File
... rule the country CIVIC: Relating to citizenship or your role within government PATRONS: people who pay artists to produce artwork ...
... rule the country CIVIC: Relating to citizenship or your role within government PATRONS: people who pay artists to produce artwork ...
Art and Artist of the Renaissance Worksheet Work Artist/Author
... behave like and what they should strive to be, classically educated and have skills for the military. Written in 1353, it is a collection of novellas (stories) that demonstrate life in the times and portrays many of the Renaissance attitudes. ...
... behave like and what they should strive to be, classically educated and have skills for the military. Written in 1353, it is a collection of novellas (stories) that demonstrate life in the times and portrays many of the Renaissance attitudes. ...
RENAISSANCEbrief
... • Fervent Christian beliefs did provided protection from it. • This led people to think more about life rather than the afterlife. During the Middle (Dark) Ages the people of Europe believed their time on earth was to prove there worth for entering heaven. Their emphasis was more on the hereafter th ...
... • Fervent Christian beliefs did provided protection from it. • This led people to think more about life rather than the afterlife. During the Middle (Dark) Ages the people of Europe believed their time on earth was to prove there worth for entering heaven. Their emphasis was more on the hereafter th ...
Hansen
... the clock? How did Europeans improve on the basic Chinese form of printing? How did the role of women (noble and commoner) change? Did they ‘have a Renaissance’? Does it seem as if homosexuality was common or rare? What was the basic situation of blacks in Europe (both before and after the 15c when ...
... the clock? How did Europeans improve on the basic Chinese form of printing? How did the role of women (noble and commoner) change? Did they ‘have a Renaissance’? Does it seem as if homosexuality was common or rare? What was the basic situation of blacks in Europe (both before and after the 15c when ...
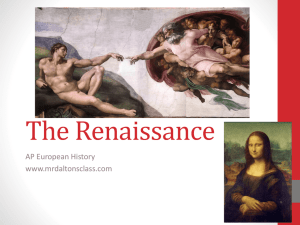
The Renaissance - Mr. Dalton`s Class
... • She set an example for women to break away from their traditional roles as ornaments to their husbands. ...
... • She set an example for women to break away from their traditional roles as ornaments to their husbands. ...
Sejarah Senibina Barat
... From World Book © 2001 World Book, Inc., 233 N. Michigan Avenue, Suite 2000, Chicago, IL 60601. All rights reserved. © Loyola University Chicago: R. V. Schoder, SJ, photographer ...
... From World Book © 2001 World Book, Inc., 233 N. Michigan Avenue, Suite 2000, Chicago, IL 60601. All rights reserved. © Loyola University Chicago: R. V. Schoder, SJ, photographer ...
Types of Paragraphs
... will smile knowing that the next five to eight minutes of my life will be filled with joy and happiness. During the Church-dominated Middle Ages, artistic expression took a huge step backwards and was finally saved with the rebirth of Classical ideas during the Renaissance. From the fall of the Roma ...
... will smile knowing that the next five to eight minutes of my life will be filled with joy and happiness. During the Church-dominated Middle Ages, artistic expression took a huge step backwards and was finally saved with the rebirth of Classical ideas during the Renaissance. From the fall of the Roma ...
Recovery and Rebirth: The Age of the Renaissance
... He turned his attention to political thought He wrote The Prince ▪ Based on his concerns for Italy’s political problems and his knowledge of ancient Rome ▪ All about “the acquisition and expansion of political power as a means to restore and maintain order in his ...
... He turned his attention to political thought He wrote The Prince ▪ Based on his concerns for Italy’s political problems and his knowledge of ancient Rome ▪ All about “the acquisition and expansion of political power as a means to restore and maintain order in his ...
The Northern and Late Renaissance
... Portrait of a Merchant, c. 1530 oil on panel (25 x 18 3/4 in.) ...
... Portrait of a Merchant, c. 1530 oil on panel (25 x 18 3/4 in.) ...
Recovery and Rebirth: The Age of the Renaissance
... He turned his attention to political thought He wrote The Prince ▪ Based on his concerns for Italy’s political problems and his knowledge of ancient Rome ▪ All about “the acquisition and expansion of political power as a means to restore and maintain order in his ...
... He turned his attention to political thought He wrote The Prince ▪ Based on his concerns for Italy’s political problems and his knowledge of ancient Rome ▪ All about “the acquisition and expansion of political power as a means to restore and maintain order in his ...
Name: Date: ______ Period: ____ Chapter 27: The Renaissance
... and other artifacts that could help them learn about the classical world. One of the first humanists was an Italian poet named Francesco Petrarch. Petrarch especially loved old books. He searched for them all over Europe and encouraged his friends to bring him any they found. Eventually, he created ...
... and other artifacts that could help them learn about the classical world. One of the first humanists was an Italian poet named Francesco Petrarch. Petrarch especially loved old books. He searched for them all over Europe and encouraged his friends to bring him any they found. Eventually, he created ...
The Renaissance, Reformation, and Exploration
... What were the chief features of the Renaissance? How would you describe the political world that existed in the Italian states and what role did women play? What were the chief characteristics of Italian Renaissance humanism and how did it differ from Northern Italian humanism? What were the chief a ...
... What were the chief features of the Renaissance? How would you describe the political world that existed in the Italian states and what role did women play? What were the chief characteristics of Italian Renaissance humanism and how did it differ from Northern Italian humanism? What were the chief a ...
Chapter 14 Section 1 notes
... Medieval monks/nuns & scholars copied manuscripts • Latin – survived as language of the Catholic Church and of educated people ...
... Medieval monks/nuns & scholars copied manuscripts • Latin – survived as language of the Catholic Church and of educated people ...
File
... Chanson • Some had more simpler expression of love • L’autre d’antan (The other year) by Johannes Ockeghem (1410-1497) • 16th century chanson set in 4 voices in homophonic or choral style ...
... Chanson • Some had more simpler expression of love • L’autre d’antan (The other year) by Johannes Ockeghem (1410-1497) • 16th century chanson set in 4 voices in homophonic or choral style ...
The Renaissance
... “A man forgets more easily the death of his father than the loss of money” “Men are ungrateful, changeable pretenders, runaways in danger, eager for ...
... “A man forgets more easily the death of his father than the loss of money” “Men are ungrateful, changeable pretenders, runaways in danger, eager for ...
Leonardo Da Vinci RENAISSANCE MAN
... Da Vinci was born in Florence, Italy in 1452. From a young age people knew he was a very talented drawer and painter. When he was 14 he went to live with a master sculpter and painter to focus on art. ...
... Da Vinci was born in Florence, Italy in 1452. From a young age people knew he was a very talented drawer and painter. When he was 14 he went to live with a master sculpter and painter to focus on art. ...
Lecture 1 – Middle Ages to Rococo
... The architecture of the Romanesque, or Norman, period is signified by solidity and stability. The general shapes of earliest roman basilicas were largely kept in the Romanesque church, however som ...
... The architecture of the Romanesque, or Norman, period is signified by solidity and stability. The general shapes of earliest roman basilicas were largely kept in the Romanesque church, however som ...
Chapter 13 The High Renaissance in Italy
... Human quality of the divine Quite a departure from medieval representations of Jesus ...
... Human quality of the divine Quite a departure from medieval representations of Jesus ...
File - Mr. Challis-Jones` Social Studies Website
... The Italian Renaissance is best known for its cultural achievements credited to writers, poets, artists, sculptors, and “Renaissance Men” (or women!). Figures such as Petrarch (The “Father of Humanism”), Leonardo da Vinci (The ideal Renaissance Man known for the Mona Lisa, the Vitruvian Man, and man ...
... The Italian Renaissance is best known for its cultural achievements credited to writers, poets, artists, sculptors, and “Renaissance Men” (or women!). Figures such as Petrarch (The “Father of Humanism”), Leonardo da Vinci (The ideal Renaissance Man known for the Mona Lisa, the Vitruvian Man, and man ...
Italian Renaissance and the Northern Renaissance Differences
... The Italian Renaissance is best known for its cultural achievements credited to writers, poets, artists, sculptors, and “Renaissance Men” (or women!). Figures such as Petrarch (The “Father of Humanism”), Leonardo da Vinci (The ideal Renaissance Man known for the Mona Lisa, the Vitruvian Man, and man ...
... The Italian Renaissance is best known for its cultural achievements credited to writers, poets, artists, sculptors, and “Renaissance Men” (or women!). Figures such as Petrarch (The “Father of Humanism”), Leonardo da Vinci (The ideal Renaissance Man known for the Mona Lisa, the Vitruvian Man, and man ...
Reformation
... To explain the conditions in Italy that gave rise to the Renaissance. Thriving cities, wealthy merchants, Greco-Roman culture To identify the values and ideas prized during the Renaissance. Humanists, secular, patrons, ‘Renaissance Man’ To describe the artistic breakthrough and achievements of Renai ...
... To explain the conditions in Italy that gave rise to the Renaissance. Thriving cities, wealthy merchants, Greco-Roman culture To identify the values and ideas prized during the Renaissance. Humanists, secular, patrons, ‘Renaissance Man’ To describe the artistic breakthrough and achievements of Renai ...
Italy`s Advantages (pages 37-38)
... Renaissance: This rebirth spread north from Italy. It began there for three reasons. First, Italy had several important cities. Cities were places where people exchanged ideas. Second, these cities included a class of merchants and bankers who were becoming wealthy and powerful. This class strongly ...
... Renaissance: This rebirth spread north from Italy. It began there for three reasons. First, Italy had several important cities. Cities were places where people exchanged ideas. Second, these cities included a class of merchants and bankers who were becoming wealthy and powerful. This class strongly ...
Out of the doom and gloom of the Dark Ages…
... • Just as these merchants competed with one another in business, they also competed as patrons, or sponsors, of the ARTS. ...
... • Just as these merchants competed with one another in business, they also competed as patrons, or sponsors, of the ARTS. ...
The Renaissance: The Beginning Notes
... At first, Renaissance art was religious but with a twist. The Journey of the Magi, painting of wise men journey but it was commissioned by the Medici’s so, includes portraits of the family as if they were actually there. Eventually art focused on Greek and Roman mythology themes, individual portrait ...
... At first, Renaissance art was religious but with a twist. The Journey of the Magi, painting of wise men journey but it was commissioned by the Medici’s so, includes portraits of the family as if they were actually there. Eventually art focused on Greek and Roman mythology themes, individual portrait ...
Renaissance in Scotland

The Renaissance in Scotland was a cultural, intellectual and artistic movement in Scotland, from the late fifteenth century to the beginning of the seventeenth century. It is associated with the pan-European Renaissance that is usually regarded as beginning in Italy in the late fourteenth century and reaching northern Europe as a Northern Renaissance in the fifteenth century. It involved an attempt to revive the principles of the classical era, including humanism, a spirit of scholarly enquiry, scepticism, and concepts of balance and proportion. Since the twentieth century the uniqueness and unity of the Renaissance has been challenged by historians, but significant changes in Scotland can be seen to have taken place in education, intellectual life, literature, art, architecture, music and politics.The court was central to the patronage and dissemination of Renaissance works and ideas. It was also central to the staging of lavish display that portrayed the political and religious role of the monarchy. The Renaissance led to the adoption of ideas of imperial monarchy, encouraging the Scottish crown to join the new monarchies by asserting imperial jurisdiction and distinction. The growing emphasis on education in the Middle Ages became part of a humanist and then Protestant programme to extend and reform learning. It resulted in the expansion of the school system and the foundation of six university colleges by the end of the sixteenth century. Relatively large numbers of Scottish scholars studied on the continent or in England and some, such as Hector Boece, John Mair, Andrew Melville and George Buchanan, returned to Scotland to play a major part in developing Scottish intellectual life. Vernacular works in Scots began to emerge in the fifteenth century, while Latin remained a major literary language. With the patronage of James V and James VI, writers included William Stewart, John Bellenden, David Lyndsay, William Fowler and Alexander Montgomerie.In the sixteenth century, Scottish kings, particularly James V, built palaces in a Renaissance style, beginning at Linlithgow. The trend soon spread to members of the aristocracy. Painting was strongly influenced by Flemish art, with works commissioned from the continent and Flemings serving as court artists. While church art suffered iconoclasm and a loss of patronage as a result of the Reformation, house decoration and portraiture became significant for the wealthy, with George Jamesone emerging as the first major named artist in the early seventeenth century. Music also incorporated wider European influences although the Reformation caused a move from complex polyphonic church music to the simpler singing of metrical psalms. Combined with the Union of Crowns in 1603, the Reformation also removed the church and the court as sources of patronage, changing the direction of artistic creation and limiting its scope. In the early seventeenth century the major elements of the Renaissance began to give way to Stoicism, Mannerism and the Baroque.