Natural Ecosystem Change Loss of Biodiversity
... Climate shifts – organisms that cannot adjust to changes in climate are more likely to become extinct species movement – Wings, Waves & Wind carry seeds, eggs, organisms from one place to another. ecological succession - natural changes & species replacement in an ecosystem over time o A Primary (1 ...
... Climate shifts – organisms that cannot adjust to changes in climate are more likely to become extinct species movement – Wings, Waves & Wind carry seeds, eggs, organisms from one place to another. ecological succession - natural changes & species replacement in an ecosystem over time o A Primary (1 ...
FF-12C: Foothill Banner - Environmental Volunteers
... What decomposers and scavengers? (Turkey vulture, flies, possibly some earthworms, tiny fungi, microorganisms). What would be a possible foodweb here with these or other animals? Encourage the students to figure out a food web here, as there are many possibilities, then talk them through the example ...
... What decomposers and scavengers? (Turkey vulture, flies, possibly some earthworms, tiny fungi, microorganisms). What would be a possible foodweb here with these or other animals? Encourage the students to figure out a food web here, as there are many possibilities, then talk them through the example ...
Los Angeles Biofilters - UCI Water-PIRE
... Selection in Los Angeles • Generally native species or “climate-appropriate” • Irrigation often used, but ideally would tolerate dry season without irrigation • Criteria for selection of particular species not generally stated • No data on effectiveness of different species or groups of species for ...
... Selection in Los Angeles • Generally native species or “climate-appropriate” • Irrigation often used, but ideally would tolerate dry season without irrigation • Criteria for selection of particular species not generally stated • No data on effectiveness of different species or groups of species for ...
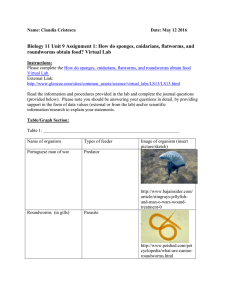
Biology 11 Unit 9 Assignment 1 How do sponges
... 1. Describe each of the four types of feeders identified in this activity. Explain how various invertebrates have adapted to feeding in their environment. Filter feeders filter bacteria, algae, protozoans and other bacteria from the water in which they live. Types of organisms with this method of fe ...
... 1. Describe each of the four types of feeders identified in this activity. Explain how various invertebrates have adapted to feeding in their environment. Filter feeders filter bacteria, algae, protozoans and other bacteria from the water in which they live. Types of organisms with this method of fe ...
Document
... Herbivorous chitons and limpets for lack of space and food. Sponges were also crowded out. A nudibranch that feeds on sponges also left. Five years – pools dominated by the mussel M. californianus and gooseneck barnacles, P. polymerus. ...
... Herbivorous chitons and limpets for lack of space and food. Sponges were also crowded out. A nudibranch that feeds on sponges also left. Five years – pools dominated by the mussel M. californianus and gooseneck barnacles, P. polymerus. ...
Chapter 6 Highlights - Orting School District
... • How many individuals of a species are found within a defined area • Count them…..but what if we can’t count them all? • We will do a catch and release lab to address ...
... • How many individuals of a species are found within a defined area • Count them…..but what if we can’t count them all? • We will do a catch and release lab to address ...
Lecture 02 Ch 05 BIOMES
... The previous author argued that warming temperatures are not affecting organisms because they normally experience a wide range of temperature. Furthermore, she claimed that organisms are not showing responses to the rising in temperatures. I differ and suggest that she did not have sufficient knowle ...
... The previous author argued that warming temperatures are not affecting organisms because they normally experience a wide range of temperature. Furthermore, she claimed that organisms are not showing responses to the rising in temperatures. I differ and suggest that she did not have sufficient knowle ...
Cycling of Matter in an Ecosystem
... Cycle imbalances • When nitrogen and phosphorus are used as part of fertilizers they end up in the water supply. • The algae over grow when nitrogen and phosphorus are at high levels. The algae can release toxins that poison the local wildlife. • When the algae die the bacteria doing decomposition ...
... Cycle imbalances • When nitrogen and phosphorus are used as part of fertilizers they end up in the water supply. • The algae over grow when nitrogen and phosphorus are at high levels. The algae can release toxins that poison the local wildlife. • When the algae die the bacteria doing decomposition ...
Chapter 3
... Some decomposers get energy by breaking down glucose without oxygen. The end products vary based on the chemical ...
... Some decomposers get energy by breaking down glucose without oxygen. The end products vary based on the chemical ...
ES Chapter 4 modified
... fur, short ears, short legs, short nose. White fur matches snow for camouflage. ...
... fur, short ears, short legs, short nose. White fur matches snow for camouflage. ...
lesson one: species and distribution
... seven species and all but two are found in every ocean basin around the world. The seven species that live in our oceans are the loggerhead (Caretta caretta), leatherback (Dermochelys coriacea), hawksbill (Eretmochelys imbricata), green (Chelonia mydas), olive ridley (Lepidochelys olivacea), Kemp’s ...
... seven species and all but two are found in every ocean basin around the world. The seven species that live in our oceans are the loggerhead (Caretta caretta), leatherback (Dermochelys coriacea), hawksbill (Eretmochelys imbricata), green (Chelonia mydas), olive ridley (Lepidochelys olivacea), Kemp’s ...
test - Scioly.org
... 87. Zoonotic disease a. describes sub-organismal pathogens such as viruses, viroids, and prions. b. is caused by pathogens that are transferred from other animals to humans by direct contact or by means of a vector. c. can only be spread from animals to humans through direct contact. d. can only be ...
... 87. Zoonotic disease a. describes sub-organismal pathogens such as viruses, viroids, and prions. b. is caused by pathogens that are transferred from other animals to humans by direct contact or by means of a vector. c. can only be spread from animals to humans through direct contact. d. can only be ...
Ecosystems Overview - earth science and environmental
... Ecosystem defined • Ecosystem – abiotic and biotic factors • Biotic factors = Biological Community – all the populations of organisms living and interacting in a particular area ...
... Ecosystem defined • Ecosystem – abiotic and biotic factors • Biotic factors = Biological Community – all the populations of organisms living and interacting in a particular area ...
Cowels - Prairie Ecosystems
... Reduction in soil drainage • Addition of dead organic matter into the soil matrix reduces soil drainage • In some sites, this leads to an increase of soil moisture over time • Moss invades mature spruce/hemlock forests – produces more organic matter that reduces soil drainage creates highly acidi ...
... Reduction in soil drainage • Addition of dead organic matter into the soil matrix reduces soil drainage • In some sites, this leads to an increase of soil moisture over time • Moss invades mature spruce/hemlock forests – produces more organic matter that reduces soil drainage creates highly acidi ...
biology - TeacherWeb
... ____ Describe changes in ecosystems resulting from seasonal variations, climate change, and succession ____ Analyze how population size is determine by births, deaths, immigration, emigration, and limiting factors (biotic and abiotic) that determine carrying capacity ____ Evaluate the costs and bene ...
... ____ Describe changes in ecosystems resulting from seasonal variations, climate change, and succession ____ Analyze how population size is determine by births, deaths, immigration, emigration, and limiting factors (biotic and abiotic) that determine carrying capacity ____ Evaluate the costs and bene ...
Ecology Test Review
... Nitrogen is a major component of amino acids and proteins 15. Define nitrogen fixation and denitrification. Nitrogen fixation is the conversion of nitrogen gas into solid nitrogen compounds. Trees cannot absorb nitrogen gas, so bacteria in the soil convert it to usable forms that are passed on to pr ...
... Nitrogen is a major component of amino acids and proteins 15. Define nitrogen fixation and denitrification. Nitrogen fixation is the conversion of nitrogen gas into solid nitrogen compounds. Trees cannot absorb nitrogen gas, so bacteria in the soil convert it to usable forms that are passed on to pr ...
policy regarding the sale of rare plants
... individuals are likely to be too few to capture much of the genetic diversity of the original wild population. While such plants as Franklinia and Ginkgo have been celebrated as species saved from extinction by gardeners, we cannot rely on horticultural activities to do what is needed to protect pla ...
... individuals are likely to be too few to capture much of the genetic diversity of the original wild population. While such plants as Franklinia and Ginkgo have been celebrated as species saved from extinction by gardeners, we cannot rely on horticultural activities to do what is needed to protect pla ...
Chapter 12
... • Extinction: elimination of all individuals of a particular species (local and global). • Natural phenomenon .... estimated that only about 1 or 2% of all species which have existed are still alive today. • Speciation: appearance of a new species. • Since things change, a species must adapt or beco ...
... • Extinction: elimination of all individuals of a particular species (local and global). • Natural phenomenon .... estimated that only about 1 or 2% of all species which have existed are still alive today. • Speciation: appearance of a new species. • Since things change, a species must adapt or beco ...
Ecology
... • To identify the effects that destruction of habitats, pollution, urbanization, and natural disasters have on population. ...
... • To identify the effects that destruction of habitats, pollution, urbanization, and natural disasters have on population. ...
Effects of Weather on Living Things in the Foothills
... hot, dry summers with about 80% of the annual precipitation falling between November and March. Plants and animals living in this type of climate must be tolerant of these long, hot, dry periods. This is an example of how weather limits the kinds of life that can exist in a particular environment. C ...
... hot, dry summers with about 80% of the annual precipitation falling between November and March. Plants and animals living in this type of climate must be tolerant of these long, hot, dry periods. This is an example of how weather limits the kinds of life that can exist in a particular environment. C ...
1st Nine Weeks Study Guide II
... ____ 45. Why are viruses like parasites? a. They harm the cells they enter. b. They multiply. c. They use their own energy to develop. d. They make their own food. ____ 46. A virus’s proteins are important because they a. contain genetic material. b. make new virus particles. c. provide energy for t ...
... ____ 45. Why are viruses like parasites? a. They harm the cells they enter. b. They multiply. c. They use their own energy to develop. d. They make their own food. ____ 46. A virus’s proteins are important because they a. contain genetic material. b. make new virus particles. c. provide energy for t ...
Habitat
A habitat is an ecological or environmental area that is inhabited by human, a particular species of animal, plant, or other type of organism.A place where a living thing lives is its habitat. It is a place where it can find food, shelter, protection and mates for reproduction. It is the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the physical environment that surrounds a species population.A habitat is made up of physical factors such as soil, moisture, range of temperature, and availability of light as well as biotic factors such as the availability of food and the presence of predators. A habitat is not necessarily a geographic area—for a parasitic organism it is the body of its host, part of the host's body such as the digestive tract, or a cell within the host's body.