Symbiotic Relationships
... – b/c of these interactions the ability to reproduce and or survive is influenced. • Natural selection takes place through interactions. • The most common interaction is competition. – For limited resources – Requires one species to have the ability to be more efficient than another when finding and ...
... – b/c of these interactions the ability to reproduce and or survive is influenced. • Natural selection takes place through interactions. • The most common interaction is competition. – For limited resources – Requires one species to have the ability to be more efficient than another when finding and ...
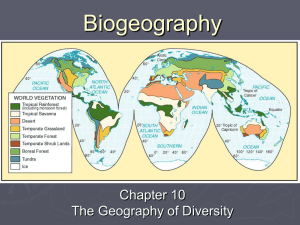
Chapter 10: The Geography of Diversity
... Bergmann’s Rule (1847) – Animals with larger body forms occur at high latitudes. Larger animals have a lower surface area to volume ration. Allen’s Rule (1877) – Endothermic vertebrates that live in warmer climates have longer appendages. Gloger’s Rule (1883) – Coloration of related forms is correla ...
... Bergmann’s Rule (1847) – Animals with larger body forms occur at high latitudes. Larger animals have a lower surface area to volume ration. Allen’s Rule (1877) – Endothermic vertebrates that live in warmer climates have longer appendages. Gloger’s Rule (1883) – Coloration of related forms is correla ...
Microbial Interactions
... • Negative impact of one organism on another based on release of a specific compound • Some examples – antibiotic production by fungi and bacteria – use of antibiotic-producing streptomycin by ants to control fungal parasites – bacteriocin production by bacteria – production of antibacterial peptide ...
... • Negative impact of one organism on another based on release of a specific compound • Some examples – antibiotic production by fungi and bacteria – use of antibiotic-producing streptomycin by ants to control fungal parasites – bacteriocin production by bacteria – production of antibacterial peptide ...
PowerPoint
... • Negative impact of one organism on another based on release of a specific compound • Some examples – antibiotic production by fungi and bacteria ...
... • Negative impact of one organism on another based on release of a specific compound • Some examples – antibiotic production by fungi and bacteria ...
woodland caribou - National Wildlife Federation
... segregate Endangered Species Act expenditures from other related expenditures. However, for most listed species, no other funding data is available. ...
... segregate Endangered Species Act expenditures from other related expenditures. However, for most listed species, no other funding data is available. ...
Ecosystems - Craigie High School
... a) Between two organisms that are attempting to use different resources that are in short supply b) Between two organisms that are attempting to use the same resource that is in short supply c) Between two organisms that are attempting to use the same resource that is in limitless supply 9. Which of ...
... a) Between two organisms that are attempting to use different resources that are in short supply b) Between two organisms that are attempting to use the same resource that is in short supply c) Between two organisms that are attempting to use the same resource that is in limitless supply 9. Which of ...
Change and the Environment Completed Notes
... each other for resources such as food, water, sunlight and living spaces ...
... each other for resources such as food, water, sunlight and living spaces ...
Pg. RTW: What topic do you need to review for the test?
... on our economy, our environment, or our health. Not all introduced species are invasive. Invasive plants and animals are the second greatest ...
... on our economy, our environment, or our health. Not all introduced species are invasive. Invasive plants and animals are the second greatest ...
Lecture 17, adaptive radiation + ecology
... Radiations often follow mass extinctions, when the dominant organisms are wiped out new ecological opportunities open up for the lucky survivors, who fill all the empty niches Mass extinction is when >60% of all living species are wiped out within 1 million years Results from extreme, sudden, temp ...
... Radiations often follow mass extinctions, when the dominant organisms are wiped out new ecological opportunities open up for the lucky survivors, who fill all the empty niches Mass extinction is when >60% of all living species are wiped out within 1 million years Results from extreme, sudden, temp ...
Ecology Introduction File
... parts of the environment (i.e. temperature, soil, light, moisture, air currents) ...
... parts of the environment (i.e. temperature, soil, light, moisture, air currents) ...
BIO100 KEY CONCEPTS-INTRODUCTION-
... Distribution of Living Organisms across the landscape is determined by a combination of (things are where they are because): ...
... Distribution of Living Organisms across the landscape is determined by a combination of (things are where they are because): ...
Control of Invasive Animals in Parks Victoria`s parks and reserves
... • Grazers: rabbits, deer, goats, horses • Omnivores: pigs • Freshwater: trout, European carp • Marine: North Pacific seastar, European shore crab, NZ screw shell, Mediterranean fanworm ...
... • Grazers: rabbits, deer, goats, horses • Omnivores: pigs • Freshwater: trout, European carp • Marine: North Pacific seastar, European shore crab, NZ screw shell, Mediterranean fanworm ...
Ecosystems and Communities
... O The first species to take hold in an area like this are called pioneer species, usually lichens O Decaying lichens, along with bits of sediment in cracks and crevices of rock, make up the first stage of soil development O New soil makes it possible for small weedy plants, small ferns, fungi, and i ...
... O The first species to take hold in an area like this are called pioneer species, usually lichens O Decaying lichens, along with bits of sediment in cracks and crevices of rock, make up the first stage of soil development O New soil makes it possible for small weedy plants, small ferns, fungi, and i ...
Population
... Those lacking natural defenses may die or grow sick Ex: 1900s – American chestnut trees infected by fungus ...
... Those lacking natural defenses may die or grow sick Ex: 1900s – American chestnut trees infected by fungus ...
Slide 1 - Amazon S3
... All of these nutrients cycle through the water system in a CLOSED SYSTEM…..meaning they get recycled and reused, not lost. ...
... All of these nutrients cycle through the water system in a CLOSED SYSTEM…..meaning they get recycled and reused, not lost. ...
Ecology Introduction – Part 1 Ecology – Is the study of the
... of the high heat and mixed with water vapor from the oceans to rise into the atmosphere. As it rises and continues to move toward the poles, it condenses and rains or snows below the polar circles. So we see lots of vegetation in this area. Because all the moisture is gone by the time the wind reach ...
... of the high heat and mixed with water vapor from the oceans to rise into the atmosphere. As it rises and continues to move toward the poles, it condenses and rains or snows below the polar circles. So we see lots of vegetation in this area. Because all the moisture is gone by the time the wind reach ...
Accumulation of pollutants in the Flemish Chinese mitten crab
... The Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis) is a successful invasive, marine species, mainly living in estuaries. This species might cause damage in the nearby future in Belgium and other invaded European and American countries, e.g. raising economic costs due to weakening of the dikes as a result ...
... The Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis) is a successful invasive, marine species, mainly living in estuaries. This species might cause damage in the nearby future in Belgium and other invaded European and American countries, e.g. raising economic costs due to weakening of the dikes as a result ...
File - J. Seguin Science
... Every species interacts with other species and with its environment in a unique way. ...
... Every species interacts with other species and with its environment in a unique way. ...
Populations And Communities
... • Definition: an ecological factor that causes the density of a population to decrease. EXAMPLE: If there is too much water in the ground, cactus roots rot and the cactus populations decreases. The limiting factor is the amount of water. ...
... • Definition: an ecological factor that causes the density of a population to decrease. EXAMPLE: If there is too much water in the ground, cactus roots rot and the cactus populations decreases. The limiting factor is the amount of water. ...
Ecosystem and Genetic Diversity
... different characteristics, either physical or behavioral, that may cause one to have a better chance to survive as conditions in their ecosystem change. This is why it is important for there to be diversity not only among the different species, but within the species as well. If all the individuals ...
... different characteristics, either physical or behavioral, that may cause one to have a better chance to survive as conditions in their ecosystem change. This is why it is important for there to be diversity not only among the different species, but within the species as well. If all the individuals ...
Ecology - My eCoach
... As _______ develops, these organisms are overgrown by grasses, shrubs and trees that are blown in or brought in by animals. Eventually, the area is colonized by __________ that become the main form of vegetation. This process can take hundreds to thousands of ________. ...
... As _______ develops, these organisms are overgrown by grasses, shrubs and trees that are blown in or brought in by animals. Eventually, the area is colonized by __________ that become the main form of vegetation. This process can take hundreds to thousands of ________. ...
Energy Flows
... Energy Flows Roles in an Ecosystem • Habitat – an area in an ecosystem where an organism or species lives • Niche – the specific role an organism or species plays within a habitat • Producers – a group of organisms that produce their own food through the process of photosynthesis • Also called autot ...
... Energy Flows Roles in an Ecosystem • Habitat – an area in an ecosystem where an organism or species lives • Niche – the specific role an organism or species plays within a habitat • Producers – a group of organisms that produce their own food through the process of photosynthesis • Also called autot ...
Habitat
A habitat is an ecological or environmental area that is inhabited by human, a particular species of animal, plant, or other type of organism.A place where a living thing lives is its habitat. It is a place where it can find food, shelter, protection and mates for reproduction. It is the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the physical environment that surrounds a species population.A habitat is made up of physical factors such as soil, moisture, range of temperature, and availability of light as well as biotic factors such as the availability of food and the presence of predators. A habitat is not necessarily a geographic area—for a parasitic organism it is the body of its host, part of the host's body such as the digestive tract, or a cell within the host's body.