Lecture Slides - Austin Community College
... Parieto-occipital sulcus - separates the occipital from the parietal lobe Lateral sulcus - separates temporal lobe from parietal and frontal lobes Deeper sulci divide cerebrum into lobes ...
... Parieto-occipital sulcus - separates the occipital from the parietal lobe Lateral sulcus - separates temporal lobe from parietal and frontal lobes Deeper sulci divide cerebrum into lobes ...
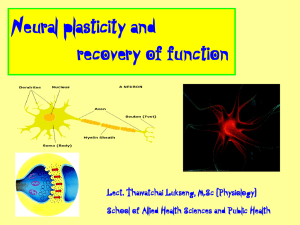
Neural plasticity and recovery of function
... • Neural (adj.) = involving a nerve or the system of nerves that includes the brain • Plastic (adj.) = soft enough to be changed into a new shape • Neuroplasticity, brain plasticity or brain malleability • The brain's ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections • Neurons (nerve ce ...
... • Neural (adj.) = involving a nerve or the system of nerves that includes the brain • Plastic (adj.) = soft enough to be changed into a new shape • Neuroplasticity, brain plasticity or brain malleability • The brain's ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections • Neurons (nerve ce ...
Slide 1 - Elsevier
... (subtypes a, b, A, B), bipolar cells (subtypes c, d), and ganglion cells (subtypes e, D, E). A specific neuron type’s cardinal feature is its axon’s distribution—the neuron’s function in terms of output. Photoreceptors detect light and their axon innervates bipolar cells. The latter in turn innervat ...
... (subtypes a, b, A, B), bipolar cells (subtypes c, d), and ganglion cells (subtypes e, D, E). A specific neuron type’s cardinal feature is its axon’s distribution—the neuron’s function in terms of output. Photoreceptors detect light and their axon innervates bipolar cells. The latter in turn innervat ...
12-2cut
... 2) extra K+ channels open and lots of K+ flows out This repolarizes membrane 3) Refractory period: time during which original state is regenerated by Na-K pumps. During this time, neuron __________ fire again. ...
... 2) extra K+ channels open and lots of K+ flows out This repolarizes membrane 3) Refractory period: time during which original state is regenerated by Na-K pumps. During this time, neuron __________ fire again. ...
Significant Mirrorings in the Process of Teaching and Learning
... certain time of his learning process; it is defined as the distance between the current level of development and the level of potential development that can be achieved with the help of other more skilled people, adults or peers) that, from the second half of the twentieth century until today, has m ...
... certain time of his learning process; it is defined as the distance between the current level of development and the level of potential development that can be achieved with the help of other more skilled people, adults or peers) that, from the second half of the twentieth century until today, has m ...
Slide ()
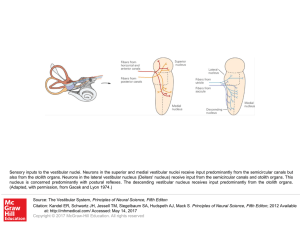
... Sensory inputs to the vestibular nuclei. Neurons in the superior and medial vestibular nuclei receive input predominantly from the semicircular canals but also from the otolith organs. Neurons in the lateral vestibular nucleus (Deiters' nucleus) receive input from the semicircular canals and otolith ...
... Sensory inputs to the vestibular nuclei. Neurons in the superior and medial vestibular nuclei receive input predominantly from the semicircular canals but also from the otolith organs. Neurons in the lateral vestibular nucleus (Deiters' nucleus) receive input from the semicircular canals and otolith ...
File
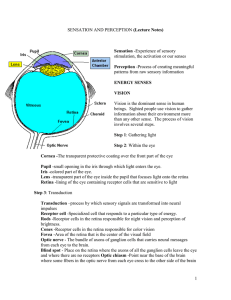
... processes involved in hearing pitch: place theory and frequency theory. Place theory -Theory that pitch is determined by the location of greatest vibration of the basilar membrane Frequency theory -Theory that pitch is determined by the frequency with which hair cells in the cochlea fire ...
... processes involved in hearing pitch: place theory and frequency theory. Place theory -Theory that pitch is determined by the location of greatest vibration of the basilar membrane Frequency theory -Theory that pitch is determined by the frequency with which hair cells in the cochlea fire ...
The neural basis of the speed–accuracy tradeoff - Eric
... in humans [4–6]. BOLD is an fMRI technique that reveals the local changes in blood oxygenation that are closely coupled with local increases in neural activation [26]. Compared to cell recordings in animals, human fMRI has distinct advantages as a method for studying SAT. First, unlike animals, huma ...
... in humans [4–6]. BOLD is an fMRI technique that reveals the local changes in blood oxygenation that are closely coupled with local increases in neural activation [26]. Compared to cell recordings in animals, human fMRI has distinct advantages as a method for studying SAT. First, unlike animals, huma ...
Biology 621 - Chapter 12 Midterm Exam Review
... a. They follow an all-or-none principle. c. They jump from node to node. b. They flow at various speeds. d. They flow in only one direction. 18. If you accidentally touch a hot stove, you pull your finger away before the impulse is relayed to the a. spinal cord b. effector c. brain d. receptor 19. T ...
... a. They follow an all-or-none principle. c. They jump from node to node. b. They flow at various speeds. d. They flow in only one direction. 18. If you accidentally touch a hot stove, you pull your finger away before the impulse is relayed to the a. spinal cord b. effector c. brain d. receptor 19. T ...
This Week in The Journal - The Journal of Neuroscience
... MeCP2 in transcriptional regulation, however, brain-wide gene expression is relatively normal in MeCP2-deficient mice, suggesting that gene expression changes are subtle or restricted to a small subset of cells. MeCP2ishighlyexpressedinneurons,and neuron-specific expression of MeCP2 can rescue RTT-l ...
... MeCP2 in transcriptional regulation, however, brain-wide gene expression is relatively normal in MeCP2-deficient mice, suggesting that gene expression changes are subtle or restricted to a small subset of cells. MeCP2ishighlyexpressedinneurons,and neuron-specific expression of MeCP2 can rescue RTT-l ...
Textures of Natural Images in the Human Brain. Focus on
... Texture patterns— homogeneous regions of repeated structures—are the predominant feature of natural visual scenes. The zebra, a 1938 optical art painting by Victor Vasarely, illustrates how different textures segregate and define figures from their background. Despite the ease with which we perceive ...
... Texture patterns— homogeneous regions of repeated structures—are the predominant feature of natural visual scenes. The zebra, a 1938 optical art painting by Victor Vasarely, illustrates how different textures segregate and define figures from their background. Despite the ease with which we perceive ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 13.1 Ectodermis subdivided into
... spreads laterally. Asymmetric responses by receiving cells to the green morphogen may depend either on prepatterned difference in competence (blue cells become yellow, and red cells become either both mauve and pink), and on morphogen concentration (mauve at high level, pink at lower level). The dif ...
... spreads laterally. Asymmetric responses by receiving cells to the green morphogen may depend either on prepatterned difference in competence (blue cells become yellow, and red cells become either both mauve and pink), and on morphogen concentration (mauve at high level, pink at lower level). The dif ...
Common Neurotransmitters: Criteria for Neurotransmitters, Key
... Abstract: The criteria, key locations, classifications and functions of common neuro transmitters is reviewed and discussed. Neurotransmitters are the brain chemicals that communicate information throughout our brain and body. They relay signals between neurons. To be neurotransmitter the molecule m ...
... Abstract: The criteria, key locations, classifications and functions of common neuro transmitters is reviewed and discussed. Neurotransmitters are the brain chemicals that communicate information throughout our brain and body. They relay signals between neurons. To be neurotransmitter the molecule m ...
bio 342 human physiology
... d) Axons of second order neurons travel in the medial lemniscus. e) Axons of first order neurons ascend in the dorsal columns and synapse onto second order neurons in the dorsal column nuclei. ...
... d) Axons of second order neurons travel in the medial lemniscus. e) Axons of first order neurons ascend in the dorsal columns and synapse onto second order neurons in the dorsal column nuclei. ...
Lesion Mapping the Four-Factor Structure of Emotional Intelligence
... between emotional processes, general intelligence, and their neural correlates that are the subject of ongoing research and scientific exchange. In particular, questions about the unitary nature of EI and whether specific facets of EI share common or distinct neural mechanisms from one another are int ...
... between emotional processes, general intelligence, and their neural correlates that are the subject of ongoing research and scientific exchange. In particular, questions about the unitary nature of EI and whether specific facets of EI share common or distinct neural mechanisms from one another are int ...
Symbolic Reasoning in Spiking Neurons:
... In the simplest case, 100 neurons could represent a 100 dimensional vector x by having each e be a different unit vector in each of the 100 dimensions. This would provide a completely local representation of each value in the vector. More realistically, 100 neurons could represent one or two dimensi ...
... In the simplest case, 100 neurons could represent a 100 dimensional vector x by having each e be a different unit vector in each of the 100 dimensions. This would provide a completely local representation of each value in the vector. More realistically, 100 neurons could represent one or two dimensi ...
Neural Network Dynamics
... sustained responses to transient stimuli. Neuronal activity evoked by a transient stimulus often continues beyond the period of stimulus presentation and, in cases where shortterm memory of the stimulus is required for a task, such sustained activity can last for tens of seconds (Wang & Goldman-Raki ...
... sustained responses to transient stimuli. Neuronal activity evoked by a transient stimulus often continues beyond the period of stimulus presentation and, in cases where shortterm memory of the stimulus is required for a task, such sustained activity can last for tens of seconds (Wang & Goldman-Raki ...
Practice questions 1. How are functionalism and behaviourism
... towards the synaptic buttons in the form of __________ potentials. These in turn contribute to the release of _________________ to the synaptic gap. a) axons, graded, dendrites, action, neurotransmitters b) cell body, action, axon, graded, ions c) dendrites, graded, axon, action, neurotransmitters d ...
... towards the synaptic buttons in the form of __________ potentials. These in turn contribute to the release of _________________ to the synaptic gap. a) axons, graded, dendrites, action, neurotransmitters b) cell body, action, axon, graded, ions c) dendrites, graded, axon, action, neurotransmitters d ...
Neuroscience 14a – Introduction to Consciousness
... o Cholinergic projections to reticular nuclei regulate flow of information through other thalamic nuclei to the cortex. Tuberomammillary nucleus in the hypothalamus projects to the cortex and is involved in maintaining the awake state. This collectively is known as the reticular activating system, w ...
... o Cholinergic projections to reticular nuclei regulate flow of information through other thalamic nuclei to the cortex. Tuberomammillary nucleus in the hypothalamus projects to the cortex and is involved in maintaining the awake state. This collectively is known as the reticular activating system, w ...
Neuroembryology of Neural Tube Defects
... Most are the result of defective closure of the neural tube during the 4th week of development. The resulting neural tube defects (NTDs) also involve tissue overlying the spinal cord: meninges, vertebral arch, muscles, skin. ...
... Most are the result of defective closure of the neural tube during the 4th week of development. The resulting neural tube defects (NTDs) also involve tissue overlying the spinal cord: meninges, vertebral arch, muscles, skin. ...
NOT FOR SALE - Cengage Learning
... Neurons vary according to their functions and their location. Neurons in the brain may be only a fraction of an inch in length, whereas others in the legs are several feet long. Most neurons include a cell body, dendrites, and an axon (see Figure 2.1). The cell body contains the core or nucleus of t ...
... Neurons vary according to their functions and their location. Neurons in the brain may be only a fraction of an inch in length, whereas others in the legs are several feet long. Most neurons include a cell body, dendrites, and an axon (see Figure 2.1). The cell body contains the core or nucleus of t ...
Pathogenicity and Effects of Prions Misfolding
... Although prions are generally given a bad reputation in popular news outlets due to the debilitating diseases they have been preported to have caused, prions are naturally found throughout the body. Although much about the specific functions prions is unknown, what is known is that they serve a func ...
... Although prions are generally given a bad reputation in popular news outlets due to the debilitating diseases they have been preported to have caused, prions are naturally found throughout the body. Although much about the specific functions prions is unknown, what is known is that they serve a func ...