Chapter 24 Electric Potential
... 24-12 Potential of a Charged Isolated Conductor m2-042 Which of the following statements are CORRECT: (1) The electric flux through a Gaussian surface depends on the shape of the surface. (2) The electric flux through a closed surface depends on the net charge enclosed by the surface. (3) The elect ...
... 24-12 Potential of a Charged Isolated Conductor m2-042 Which of the following statements are CORRECT: (1) The electric flux through a Gaussian surface depends on the shape of the surface. (2) The electric flux through a closed surface depends on the net charge enclosed by the surface. (3) The elect ...
Membrane
... form of ATP • Active transport is performed by specific proteins embedded in the membranes ...
... form of ATP • Active transport is performed by specific proteins embedded in the membranes ...
Chapter 15a
... By summing the initial concentrations and change in concentrations, we have the algebraic amount of each species in solution at equilibrium: ...
... By summing the initial concentrations and change in concentrations, we have the algebraic amount of each species in solution at equilibrium: ...
Cell Membrane and Sub Cellular Components
... acids, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, proteins, and ions) from diffusing across the membrane, but generally allows for the passive diffusion of hydrophobic molecules. This affords the cell the ability to control the movement of these substances via transmembrane protein complexes such as pores, chann ...
... acids, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, proteins, and ions) from diffusing across the membrane, but generally allows for the passive diffusion of hydrophobic molecules. This affords the cell the ability to control the movement of these substances via transmembrane protein complexes such as pores, chann ...
Slide 1
... Membrane permeability to Na+ and K+ determines transmembrane potential They are either passive or active Passive channels (also called leak channels): – are always open – permeability changes with conditions ...
... Membrane permeability to Na+ and K+ determines transmembrane potential They are either passive or active Passive channels (also called leak channels): – are always open – permeability changes with conditions ...
Malpighian tubules and formation of uric acid
... Other small molecules (small enough to cross the basement membrane) will also move into the tubule through this pathway. The transport of a substance which depends directly on ATP, such as the pumping of the protons in the Malpighian tubule, is called active transport. The transport of the other ion ...
... Other small molecules (small enough to cross the basement membrane) will also move into the tubule through this pathway. The transport of a substance which depends directly on ATP, such as the pumping of the protons in the Malpighian tubule, is called active transport. The transport of the other ion ...
31.1 The Neuron - science-b
... Na pumped out K pumped in More k inside than out so net movement of K out of cell So inside cell becomes negative compared to outside This is called a RESTING POTENTIAL When stimulated Na channels open Na rushes in causing a POLARIZATION of the inside of the cell (BECOMES POSTIVE) Reversal of charge ...
... Na pumped out K pumped in More k inside than out so net movement of K out of cell So inside cell becomes negative compared to outside This is called a RESTING POTENTIAL When stimulated Na channels open Na rushes in causing a POLARIZATION of the inside of the cell (BECOMES POSTIVE) Reversal of charge ...
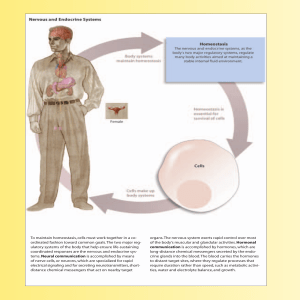
To maintain homeostasis, cells must work together in a co
... cell membrane; (3) a stimulus, such as sound waves stimulating specialized nerve cells in your ear; or (4) a spontaneous change of potential caused by inherent imbalances in the leak– pump cycle. (You will learn more about the nature of these various triggering events as our discussion of electrical ...
... cell membrane; (3) a stimulus, such as sound waves stimulating specialized nerve cells in your ear; or (4) a spontaneous change of potential caused by inherent imbalances in the leak– pump cycle. (You will learn more about the nature of these various triggering events as our discussion of electrical ...
effect of ion concentration changes in t
... membrane and Ca2+ transient in the cytosol, the simulations were repeated while [Ca2+ ] in the t-tubule lumen was held constant at the concentration in the external bulk space (dotted lines). The differences between the results indicate that the decrease of luminal [Ca2+ ] has an effect on Ca2+ fluxes ...
... membrane and Ca2+ transient in the cytosol, the simulations were repeated while [Ca2+ ] in the t-tubule lumen was held constant at the concentration in the external bulk space (dotted lines). The differences between the results indicate that the decrease of luminal [Ca2+ ] has an effect on Ca2+ fluxes ...
Six-Way Galvanic Cell
... by connecting the half-cells internally by means of a salt bridge, a porous barrier containing potassium nitrate or another electrolyte. Dissolved ions flow through the salt bridge to either electrode, thus completing the electrical circuit. The ability of a voltaic cell to produce an electric curre ...
... by connecting the half-cells internally by means of a salt bridge, a porous barrier containing potassium nitrate or another electrolyte. Dissolved ions flow through the salt bridge to either electrode, thus completing the electrical circuit. The ability of a voltaic cell to produce an electric curre ...
Concentration Fluctuations and Capacitive
... where ⟨(δQs) ⟩ and ⟨(δQi) ⟩ are due to the solvent and ions respectively, and ⟨δQsδQi⟩ are fluctuations induced by ion− solvent correlations. This decomposition is possible for a conductor where the electrode charges are linear functions of the partial charges of the electrolyte.26 Microscopically, t ...
... where ⟨(δQs) ⟩ and ⟨(δQi) ⟩ are due to the solvent and ions respectively, and ⟨δQsδQi⟩ are fluctuations induced by ion− solvent correlations. This decomposition is possible for a conductor where the electrode charges are linear functions of the partial charges of the electrolyte.26 Microscopically, t ...
Chapter 2: Communication Within the Nervous System
... precedes the chapter on the nervous system, because I believe that you can’t understand how the brain works unless you know how its neurons work. And I reversed the usual order of the vision and audition chapters, because I came to understand that audition provides a friendlier context for introduci ...
... precedes the chapter on the nervous system, because I believe that you can’t understand how the brain works unless you know how its neurons work. And I reversed the usual order of the vision and audition chapters, because I came to understand that audition provides a friendlier context for introduci ...
handout
... ligand gated ion channels (iGluRs) and metabotropic G-protein coupled receptors(mGluR). Activation of these receptors is responsible for basal excitatory synaptic transmission and many forms of synaptic plasticity such as long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD), which are thought ...
... ligand gated ion channels (iGluRs) and metabotropic G-protein coupled receptors(mGluR). Activation of these receptors is responsible for basal excitatory synaptic transmission and many forms of synaptic plasticity such as long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD), which are thought ...
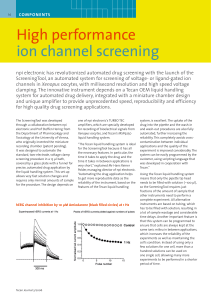
High performance ion channel screening
... npi’s TURBO TEC series of amplifiers, as Hans Reiner explained, “The npi amplifiers are based on a unique, sophisticated design that we developed years ago and their high speed of response makes them superior to similar systems. The amplifiers also have a very high degree of precision, so they are i ...
... npi’s TURBO TEC series of amplifiers, as Hans Reiner explained, “The npi amplifiers are based on a unique, sophisticated design that we developed years ago and their high speed of response makes them superior to similar systems. The amplifiers also have a very high degree of precision, so they are i ...
Interactive comment on “On the composition of ammonia
... Title: “On the composition of ammonia-sulfuric acid clusters during aerosol particle formation” This title is a bit misleading. The clusters that were observed in this study are ions and not electrically neutral clusters. Consider adding the word “ions” in the title to remove confusion. Line 15 pg 1 ...
... Title: “On the composition of ammonia-sulfuric acid clusters during aerosol particle formation” This title is a bit misleading. The clusters that were observed in this study are ions and not electrically neutral clusters. Consider adding the word “ions” in the title to remove confusion. Line 15 pg 1 ...
Nanostructured Li Ion Insertion Electrodes. 1
... impedance on frequency and/or position is determined by the transport properties in each phase, whereas ζ is an impedance length describing faradaic currents and polarization at the distributed interface. The model of eq 1 represented in the scheme of Figure 2a is formulated in terms of differential ...
... impedance on frequency and/or position is determined by the transport properties in each phase, whereas ζ is an impedance length describing faradaic currents and polarization at the distributed interface. The model of eq 1 represented in the scheme of Figure 2a is formulated in terms of differential ...
Membrane potential

Membrane potential (also transmembrane potential or membrane voltage) is the difference in electric potential between the interior and the exterior of a biological cell. With respect to the exterior of the cell, typical values of membrane potential range from –40 mV to –80 mV.All animal cells are surrounded by a membrane composed of a lipid bilayer with proteins embedded in it. The membrane serves as both an insulator and a diffusion barrier to the movement of ions. Ion transporter/pump proteins actively push ions across the membrane and establish concentration gradients across the membrane, and ion channels allow ions to move across the membrane down those concentration gradients. Ion pumps and ion channels are electrically equivalent to a set of batteries and resistors inserted in the membrane, and therefore create a voltage difference between the two sides of the membrane.Virtually all eukaryotic cells (including cells from animals, plants, and fungi) maintain a non-zero transmembrane potential, usually with a negative voltage in the cell interior as compared to the cell exterior ranging from –40 mV to –80 mV. The membrane potential has two basic functions. First, it allows a cell to function as a battery, providing power to operate a variety of ""molecular devices"" embedded in the membrane. Second, in electrically excitable cells such as neurons and muscle cells, it is used for transmitting signals between different parts of a cell. Signals are generated by opening or closing of ion channels at one point in the membrane, producing a local change in the membrane potential. This change in the electric field can be quickly affected by either adjacent or more distant ion channels in the membrane. Those ion channels can then open or close as a result of the potential change, reproducing the signal.In non-excitable cells, and in excitable cells in their baseline states, the membrane potential is held at a relatively stable value, called the resting potential. For neurons, typical values of the resting potential range from –70 to –80 millivolts; that is, the interior of a cell has a negative baseline voltage of a bit less than one-tenth of a volt. The opening and closing of ion channels can induce a departure from the resting potential. This is called a depolarization if the interior voltage becomes less negative (say from –70 mV to –60 mV), or a hyperpolarization if the interior voltage becomes more negative (say from –70 mV to –80 mV). In excitable cells, a sufficiently large depolarization can evoke an action potential, in which the membrane potential changes rapidly and significantly for a short time (on the order of 1 to 100 milliseconds), often reversing its polarity. Action potentials are generated by the activation of certain voltage-gated ion channels.In neurons, the factors that influence the membrane potential are diverse. They include numerous types of ion channels, some of which are chemically gated and some of which are voltage-gated. Because voltage-gated ion channels are controlled by the membrane potential, while the membrane potential itself is influenced by these same ion channels, feedback loops that allow for complex temporal dynamics arise, including oscillations and regenerative events such as action potentials.