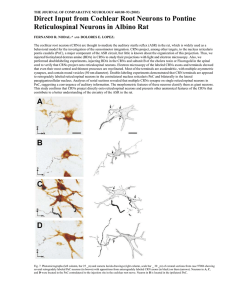
THE JOURNAL OF COMPARATIVE NEUROLOGY 460:80–93 (2003)
... cord to verify that CRNs project onto reticulospinal neurons. Electron microscopy of the labeled CRNs axons and terminals showed that even their most central and thinnest processes are myelinated. Most of the terminals are axodendritic, with multiple asymmetric synapses, and contain round vesicles ( ...
... cord to verify that CRNs project onto reticulospinal neurons. Electron microscopy of the labeled CRNs axons and terminals showed that even their most central and thinnest processes are myelinated. Most of the terminals are axodendritic, with multiple asymmetric synapses, and contain round vesicles ( ...
The Nanostructure of the Nervous System and the Impact
... up of many complex ascending and descending pathways to the brain (afferent and efferent pathways, respectively) with specific off shoots along its length (the dorsal and ventral roots) that innervate all the structures outside the CNS that are controlled by the brain. Most sensory and control infor ...
... up of many complex ascending and descending pathways to the brain (afferent and efferent pathways, respectively) with specific off shoots along its length (the dorsal and ventral roots) that innervate all the structures outside the CNS that are controlled by the brain. Most sensory and control infor ...
THE_NERVOUS_SYSTEM_(Part_I)
... from one cell to another Has cell body with cytoplasm Nucleus inside the cell body Dendrites – nerve cell process that carry impulse to cell body (may be one or many) ...
... from one cell to another Has cell body with cytoplasm Nucleus inside the cell body Dendrites – nerve cell process that carry impulse to cell body (may be one or many) ...
One difference between axons and dendrites is that
... One thing that differentiates neurons from other body cells is that only neurons A. contain mitochondria. B. have a nucleus in their cell body. C. have an outer membrane that acts as a filter. D. have axons and dendrites. One difference between axons and dendrites is that A. axons carry signals to t ...
... One thing that differentiates neurons from other body cells is that only neurons A. contain mitochondria. B. have a nucleus in their cell body. C. have an outer membrane that acts as a filter. D. have axons and dendrites. One difference between axons and dendrites is that A. axons carry signals to t ...
The Nervous System - Zen Shiatsu Chicago
... • Nervous system consists mostly of nervous tissue, which is highly cellular. • Less than 20% of the CNS is extracellular space which means that the cells are densely packed and tightly intertwined. • Nervous tissue is made up of just two principal types of cells o Neuroglia (glial cells) = supporti ...
... • Nervous system consists mostly of nervous tissue, which is highly cellular. • Less than 20% of the CNS is extracellular space which means that the cells are densely packed and tightly intertwined. • Nervous tissue is made up of just two principal types of cells o Neuroglia (glial cells) = supporti ...
The Neural Mechanisms of Learning
... Reorganisation of brain structure that occurs can be immediately or continue for years involving a number of different processes. (e.g. Neuronal level, larger areas of brain tissue, transfer of function to another ...
... Reorganisation of brain structure that occurs can be immediately or continue for years involving a number of different processes. (e.g. Neuronal level, larger areas of brain tissue, transfer of function to another ...
What is memory? How does the brain perceive the outside
... barrier Remove dead cells Transport of nutrients Destroy neurotransmitters in extra cellular space ...
... barrier Remove dead cells Transport of nutrients Destroy neurotransmitters in extra cellular space ...
This Week in The Journal - Journal of Neuroscience
... A1-42 is strongly tied to Alzheimer’s disease (AD), but the critical cellular events leading to loss of synapses and neurodegeneration remain uncertain. To understand how AD pathologydevelopsinamodelsystem,Zhaoetal. overexpressed A isoforms in flight-related motor and interneurons in Drosophila an ...
... A1-42 is strongly tied to Alzheimer’s disease (AD), but the critical cellular events leading to loss of synapses and neurodegeneration remain uncertain. To understand how AD pathologydevelopsinamodelsystem,Zhaoetal. overexpressed A isoforms in flight-related motor and interneurons in Drosophila an ...
10-21-09
... (Extinction eliminates this firing.) Next, they sought to relate the firing to performance. All-or-none burst firing, typical of the neuron population, predicted successful tone detection. This pattern is consistent in all neurons that show the bursting response. Next experiments involved ERPs in hu ...
... (Extinction eliminates this firing.) Next, they sought to relate the firing to performance. All-or-none burst firing, typical of the neuron population, predicted successful tone detection. This pattern is consistent in all neurons that show the bursting response. Next experiments involved ERPs in hu ...
Pathophysiology of Disease
... First described by C. Waddington (1940s) to describe the developmental program where genes determine individual phenotype and internal and external environmental cues are also taken into consideration “beyond or above genetics” Currently describes the study of mitotically and meiotically heritab ...
... First described by C. Waddington (1940s) to describe the developmental program where genes determine individual phenotype and internal and external environmental cues are also taken into consideration “beyond or above genetics” Currently describes the study of mitotically and meiotically heritab ...
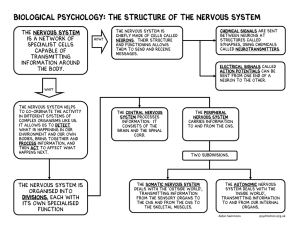
Biological Psychology: The structure of the nervous system
... capable of transmitting information around the body. ...
... capable of transmitting information around the body. ...
Nervous System • Steers, controls and watches over our bodily
... The afferent pathway consists of two neurons – one sends information from the periphery to the dorsal section of the spinal cord, the second neuron runs from here to the brain. The efferent pathway also consists of two neurons – one down the spinal cord to the required level of the spine, the secon ...
... The afferent pathway consists of two neurons – one sends information from the periphery to the dorsal section of the spinal cord, the second neuron runs from here to the brain. The efferent pathway also consists of two neurons – one down the spinal cord to the required level of the spine, the secon ...
Chapter 12: Neural Tissue
... Just like previous chapters – color code each part of the brain that we labeled Use this time to review as you color coordinate You have 12 minutes for this activity ...
... Just like previous chapters – color code each part of the brain that we labeled Use this time to review as you color coordinate You have 12 minutes for this activity ...
The Review
... 13. What is a split brain operation? Why would it be performed? Why is it that a split brain person can not describe what they are holding in their left hand? 14. What is and EEG, CAT, MRI, and PET? 15. What is the difference between a neurotransmitter and hormone? 16. Know your glands! ...
... 13. What is a split brain operation? Why would it be performed? Why is it that a split brain person can not describe what they are holding in their left hand? 14. What is and EEG, CAT, MRI, and PET? 15. What is the difference between a neurotransmitter and hormone? 16. Know your glands! ...
chapter42_part1wUnderline
... and release short-range signals that cause nearby cells to move about, either singly or as a cohesive group • By the process of embryonic induction, cells of one embryonic tissue alter the behavior of cells in an adjacent tissue • Example: Cells of a salamander gastrula’s dorsal lip induce adjacent ...
... and release short-range signals that cause nearby cells to move about, either singly or as a cohesive group • By the process of embryonic induction, cells of one embryonic tissue alter the behavior of cells in an adjacent tissue • Example: Cells of a salamander gastrula’s dorsal lip induce adjacent ...
Artificial Neural Networks
... mission of the Department of Defense. • Automated target recognition, localization, and tracking in the presence of ……………. is an important signal processing problem • Algorithms have been developed for …………………………… such as those that occur during active jamming, non-cooperative maneuvering & complex ...
... mission of the Department of Defense. • Automated target recognition, localization, and tracking in the presence of ……………. is an important signal processing problem • Algorithms have been developed for …………………………… such as those that occur during active jamming, non-cooperative maneuvering & complex ...
overview imagenet neural networks alexnet meta-network
... L E N ET, but was expanded in every dimension and used several stacked convolutional layers, as opposed to a single convolutional layer immediately followed by a POOL-layer, which as common at the time. AlexNet has led to many significant improvements in the field and as such is an interesting targe ...
... L E N ET, but was expanded in every dimension and used several stacked convolutional layers, as opposed to a single convolutional layer immediately followed by a POOL-layer, which as common at the time. AlexNet has led to many significant improvements in the field and as such is an interesting targe ...
{ How Neurosciences help us to understand some (psycho)therapeutic processes
... skin cells and others to become neurons. ...
... skin cells and others to become neurons. ...
Central nervous system
... pseudo-unipolar cells. As the cell develops, a single process splits into two, both of which function as axons—one going to skin or muscle and another to the spinal cord. ...
... pseudo-unipolar cells. As the cell develops, a single process splits into two, both of which function as axons—one going to skin or muscle and another to the spinal cord. ...
Motor Neuron - papbiobellaire
... 4. Neurofibrils - protein tubules which carry impulses throughout cell 5. Schwann cell - cell around axon - membrane (neurilemma) essential to regeneration of neuron 6. Myelin sheath - lipid layer around axon; an insulator and also increases rate of impulse conduction 7. Axis cylinder - composed of ...
... 4. Neurofibrils - protein tubules which carry impulses throughout cell 5. Schwann cell - cell around axon - membrane (neurilemma) essential to regeneration of neuron 6. Myelin sheath - lipid layer around axon; an insulator and also increases rate of impulse conduction 7. Axis cylinder - composed of ...
04 Early Development - Biology Courses Server
... It also implants into the uterine wall and initiates the development of the placenta. The focus of this section will be on the embryo. We will come back to the extraembryonic membranes and implantation in a later lecture. ...
... It also implants into the uterine wall and initiates the development of the placenta. The focus of this section will be on the embryo. We will come back to the extraembryonic membranes and implantation in a later lecture. ...
Nervous System
... terminal. All of these lie close to a dendrite or the cell body of another neuron. Pre-synaptic and Postsynaptic region. Between them is the Synaptic cleft. ...
... terminal. All of these lie close to a dendrite or the cell body of another neuron. Pre-synaptic and Postsynaptic region. Between them is the Synaptic cleft. ...