Maintaining Balance
... cattle, sheep, and native wallabies for resources. Questions to Consider: 1. Why is one biotic community eventually replaced by another during succession? Successional forces result in this replacement: A new plant species immigrates into an area via seed dispersal. This new species competes with ex ...
... cattle, sheep, and native wallabies for resources. Questions to Consider: 1. Why is one biotic community eventually replaced by another during succession? Successional forces result in this replacement: A new plant species immigrates into an area via seed dispersal. This new species competes with ex ...
American Fisheries Society Annual Meeting, Seattle, Wa. September 2011
... genetic introgression, and degraded habitat, and now face further stress from climate warming. Their native habitat on the Kern Plateau meadows, primarily within the Golden Trout Wilderness (GTW), currently includes stream areas impacted by cattle grazing. As a result, some areas have reduced stream ...
... genetic introgression, and degraded habitat, and now face further stress from climate warming. Their native habitat on the Kern Plateau meadows, primarily within the Golden Trout Wilderness (GTW), currently includes stream areas impacted by cattle grazing. As a result, some areas have reduced stream ...
Chapter 9 Marine Ecology
... Monera are the bacteria and blue-green algae. Protista are single-celled organisms with a nucleus. Fungi are abundant in the intertidal zone and are important in decomposition. Metaphyta are the plants that grow attached to the sea floor. Metazoa include all multicellular animals in the ocean. ...
... Monera are the bacteria and blue-green algae. Protista are single-celled organisms with a nucleus. Fungi are abundant in the intertidal zone and are important in decomposition. Metaphyta are the plants that grow attached to the sea floor. Metazoa include all multicellular animals in the ocean. ...
LevelsandRelationshipsintheEcosystem
... It is essential for students to know the levels of organization within the environment. The organization in the natural environment from most simple to most complex includes the species (individual organisms), populations, communities, ecosystems, and biomes. Each level is defined by the type and nu ...
... It is essential for students to know the levels of organization within the environment. The organization in the natural environment from most simple to most complex includes the species (individual organisms), populations, communities, ecosystems, and biomes. Each level is defined by the type and nu ...
and plants - St. Olaf Pages
... Tight and coevolved mutualisms • leaf cutter ants and their fungus they farm Loose, facultative mutualisms • plants that have seed dispersal by vertebrates •plants that nurse other plants by making suitable conditions underneath them •you and your surface bacteria •kelp that provides home for inver ...
... Tight and coevolved mutualisms • leaf cutter ants and their fungus they farm Loose, facultative mutualisms • plants that have seed dispersal by vertebrates •plants that nurse other plants by making suitable conditions underneath them •you and your surface bacteria •kelp that provides home for inver ...
3rd Nine Weeks Exam
... Which of the following is a biotic factor in the prairie ecosystem? a. water b. sunlight c. soil d. grass The place where an organism lives and that provides the things the organism needs is called its Give an example of a population in a northern forest. The struggle between organisms to survive in ...
... Which of the following is a biotic factor in the prairie ecosystem? a. water b. sunlight c. soil d. grass The place where an organism lives and that provides the things the organism needs is called its Give an example of a population in a northern forest. The struggle between organisms to survive in ...
File
... A niche is the range of physical and biological conditions in which a species lives and the way the species obtains what it needs to survive and reproduce. A niche is defined by: Resources of the niche – any necessity for life such as water, food, or space. Physical aspects of the niche – abiotic fa ...
... A niche is the range of physical and biological conditions in which a species lives and the way the species obtains what it needs to survive and reproduce. A niche is defined by: Resources of the niche – any necessity for life such as water, food, or space. Physical aspects of the niche – abiotic fa ...
evolution, biological communities, & species
... • If edge is less distinct, animals move in & out of each habitat- open community ...
... • If edge is less distinct, animals move in & out of each habitat- open community ...
Biodiversity Overview 2
... The organisms in one species share many genes but each organism also has some genes that differ from those of other individuals. ...
... The organisms in one species share many genes but each organism also has some genes that differ from those of other individuals. ...
The Biosphere: Guided Notes
... All living organisms have a _________________ of temperature in which they best operate At or below _____________and above _______________ will destroy the enzymes of most organisms. WATER: Is essential for all life. Critical for most ______________________ chemical reactions Helps maintain ________ ...
... All living organisms have a _________________ of temperature in which they best operate At or below _____________and above _______________ will destroy the enzymes of most organisms. WATER: Is essential for all life. Critical for most ______________________ chemical reactions Helps maintain ________ ...
Questions For Scantron
... c. Living organisms modify their environment a little at a time. d. Parts of communities split off to form new communities. ...
... c. Living organisms modify their environment a little at a time. d. Parts of communities split off to form new communities. ...
Ch. 4 Answer Key - Lawndale High School
... forest.; B: This biome is dry and has a short cool summer. It must be a tundra. ...
... forest.; B: This biome is dry and has a short cool summer. It must be a tundra. ...
Energy Flow In Ecosystems - Floyd County School District
... Climate can limit dispersal. For example: Conditions at the top of the mountain are different than those at the bottom. Shrubs and cactus can not grow at the top in the freezing cold weather. ...
... Climate can limit dispersal. For example: Conditions at the top of the mountain are different than those at the bottom. Shrubs and cactus can not grow at the top in the freezing cold weather. ...
Life Science Study Guide Environment – Everything that surrounds
... Ecosystems – An ecosystem is a community of organisms interacting with each other and with the non-living environment. ...
... Ecosystems – An ecosystem is a community of organisms interacting with each other and with the non-living environment. ...
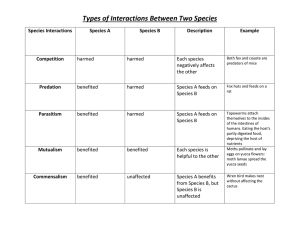
Species Competition
... Commensalism – benefits one species but doesn't harm or help the other Mutualism – both species benefit ...
... Commensalism – benefits one species but doesn't harm or help the other Mutualism – both species benefit ...
ecology web page
... Habitat – specific environment a Species lives in. Ex=fields, forest, Desert. ...
... Habitat – specific environment a Species lives in. Ex=fields, forest, Desert. ...
chapter 4 study guide environmental science
... 3. Name the six kingdoms of life, and give to characteristics of each. a. ____________________ ; ex 1: __________________________ ex 2: __________________________ b. ____________________ ; ex 1: __________________________ ex 2: __________________________ c. ____________________ ; ex 1: _____________ ...
... 3. Name the six kingdoms of life, and give to characteristics of each. a. ____________________ ; ex 1: __________________________ ex 2: __________________________ b. ____________________ ; ex 1: __________________________ ex 2: __________________________ c. ____________________ ; ex 1: _____________ ...
Intro PPT2016
... B. Usually natural disasters like severe storms, drought or other climatic conditions. ...
... B. Usually natural disasters like severe storms, drought or other climatic conditions. ...
SOL Study Book Fourth Grade Living Systems
... Organization of Communities The organization of communities is based on the utilization of the energy from the sun within a given ecosystem. The greatest amount of energy in a community is in the producers. Ecosystems include both living and nonliving things. The living part is called a community w ...
... Organization of Communities The organization of communities is based on the utilization of the energy from the sun within a given ecosystem. The greatest amount of energy in a community is in the producers. Ecosystems include both living and nonliving things. The living part is called a community w ...
history - River Partners
... sensitive species and enhance recreation on the site. The project has been identified as a priority because of the site’s proximity to the existing habitat and existing slow rate of native recruitment. HISTORY Half of the property to the north was involved in active row crop farming until 1993. Five ...
... sensitive species and enhance recreation on the site. The project has been identified as a priority because of the site’s proximity to the existing habitat and existing slow rate of native recruitment. HISTORY Half of the property to the north was involved in active row crop farming until 1993. Five ...
Habitat
A habitat is an ecological or environmental area that is inhabited by human, a particular species of animal, plant, or other type of organism.A place where a living thing lives is its habitat. It is a place where it can find food, shelter, protection and mates for reproduction. It is the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the physical environment that surrounds a species population.A habitat is made up of physical factors such as soil, moisture, range of temperature, and availability of light as well as biotic factors such as the availability of food and the presence of predators. A habitat is not necessarily a geographic area—for a parasitic organism it is the body of its host, part of the host's body such as the digestive tract, or a cell within the host's body.