Chapter Five: Populations and Communities
... introduced from Europe. By the 1950’s there were 600,000,000 rabbits. What conditions were favorable for this huge growth? ...
... introduced from Europe. By the 1950’s there were 600,000,000 rabbits. What conditions were favorable for this huge growth? ...
Outline
... Keystone species exert an important regulating effect on other species in a community. ...
... Keystone species exert an important regulating effect on other species in a community. ...
Organismal ecology - Pine Plains Central School District
... Concept 52.1: Earth’s climate varies by latitude and season and is changing rapidly • The long-term prevailing weather conditions in an area constitute its climate • Four major abiotic components of climate are temperature, precipitation, sunlight, and wind • Macroclimate consists of patterns on th ...
... Concept 52.1: Earth’s climate varies by latitude and season and is changing rapidly • The long-term prevailing weather conditions in an area constitute its climate • Four major abiotic components of climate are temperature, precipitation, sunlight, and wind • Macroclimate consists of patterns on th ...
Ecosystems and Evolution
... • Communities: various populations living together and interacting with each other • An example of a community is plants, fish, insects, amphibians and microorganisms that live in and around a pond. ...
... • Communities: various populations living together and interacting with each other • An example of a community is plants, fish, insects, amphibians and microorganisms that live in and around a pond. ...
Chapter 4 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions
... organisms attempt to use the same limited ecological resource in the same place at the same time. – Plant roots compete for resources such as water and nutrients in the soil. Animals compete for resources such as food, mates, and places to live and raise their young. – Competition can occur both bet ...
... organisms attempt to use the same limited ecological resource in the same place at the same time. – Plant roots compete for resources such as water and nutrients in the soil. Animals compete for resources such as food, mates, and places to live and raise their young. – Competition can occur both bet ...
Managing Post-Fire Habitat for Birds
... Moderate to high severity post-fire habitat is an important component of Sierra Nevada for sustaining biodiversity. Many bird species reach their greatest abundance in these habitats with most sensitive to management actions prescribed following fires, such as salvage logging and shrub abatement. 1. ...
... Moderate to high severity post-fire habitat is an important component of Sierra Nevada for sustaining biodiversity. Many bird species reach their greatest abundance in these habitats with most sensitive to management actions prescribed following fires, such as salvage logging and shrub abatement. 1. ...
Chapter 4 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions
... organisms attempt to use the same limited ecological resource in the same place at the same time. – Plant roots compete for resources such as water and nutrients in the soil. Animals compete for resources such as food, mates, and places to live and raise their young. – Competition can occur both bet ...
... organisms attempt to use the same limited ecological resource in the same place at the same time. – Plant roots compete for resources such as water and nutrients in the soil. Animals compete for resources such as food, mates, and places to live and raise their young. – Competition can occur both bet ...
Biodiversity on the land and in the sea: when it converges,
... its variable response, a flip of the systems to another trajectory or a phenomenon known as hysteresis by which the community “gives up” and transforms itself into another or several systems (SUDING & al., 2008). A regrettably renowned example of this threshold effect is the complete collapse in the ...
... its variable response, a flip of the systems to another trajectory or a phenomenon known as hysteresis by which the community “gives up” and transforms itself into another or several systems (SUDING & al., 2008). A regrettably renowned example of this threshold effect is the complete collapse in the ...
Look at different kinds of animal coverings under hand lenses
... animals and plants that live on each level. Choose an animal or plant from each level and explain how it is adapted to its particular place in the tropical rain forest. (Canopy examples: monkeys can use arms and legs and sometimes even tails to swing from branch to branch; birds such as parrots have ...
... animals and plants that live on each level. Choose an animal or plant from each level and explain how it is adapted to its particular place in the tropical rain forest. (Canopy examples: monkeys can use arms and legs and sometimes even tails to swing from branch to branch; birds such as parrots have ...
Intro3-3
... 4. If there are too many changes in conditions, a species may die out, or become ______________________. (consequence/extinct) 5. Most plant roots are found in the ______________________, or the uppermost layer of soil. (broken rock/topsoil) 6. A place where animals and plants live is called a/an __ ...
... 4. If there are too many changes in conditions, a species may die out, or become ______________________. (consequence/extinct) 5. Most plant roots are found in the ______________________, or the uppermost layer of soil. (broken rock/topsoil) 6. A place where animals and plants live is called a/an __ ...
Habitat and Niche
... A species’ niche must be specific to that species; no two species can fill the same niche. They can have very similar niches, which can overlap, but there must be distinct differences between any two niches. When plants and animals are introduced, either intentionally or by accident, into a new envi ...
... A species’ niche must be specific to that species; no two species can fill the same niche. They can have very similar niches, which can overlap, but there must be distinct differences between any two niches. When plants and animals are introduced, either intentionally or by accident, into a new envi ...
Ch548thed
... ◦ sea star feeds on mussels and other organisms, remove sea star and mussels take over the region and eliminate species diversity. ...
... ◦ sea star feeds on mussels and other organisms, remove sea star and mussels take over the region and eliminate species diversity. ...
Principles of Ecology
... all organisms require N to make amino acids which in turn are used to make proteins (in protein synthesis) ...
... all organisms require N to make amino acids which in turn are used to make proteins (in protein synthesis) ...
1 ENVS 250 - Exam 2 Lab Time (Circle One): Tuesday AM Tuesday
... a. interspecific competition b. predation c. parasitism d. mutualism e. commensalism 8. When populations of two different species interact over long periods of time, changes in the gene pool of one species can lead to changes in the gene pool of the other. This is called a. competition b. coevolutio ...
... a. interspecific competition b. predation c. parasitism d. mutualism e. commensalism 8. When populations of two different species interact over long periods of time, changes in the gene pool of one species can lead to changes in the gene pool of the other. This is called a. competition b. coevolutio ...
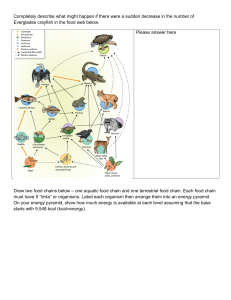
Completely describe what might happen if there were a sudden
... 2. The lowest level of environmental complexity that includes living and nonliving factors is the a. biome. b. community. c. ecosystem. d. biosphere. ...
... 2. The lowest level of environmental complexity that includes living and nonliving factors is the a. biome. b. community. c. ecosystem. d. biosphere. ...
Populations, Communities, and Species Interactions Environmental
... • Population-level phenomenon, not the individual. • * Over evolutionary time, not the lifespan of an individual. ...
... • Population-level phenomenon, not the individual. • * Over evolutionary time, not the lifespan of an individual. ...
Ecology Review Answers 87KB Jun 08 2015 10:41:25 AM
... bioaccumulation. This is not the end. The contaminated algae are consumed by zooplankton, and the mercury bioaccumulates in their tissues. In a process called biomagnification, the mercury becomes more and more concentrated in each link in the food chain as one animal eats many contaminated animals. ...
... bioaccumulation. This is not the end. The contaminated algae are consumed by zooplankton, and the mercury bioaccumulates in their tissues. In a process called biomagnification, the mercury becomes more and more concentrated in each link in the food chain as one animal eats many contaminated animals. ...
study guide for first semester final exam 2013
... along coast where mangrove trees protect shorelines from erosion; Salt marshes—where rivers deposit their nutrient rich mud, nursery to animals who live as adults in the ocean; rocky shorelines—provide areas for habitat for a diverse array of organisms; sandy shore—animals are adapted to high and lo ...
... along coast where mangrove trees protect shorelines from erosion; Salt marshes—where rivers deposit their nutrient rich mud, nursery to animals who live as adults in the ocean; rocky shorelines—provide areas for habitat for a diverse array of organisms; sandy shore—animals are adapted to high and lo ...
golden paintbrush - Draft
... Primary Habitat: The species occupies grass-dominated maritime meadows and openings with dry to moderately dry conditions and deep soils. Associated species include a range of fescue grasses, prairie lupine, wild strawberry and other drought tolerant native and introduced herbs and forbs that grow i ...
... Primary Habitat: The species occupies grass-dominated maritime meadows and openings with dry to moderately dry conditions and deep soils. Associated species include a range of fescue grasses, prairie lupine, wild strawberry and other drought tolerant native and introduced herbs and forbs that grow i ...
Animal and Plant Adaptations
... them to survive in a particular type of environment Adaptations may be such things as changes in shape, body organ functions, color and size FOR EXAMPLE ...
... them to survive in a particular type of environment Adaptations may be such things as changes in shape, body organ functions, color and size FOR EXAMPLE ...
An Introduction to Zonation
... water (as plankton!) they can only feed when underwater • Also, many marine organisms obtain oxygen from the water • Organisms living high in the intertidal zone have a limited time in which they can feed and acquire oxygen • Adaptations: - scaleless fish e.g. clingfish - feed whole time they are un ...
... water (as plankton!) they can only feed when underwater • Also, many marine organisms obtain oxygen from the water • Organisms living high in the intertidal zone have a limited time in which they can feed and acquire oxygen • Adaptations: - scaleless fish e.g. clingfish - feed whole time they are un ...
Vocabulary lists
... Adaptation – changes in an organism's physiological structure or function or habits that allow it to survive in new surroundings. For example, forests develop only where soil types, moisture and sunlight are balanced to the proper degree. Desert plants have made adjustments so as to be able to live ...
... Adaptation – changes in an organism's physiological structure or function or habits that allow it to survive in new surroundings. For example, forests develop only where soil types, moisture and sunlight are balanced to the proper degree. Desert plants have made adjustments so as to be able to live ...
B: Glossary of Terms
... are found on larger islands because the populations on smaller islands are more vulnerable to extinction. This theory can also be applied to terrestrial analogs such as forest patches in agricultural or suburban areas or nature reserves where it has become known as “insular ecology. ” Exotic species ...
... are found on larger islands because the populations on smaller islands are more vulnerable to extinction. This theory can also be applied to terrestrial analogs such as forest patches in agricultural or suburban areas or nature reserves where it has become known as “insular ecology. ” Exotic species ...
Habitat
A habitat is an ecological or environmental area that is inhabited by human, a particular species of animal, plant, or other type of organism.A place where a living thing lives is its habitat. It is a place where it can find food, shelter, protection and mates for reproduction. It is the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the physical environment that surrounds a species population.A habitat is made up of physical factors such as soil, moisture, range of temperature, and availability of light as well as biotic factors such as the availability of food and the presence of predators. A habitat is not necessarily a geographic area—for a parasitic organism it is the body of its host, part of the host's body such as the digestive tract, or a cell within the host's body.