The final determination of Xenopus ectoderm depends on intrinsic
... which cells of a single animal cap will contribute to epidermis, notochord, somites, mesenchyme, etc, So it is of interest whether dorsal or ventral ectodermal cells will participate in a random way in the formation of the terminal differentiated structures within an animal cap, We addressed this qu ...
... which cells of a single animal cap will contribute to epidermis, notochord, somites, mesenchyme, etc, So it is of interest whether dorsal or ventral ectodermal cells will participate in a random way in the formation of the terminal differentiated structures within an animal cap, We addressed this qu ...
File
... stimulation of effectors 4. The impulse can be blocked by certain chemicals (drugs) – important in controlling pain and certain psychiatric disorders ...
... stimulation of effectors 4. The impulse can be blocked by certain chemicals (drugs) – important in controlling pain and certain psychiatric disorders ...
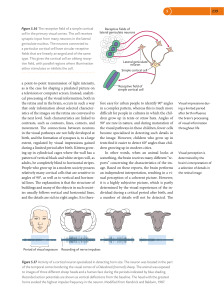
Area MST has been thought be involved in heading perception not
... single-cue conditions. In the Combined condition, psychophysical thresholds were significantly lower than in the single-cue conditions and very close to predictions of optimal cue integration theories. According to whether the visual and vestibular heading preferences were well matched or nearly opp ...
... single-cue conditions. In the Combined condition, psychophysical thresholds were significantly lower than in the single-cue conditions and very close to predictions of optimal cue integration theories. According to whether the visual and vestibular heading preferences were well matched or nearly opp ...
The Nervous System
... and much of the cytoplasm Dendrites branched extensions that spread out from the cell body receive impulses from other neurons and carry impulses to the cell body Axon the long fiber that carries impulses away from the cell body ends in a series of small swellings called axon terminals As an impul ...
... and much of the cytoplasm Dendrites branched extensions that spread out from the cell body receive impulses from other neurons and carry impulses to the cell body Axon the long fiber that carries impulses away from the cell body ends in a series of small swellings called axon terminals As an impul ...
Biological Bases Of Behaviour Central Nervous System
... The network of neurons connecting the CNS to our internal muscles and organs. Controls non-skeletal muscles such as the heart, kidneys, glands, etc. The majority of functions occur without our control, but we can gain control of some functions through biofeedback. This is a process whereby an indivi ...
... The network of neurons connecting the CNS to our internal muscles and organs. Controls non-skeletal muscles such as the heart, kidneys, glands, etc. The majority of functions occur without our control, but we can gain control of some functions through biofeedback. This is a process whereby an indivi ...
Final from 2003
... depleted cells in the neural plate, you examine the neural plate for differentiation of neurons. Focusing on regions that normally differentiate early, what would you predict would be the pattern of differentiation in the depleted and non-depleted cells? ...
... depleted cells in the neural plate, you examine the neural plate for differentiation of neurons. Focusing on regions that normally differentiate early, what would you predict would be the pattern of differentiation in the depleted and non-depleted cells? ...
neurology1ned2013 31.5 KB - d
... Potentials are classified based on the NTs associated with them. Mood altering drugs target acetylcholine, dopamine, serotonin (I), norepinephrine (I), epinephrine/adrenaline (E), and endorphins (happy) Habituation leads to problems with withdrawal. Behaviors are controlled by centrally regulated ne ...
... Potentials are classified based on the NTs associated with them. Mood altering drugs target acetylcholine, dopamine, serotonin (I), norepinephrine (I), epinephrine/adrenaline (E), and endorphins (happy) Habituation leads to problems with withdrawal. Behaviors are controlled by centrally regulated ne ...
Toxicology of the Nervous System
... Development of GABA and Glutamate Synapses in Primate Hippocampus •GABA synapses develop on contact •Glutamate synapses develop but require a developed spine to become active •GDPs dominate early developmental neuronal activity and disappear prior to birth (primates) or during early neonatal life ( ...
... Development of GABA and Glutamate Synapses in Primate Hippocampus •GABA synapses develop on contact •Glutamate synapses develop but require a developed spine to become active •GDPs dominate early developmental neuronal activity and disappear prior to birth (primates) or during early neonatal life ( ...
answers
... 7. How do efferent neurites from the ganglion cells in different regions of the retina manage to terminate in the appropriate regions of the optic tectum? In other words, briefly describe the principal molecules and cell behaviors,insofar as they are known, that involved in this pathfinding and sel ...
... 7. How do efferent neurites from the ganglion cells in different regions of the retina manage to terminate in the appropriate regions of the optic tectum? In other words, briefly describe the principal molecules and cell behaviors,insofar as they are known, that involved in this pathfinding and sel ...
Control of Motor Movement
... Receptor – detects stimulus Sensory neuron – relays info to CNS Integration – may be monosynaptic or polysynaptic Motor neuron – carries response away form CNS to effector Effector – muscle or gland ...
... Receptor – detects stimulus Sensory neuron – relays info to CNS Integration – may be monosynaptic or polysynaptic Motor neuron – carries response away form CNS to effector Effector – muscle or gland ...
Lecture Test 2 2010
... B. A nerve fiber is not a long axon, but instead it is the same thing as a nerve. C. A neuron and a nerve are the same thing. D. A neuron is the same as an axon and a nerve fiber. E. Nerves occur in the white matter of the central nervous system. D 23. What is NOT a function of astrocytes? A. nouris ...
... B. A nerve fiber is not a long axon, but instead it is the same thing as a nerve. C. A neuron and a nerve are the same thing. D. A neuron is the same as an axon and a nerve fiber. E. Nerves occur in the white matter of the central nervous system. D 23. What is NOT a function of astrocytes? A. nouris ...
ANATOMY OF A NEURON
... molecules will be removed from the receptor sites in one of the three ways: •Some neurotransmitters will be destroyed by the enzymes in the synaptic cleft. • Some neurotransmitters will be broken down into its component molecules which will be reclaimed by the axon terminal. •Some neurotransmitters ...
... molecules will be removed from the receptor sites in one of the three ways: •Some neurotransmitters will be destroyed by the enzymes in the synaptic cleft. • Some neurotransmitters will be broken down into its component molecules which will be reclaimed by the axon terminal. •Some neurotransmitters ...
Artificial Neural Networks
... asection through an animal retina, one of the first ever visualisations of a neural network produced by Golgi and Cajal who received a Nobel Prize in 1906. You can see roundish neurons with their output axons. Some leave the area (those at the bottom which form the ‘optic nerve’) and other axons inp ...
... asection through an animal retina, one of the first ever visualisations of a neural network produced by Golgi and Cajal who received a Nobel Prize in 1906. You can see roundish neurons with their output axons. Some leave the area (those at the bottom which form the ‘optic nerve’) and other axons inp ...
Brain_stemCh45
... A5/A7 are located in the pons and mainly projects to the brain stem and spinal cord where they modulate autonomic reflexes and pain C1 neurons projects to hypothalamus where they modulate cardiovascular and endocrine functions C1 neurons also projects to the spinal cord where they provide tonic exci ...
... A5/A7 are located in the pons and mainly projects to the brain stem and spinal cord where they modulate autonomic reflexes and pain C1 neurons projects to hypothalamus where they modulate cardiovascular and endocrine functions C1 neurons also projects to the spinal cord where they provide tonic exci ...
Chapter 17: Nervous System - Johnston Community College
... Alcohol may affect the inhibiting transmitter GABA or glutamate, an excitatory neurotransmitter. Alcohol is primarily metabolized in liver and heavy doses can cause liver scar tissue and cirrhosis. Alcohol is an energy source but it lacks nutrients needed for health. Cirrhosis of the liver and fetal ...
... Alcohol may affect the inhibiting transmitter GABA or glutamate, an excitatory neurotransmitter. Alcohol is primarily metabolized in liver and heavy doses can cause liver scar tissue and cirrhosis. Alcohol is an energy source but it lacks nutrients needed for health. Cirrhosis of the liver and fetal ...
Biology 11 - Human Anatomy
... C. Formation of the 3 _________ Layers begins during the 3rd week 1. An _______________ cavity forms between the inner cell mass & trophoblast 2. The inner cell mass flattens into an ______________________ and forms 3 germ layers: ...
... C. Formation of the 3 _________ Layers begins during the 3rd week 1. An _______________ cavity forms between the inner cell mass & trophoblast 2. The inner cell mass flattens into an ______________________ and forms 3 germ layers: ...
The building of the brain
... Development of the central nervous system The central nervous system consists of the brain and the spinal cord. The spinal cord matures first, followed by the lower brain, or brainstem, and, finally, by the thinking part of the brain known as the cerebral cortex. The nervous system begins to develop ...
... Development of the central nervous system The central nervous system consists of the brain and the spinal cord. The spinal cord matures first, followed by the lower brain, or brainstem, and, finally, by the thinking part of the brain known as the cerebral cortex. The nervous system begins to develop ...
Neurons and Functional Neuroanatomy
... The action potential moves down the length of the axon in one direction The action potential moves in one direction because the membrane is refractory (unable to respond) once the action potential has been initiated at any particular place on the membrane ...
... The action potential moves down the length of the axon in one direction The action potential moves in one direction because the membrane is refractory (unable to respond) once the action potential has been initiated at any particular place on the membrane ...