Text S2: Conflicting demands of localization and pattern
... However, in order to achieve invariance with respect to x and µ in the central pattern neuron, we can make use of the subtraction of the peripheries. For any given ∆x this means that rper(x+µ+∆x) - rper(x+µ-∆x) = rdir(∆x). After differentiating this equation with respect to (x+µ) and rearranging we ...
... However, in order to achieve invariance with respect to x and µ in the central pattern neuron, we can make use of the subtraction of the peripheries. For any given ∆x this means that rper(x+µ+∆x) - rper(x+µ-∆x) = rdir(∆x). After differentiating this equation with respect to (x+µ) and rearranging we ...
Hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning induces tolerance against brain
... important role in the induction of ischemic tolerance by HBOPC (Kim et al., 2001; Nie et al., 2006). Moreno et al. (1995) studied immunocytochemical localization of CAT in the central nervous system of the rat and found that intensely stained CAT-immunoreactive neurons were resistant to ischemia– re ...
... important role in the induction of ischemic tolerance by HBOPC (Kim et al., 2001; Nie et al., 2006). Moreno et al. (1995) studied immunocytochemical localization of CAT in the central nervous system of the rat and found that intensely stained CAT-immunoreactive neurons were resistant to ischemia– re ...
Nervous System
... Causes more Na+ channels to open (“downstream”) in cell membrane More Na+ ions diffuse into cell ...
... Causes more Na+ channels to open (“downstream”) in cell membrane More Na+ ions diffuse into cell ...
The Beautiful Brain - Weisman Art Museum
... important. The Beautiful Brain: The Drawings of Santiago Ramón y Cajal is the first museum exhibition to present and contextualize these amazing historical objects. Scientists the world over know Cajal as the father of modern neuroscience, the study of the structure and function of the brain. Cajal ...
... important. The Beautiful Brain: The Drawings of Santiago Ramón y Cajal is the first museum exhibition to present and contextualize these amazing historical objects. Scientists the world over know Cajal as the father of modern neuroscience, the study of the structure and function of the brain. Cajal ...
Ch 15 Chemical Senses
... – 2DG, which contains glucose, is ingested into an animal – Animal is exposed to different chemicals – Neural activation is measured by amount of radioactivity present • This technique shows the pattern of neural activation is Figure 15.10 These molecules have the same related to both chemical chemi ...
... – 2DG, which contains glucose, is ingested into an animal – Animal is exposed to different chemicals – Neural activation is measured by amount of radioactivity present • This technique shows the pattern of neural activation is Figure 15.10 These molecules have the same related to both chemical chemi ...
ADHD: The Biology Behind the Behavior Presentation
... in memory, listening, following directions, lack of follow through, persistence, transitioning between tasks, daydreaming. ...
... in memory, listening, following directions, lack of follow through, persistence, transitioning between tasks, daydreaming. ...
Loading “EBSCOhost”
... account for difficulties ranging from excessive reserve to autism. The possible failure of mirror neurons in autism is particularly intriguing. The cause and even the nature of this strange condition have eluded researchers for decades, leaving sufferers and their families and caregivers with little ...
... account for difficulties ranging from excessive reserve to autism. The possible failure of mirror neurons in autism is particularly intriguing. The cause and even the nature of this strange condition have eluded researchers for decades, leaving sufferers and their families and caregivers with little ...
ANATOMY OF A NEURON
... GLIAL GLIAL CELLS: CELLS: The The Neurons’ Neurons’ Helper Helper Cells Cells •Glial cells are specialized cells found throughout the nervous system that provide structural support and insulation for neurons. • Glial (“glue”) cells hold the nervous system together. •They are smaller than neurons bu ...
... GLIAL GLIAL CELLS: CELLS: The The Neurons’ Neurons’ Helper Helper Cells Cells •Glial cells are specialized cells found throughout the nervous system that provide structural support and insulation for neurons. • Glial (“glue”) cells hold the nervous system together. •They are smaller than neurons bu ...
Imitation, Empathy, and Mirror Neurons
... literature inspired by sensory-motor models is the so-called correspondence problem (Nehaniv & Dautenhahn 2002). This problem can be summarized with the question: how is the sensory input from somebody else’s action transformed into a matching motor output by the imitator? For the ideomotor framewor ...
... literature inspired by sensory-motor models is the so-called correspondence problem (Nehaniv & Dautenhahn 2002). This problem can be summarized with the question: how is the sensory input from somebody else’s action transformed into a matching motor output by the imitator? For the ideomotor framewor ...
The Representation of Biological Classes in the Human Brain
... estimate the average voxelwise hemodynamic responses across the entire were screened for MRI scanning and provided informed consent in acexperiment for our six stimulus categories using deconvolution using cordance with the Institutional Review Board of Dartmouth College. AFNI software (3dDeconvolve ...
... estimate the average voxelwise hemodynamic responses across the entire were screened for MRI scanning and provided informed consent in acexperiment for our six stimulus categories using deconvolution using cordance with the Institutional Review Board of Dartmouth College. AFNI software (3dDeconvolve ...
Posterior cingulate cortex: adapting behavior to a
... Bayesian learning: a set of learning models in which agents maintain knowledge as probability distributions updated by Bayes’ rule. Classical or Pavlovian conditioning: the process by which environmental stimuli become associated, via learning, with the prediction of outcomes. Cognitive set or set: ...
... Bayesian learning: a set of learning models in which agents maintain knowledge as probability distributions updated by Bayes’ rule. Classical or Pavlovian conditioning: the process by which environmental stimuli become associated, via learning, with the prediction of outcomes. Cognitive set or set: ...
Complex Cell-like Direction Selectivity through Spike
... that the receptive field sub-units are computed within the dendritic tree of individual complex cells, as suggested by Mel and colleagues for orientation- and disparity-selective complex cells [16, 171. A similar single-neuron model for direction selectivity is possible [18], but as shown by Anderso ...
... that the receptive field sub-units are computed within the dendritic tree of individual complex cells, as suggested by Mel and colleagues for orientation- and disparity-selective complex cells [16, 171. A similar single-neuron model for direction selectivity is possible [18], but as shown by Anderso ...
BECOMING AWARE OF THE WORLD AROUND US
... are termed as deep senses: vestibular and kinesthetic. They help us in maintaining body equilibrium and provide important information about body position and movement of body parts relative to each other. In this section, you will study about the structure and function of different human sense organ ...
... are termed as deep senses: vestibular and kinesthetic. They help us in maintaining body equilibrium and provide important information about body position and movement of body parts relative to each other. In this section, you will study about the structure and function of different human sense organ ...
Imitation, Empathy, and Mirror Neurons
... literature inspired by sensory-motor models is the so-called correspondence problem (Nehaniv & Dautenhahn 2002). This problem can be summarized with the question: how is the sensory input from somebody else’s action transformed into a matching motor output by the imitator? For the ideomotor framewor ...
... literature inspired by sensory-motor models is the so-called correspondence problem (Nehaniv & Dautenhahn 2002). This problem can be summarized with the question: how is the sensory input from somebody else’s action transformed into a matching motor output by the imitator? For the ideomotor framewor ...
Nervous System Worksheets
... how the body is organized from cells to tissue… organs to systems. We went into more detail about the organs in each of the different body systems. ...
... how the body is organized from cells to tissue… organs to systems. We went into more detail about the organs in each of the different body systems. ...
Transformation from temporal to rate coding in a somatosensory
... process. The latency of the response onset increased during the 8-Hz train until it stabilized at a signi®cantly longer steady-state value (Fig. 1, POm raster display and PSTHs). These latency shifts resulted in decreased spike counts in the POm neurons because offset latencies did not change. In th ...
... process. The latency of the response onset increased during the 8-Hz train until it stabilized at a signi®cantly longer steady-state value (Fig. 1, POm raster display and PSTHs). These latency shifts resulted in decreased spike counts in the POm neurons because offset latencies did not change. In th ...
Physiology and Ecology Review
... • When presented with unrealistic models – As long as some red is present, the attack behavior occurs ...
... • When presented with unrealistic models – As long as some red is present, the attack behavior occurs ...
brainstem
... Nucleus gracilis and nucleus cuneatus pass somatic sensory information to the thalamus Olivary nuclei relay info from the spinal cord, cerebral cortex, and the brainstem to the cerebellar cortex. ...
... Nucleus gracilis and nucleus cuneatus pass somatic sensory information to the thalamus Olivary nuclei relay info from the spinal cord, cerebral cortex, and the brainstem to the cerebellar cortex. ...
Fatigue and Inhibition
... Mechanisms of Learning and Development In Chapter 2 we saw that learning takes a number of forms. Some learning seems simple and easily explained by direct S-R (stimulusresponse) connections, but other kinds are more puzzling. However, it turns out that even the simpler learned responses in mammals ...
... Mechanisms of Learning and Development In Chapter 2 we saw that learning takes a number of forms. Some learning seems simple and easily explained by direct S-R (stimulusresponse) connections, but other kinds are more puzzling. However, it turns out that even the simpler learned responses in mammals ...
An ancestral axial twist explains the contralateral forebrain and the
... contralaterally organised, in the forebrain. Furthermore, to my knowledge no existing theory explains why olfaction should be the only ipsilateral sense in the forebrain. The current work proposes a very different explanation, which neither leads to better visual processing nor to better motor contr ...
... contralaterally organised, in the forebrain. Furthermore, to my knowledge no existing theory explains why olfaction should be the only ipsilateral sense in the forebrain. The current work proposes a very different explanation, which neither leads to better visual processing nor to better motor contr ...
Test.
... electronic devices do not like water”. • Implants in animals can function for at least one year. The electronics can be encased in inert polymers. • Long term stability is unclear. Implants held in place by cellular contacts, microtacks. ...
... electronic devices do not like water”. • Implants in animals can function for at least one year. The electronics can be encased in inert polymers. • Long term stability is unclear. Implants held in place by cellular contacts, microtacks. ...
Top-Down Versus Bottom-Up Control of Attention in the Prefrontal
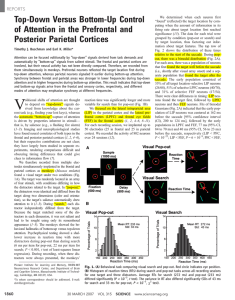
... but their respective contributions are not clear; they have largely been studied in separate experiments, rendering comparisons difficult and obscuring timing differences that could give clues to information flow (7). We therefore recorded from multiple electrodes simultaneously implanted in the fro ...
... but their respective contributions are not clear; they have largely been studied in separate experiments, rendering comparisons difficult and obscuring timing differences that could give clues to information flow (7). We therefore recorded from multiple electrodes simultaneously implanted in the fro ...
Top-Down Versus Bottom-Up Control
... but their respective contributions are not clear; they have largely been studied in separate experiments, rendering comparisons difficult and obscuring timing differences that could give clues to information flow (7). We therefore recorded from multiple electrodes simultaneously implanted in the fro ...
... but their respective contributions are not clear; they have largely been studied in separate experiments, rendering comparisons difficult and obscuring timing differences that could give clues to information flow (7). We therefore recorded from multiple electrodes simultaneously implanted in the fro ...