O rganization of the nervous system To go toward
... Anatomy of the Sympathetic Division Originates from T1 through L2 Ganglia are at the sympathetic trunk (near the spinal cord) Short pre-ganglionic neuron and long postganglionic neuron transmit impulse from CNS to the effector Norepinephrine and epinephrine are neurotransmitters to the effector orga ...
... Anatomy of the Sympathetic Division Originates from T1 through L2 Ganglia are at the sympathetic trunk (near the spinal cord) Short pre-ganglionic neuron and long postganglionic neuron transmit impulse from CNS to the effector Norepinephrine and epinephrine are neurotransmitters to the effector orga ...
Biopsychology Revision
... An action potential occurs when a neuron sends information down an axon, away from the cell body. The action potential is an explosion of electrical activity - this means that some event (a stimulus) causes the resting potential to move forward ...
... An action potential occurs when a neuron sends information down an axon, away from the cell body. The action potential is an explosion of electrical activity - this means that some event (a stimulus) causes the resting potential to move forward ...
Brain calculus: neural integration and persistent activity
... ment of the membrane potential or changes in firing rate induced with the intracellular injection of current. This supports the network hypothesis, because if the step changes were generated through mechanisms intrinsic to the cell recorded, such as through the activation of a persistent depolarizin ...
... ment of the membrane potential or changes in firing rate induced with the intracellular injection of current. This supports the network hypothesis, because if the step changes were generated through mechanisms intrinsic to the cell recorded, such as through the activation of a persistent depolarizin ...
3 Basic Nerve Cells
... The b rain consists of several large regions, each resp onsib le for sp ecific activities vital for living. (Figure b elow) The cerebral cortex, which is divided into right and left hemisp heres, encomp asses ab out two-thirds of the b rain mass and lies over and around most of the remaining structu ...
... The b rain consists of several large regions, each resp onsib le for sp ecific activities vital for living. (Figure b elow) The cerebral cortex, which is divided into right and left hemisp heres, encomp asses ab out two-thirds of the b rain mass and lies over and around most of the remaining structu ...
dendritic integration
... approach is that it is not manageable to use such computationally expensive neuronal models in large-scale networks. Another strategy is to develop abstractions of neurons that capture the essential processing power of the real thing. A paper by Polsky and colleagues1 in this issue represents a larg ...
... approach is that it is not manageable to use such computationally expensive neuronal models in large-scale networks. Another strategy is to develop abstractions of neurons that capture the essential processing power of the real thing. A paper by Polsky and colleagues1 in this issue represents a larg ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... nerves that your go from spinal the cord called central spinal nervous nerves. to system Spinal your nerves are skeletal made up of muscles. bundles of The sensory autonomic and motor system neurons controls bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious R ...
... nerves that your go from spinal the cord called central spinal nervous nerves. to system Spinal your nerves are skeletal made up of muscles. bundles of The sensory autonomic and motor system neurons controls bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious R ...
Major Divisions in the Central Nervous System
... 7. axis cylinder – composed of neurofibrils – carry impulse throughout neuron 8. nodes of ranvier – gaps between successive schwann cells 9. motor end plate – (axon terminals) site where neurotransmitters are stored and released through the synapse to an effector 10. axon – carry impulses away from ...
... 7. axis cylinder – composed of neurofibrils – carry impulse throughout neuron 8. nodes of ranvier – gaps between successive schwann cells 9. motor end plate – (axon terminals) site where neurotransmitters are stored and released through the synapse to an effector 10. axon – carry impulses away from ...
آلفا با دامنهي زياد
... only if the activity of the underlying neurons adds up. To add up the activity must be generated by parallel neurons. The neocortex is composed of pyramidal cells aligned in parallel. ...
... only if the activity of the underlying neurons adds up. To add up the activity must be generated by parallel neurons. The neocortex is composed of pyramidal cells aligned in parallel. ...
glossary - HBO.com
... that carry oxygen, glucose (the brain’s principal source of energy), nutrients, and hormones like insulin to brain cells so they can do their work, and remove carbon dioxide and cell waste products. ...
... that carry oxygen, glucose (the brain’s principal source of energy), nutrients, and hormones like insulin to brain cells so they can do their work, and remove carbon dioxide and cell waste products. ...
2. Nervous system 1 - Meninges: Dura mater, subdural space
... mesoderm, lateral mesoderm, paraxial mesoderm and most anteriorly is notochord. Cells that form notochord has passed through primitive node. Primitive groove now disappear after it instructed all cells and formed notochord. Ectoderm gives rise to epidermis and nervous system. Notochord induces ectod ...
... mesoderm, lateral mesoderm, paraxial mesoderm and most anteriorly is notochord. Cells that form notochord has passed through primitive node. Primitive groove now disappear after it instructed all cells and formed notochord. Ectoderm gives rise to epidermis and nervous system. Notochord induces ectod ...
Newswire Newswire - Rockefeller University
... Broad Institute, the annual award is given for work in any field of neuroscience. The prize is endowed through a gift from Merck and includes a $125,000 grant. Bargmann studies the relationships between genes, experience, the nervous system, and behavior in Caenorhabditis elegans, a tiny roundworm w ...
... Broad Institute, the annual award is given for work in any field of neuroscience. The prize is endowed through a gift from Merck and includes a $125,000 grant. Bargmann studies the relationships between genes, experience, the nervous system, and behavior in Caenorhabditis elegans, a tiny roundworm w ...
The Brain
... o After 5 months: Apoptosis- suicide signal for progenitor cells (tells cells to stop) o Ventricles produce 2X more neurons than necessary and unused neurons progressively die by apoptosis • There is neurogenesis in the adult brain (you can produce new neurons) o In rats: hippocampus (learning a ...
... o After 5 months: Apoptosis- suicide signal for progenitor cells (tells cells to stop) o Ventricles produce 2X more neurons than necessary and unused neurons progressively die by apoptosis • There is neurogenesis in the adult brain (you can produce new neurons) o In rats: hippocampus (learning a ...
Mechanisms of Perception: Hearing, Touch, Smell, Taste & Attention
... Medial temporal cortex next to the amygdala ...
... Medial temporal cortex next to the amygdala ...
Neuromuscular Adaptations During the Acquisition of Muscle
... • ?? Increased oscillation in the surface EMG which would theoretically approach towards the area of maximal evoked M waves (mass action potential), indicating that all MU’s are now fully synchronized (Bigland-Ritchie, 1981)??????? • Short-term training-induced shifts in forcevelocity relationship m ...
... • ?? Increased oscillation in the surface EMG which would theoretically approach towards the area of maximal evoked M waves (mass action potential), indicating that all MU’s are now fully synchronized (Bigland-Ritchie, 1981)??????? • Short-term training-induced shifts in forcevelocity relationship m ...
Neurological Control of Movement
... Sensory Motor Integration: is the communication of the sensory and motor nerve pathways. [3.1] Reflex: when sensory impulses terminate at the spinal cord and are integrated there. Motor Control: controlled by impulses conducted by motor (efferent) neurons from the brain. Muscle Spindles: create refl ...
... Sensory Motor Integration: is the communication of the sensory and motor nerve pathways. [3.1] Reflex: when sensory impulses terminate at the spinal cord and are integrated there. Motor Control: controlled by impulses conducted by motor (efferent) neurons from the brain. Muscle Spindles: create refl ...
Chapter 5: The First Two Years
... Early Brain Development: Basic Brain Structures • Neurons need to communicate with one another in order to function • They are connected by an intricate network of nerve fibers – Axon—is a nerve fiber that extends from the neuron and transmits electrical impulses from that neurons to the dendrites ...
... Early Brain Development: Basic Brain Structures • Neurons need to communicate with one another in order to function • They are connected by an intricate network of nerve fibers – Axon—is a nerve fiber that extends from the neuron and transmits electrical impulses from that neurons to the dendrites ...
Key Elements of Sensation
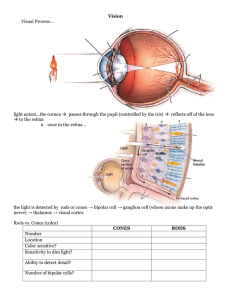
... Rods are very sensitive under ______________________ conditions but do not provide as much acuity or detail and ________________ perceive color. When you notice an object in your peripheral vision, the object will appear as a shape lacking detail because only rods along the outer edge of the ret ...
... Rods are very sensitive under ______________________ conditions but do not provide as much acuity or detail and ________________ perceive color. When you notice an object in your peripheral vision, the object will appear as a shape lacking detail because only rods along the outer edge of the ret ...
Vision Lecture Notes
... o feature detectors – neurons in the visual cortex that respond to specific features…edges, lines, angles and movements ...
... o feature detectors – neurons in the visual cortex that respond to specific features…edges, lines, angles and movements ...
Brain Presentation1
... •GHB can reduce dopamine activity, especially in the basal ganglia. This action is probably the result of the inhibition of the release of dopamine from synaptic terminals. Some studies show that GHB first inhibits the release of dopamine, then causes the release of dopamine. The effect on the dopam ...
... •GHB can reduce dopamine activity, especially in the basal ganglia. This action is probably the result of the inhibition of the release of dopamine from synaptic terminals. Some studies show that GHB first inhibits the release of dopamine, then causes the release of dopamine. The effect on the dopam ...
reading guide
... There is one neurotransmitter we want you to memorize. It is the most common neurotransmitter in both vertebrates and invertebrates, and it is released by the neurons that synapse with muscle cells at the neuromuscular junction. If you look ahead to Chapter 50, Figure 50.29, you will see a synapse b ...
... There is one neurotransmitter we want you to memorize. It is the most common neurotransmitter in both vertebrates and invertebrates, and it is released by the neurons that synapse with muscle cells at the neuromuscular junction. If you look ahead to Chapter 50, Figure 50.29, you will see a synapse b ...