excessive activity of the neurotransmitte ...
... serotonin. These can all influence the post-synaptic neuron to respond in an inhibitory way (decreases the firing of a cell) or an excitatory way (increases the firing of a cell). Schizophrenia, for example, is a mental disorder thought to be the result of excessive activity of the neurotransmitte ...