Aquatic Ecosystem
... - Flashier runoff and higher flow magnitudes (e.g., floods) • Reduced habitat availability due to substrate homogeniza@on and shiUs in sediment delivery, distribu@on, and deposi@on • Reduced volume and dura@on ...
... - Flashier runoff and higher flow magnitudes (e.g., floods) • Reduced habitat availability due to substrate homogeniza@on and shiUs in sediment delivery, distribu@on, and deposi@on • Reduced volume and dura@on ...
Best Buddies Slides
... A cuckoo may lay its eggs in a warbler’s nest. The cuckoo’s young will displace the warbler’s young and will be raised by the warbler. ...
... A cuckoo may lay its eggs in a warbler’s nest. The cuckoo’s young will displace the warbler’s young and will be raised by the warbler. ...
The Science of Life
... The biosphere is too large to study all the relationships at one time. Scientists use smaller pieces, or levels of organization, for their studies. The numbers and interactions among organisms increase at higher levels of organization. The following are levels of organization from simplest to most c ...
... The biosphere is too large to study all the relationships at one time. Scientists use smaller pieces, or levels of organization, for their studies. The numbers and interactions among organisms increase at higher levels of organization. The following are levels of organization from simplest to most c ...
Investigation 1: Goldfish and Guppies
... memorize. Research shows that students learn terms much more easily when the terms are used during the discussion of hands-on activities. The use of scientific terminology and spelling should always follow exploration of the concepts. Investigation 1: Goldfish and Guppies ...
... memorize. Research shows that students learn terms much more easily when the terms are used during the discussion of hands-on activities. The use of scientific terminology and spelling should always follow exploration of the concepts. Investigation 1: Goldfish and Guppies ...
Environments Through Time - NagleEarthandEnvironmental
... Proterozoic/Phanerozoic boundary roughly marks rapid diversification and complexification in the types of life forms (i.e. hard exo/skeletons appear = more fossils as soft bodied organisms do not fossilise easily ) Define cyanobacteria as simple photosynthetic organisms and examine the evidence of ...
... Proterozoic/Phanerozoic boundary roughly marks rapid diversification and complexification in the types of life forms (i.e. hard exo/skeletons appear = more fossils as soft bodied organisms do not fossilise easily ) Define cyanobacteria as simple photosynthetic organisms and examine the evidence of ...
Reproduction and Niches
... Do well in variable climate or with disturbance Population boom and bust cycles Rapid development Early reproduction Small body size Single reproductive effort ...
... Do well in variable climate or with disturbance Population boom and bust cycles Rapid development Early reproduction Small body size Single reproductive effort ...
Species Interactions and Community Structure
... Variance in feeding preferences and competitive relationships across environments. ...
... Variance in feeding preferences and competitive relationships across environments. ...
Threatened and pest animals of Greater Southern Sydney chapter 3
... 3. Animals of high conservation priority These species are rare and have declined substantially. They are faced with continuing threats, mainly habitat loss or alteration. Most may be conserved by managing key habitats or threats in the region. In this chapter, EPBC Act = Environment Protection and ...
... 3. Animals of high conservation priority These species are rare and have declined substantially. They are faced with continuing threats, mainly habitat loss or alteration. Most may be conserved by managing key habitats or threats in the region. In this chapter, EPBC Act = Environment Protection and ...
Chapter 5 notes - Duluth High School
... – Mutualism – Commensalism They have an impact on resources use and population size of species in an ecosystem. (sustainability!!) ...
... – Mutualism – Commensalism They have an impact on resources use and population size of species in an ecosystem. (sustainability!!) ...
Threatened species recovery plans
... species of animal or plant that is under the threat of extinction. A threat may take the form of being preyed upon by feral predators such as foxes, damage, removal or fragmentation of habitat, invasion by weed species, altered fire regimes or poisoning by pollution or pesticides. Recovery Plans ide ...
... species of animal or plant that is under the threat of extinction. A threat may take the form of being preyed upon by feral predators such as foxes, damage, removal or fragmentation of habitat, invasion by weed species, altered fire regimes or poisoning by pollution or pesticides. Recovery Plans ide ...
English
... purposes, while conservation efforts contribute to poverty alleviation. Helping people move into alternative livelihoods such as ranger, farming or tourism activities ensures the active involvement of communities on the one hand and the sustainable use of natural resources on the other. However as d ...
... purposes, while conservation efforts contribute to poverty alleviation. Helping people move into alternative livelihoods such as ranger, farming or tourism activities ensures the active involvement of communities on the one hand and the sustainable use of natural resources on the other. However as d ...
Directions: Read the following passage
... ore than 4000 plant species are known to live and grow in Florida. The majority of them, about 3000, are native plants. They are considered native because they naturally occur here and have historically been part of Florida’s environment for a very long time—perhaps thousands of years. Another crite ...
... ore than 4000 plant species are known to live and grow in Florida. The majority of them, about 3000, are native plants. They are considered native because they naturally occur here and have historically been part of Florida’s environment for a very long time—perhaps thousands of years. Another crite ...
Chapter 18: The Biosphere and Human Effects
... We compete with other species for resources, overharvest resources, and introduce exotic species to nonnative habitats. ...
... We compete with other species for resources, overharvest resources, and introduce exotic species to nonnative habitats. ...
Chapt 11: Terrestrial Flora and Fauna
... d. Neoarctic Region: nontropical portion of North America with poor faunal assemblage with the exception of reptiles e. Neotropical Region: all of South America and tropical North America with a rich and distinctive fauna that reflects both a variety of habitats and a considerable degree of isolatio ...
... d. Neoarctic Region: nontropical portion of North America with poor faunal assemblage with the exception of reptiles e. Neotropical Region: all of South America and tropical North America with a rich and distinctive fauna that reflects both a variety of habitats and a considerable degree of isolatio ...
Fit for Purpose: Are EU policies delivering for nature?
... In theory there is a lot of conservation action being undertaken in the wider countryside, most notably through agri-environment schemes as part of the Common Agricultural Policy, however these schemes are not delivering the benefits they are meant to, as demonstrated by recent analysis of the lates ...
... In theory there is a lot of conservation action being undertaken in the wider countryside, most notably through agri-environment schemes as part of the Common Agricultural Policy, however these schemes are not delivering the benefits they are meant to, as demonstrated by recent analysis of the lates ...
Chapt 11: Terrestrial Flora and Fauna
... d. Neoarctic Region: nontropical portion of North America with poor faunal assemblage with the exception of reptiles e. Neotropical Region: all of South America and tropical North America with a rich and distinctive fauna that reflects both a variety of habitats and a considerable degree of isolatio ...
... d. Neoarctic Region: nontropical portion of North America with poor faunal assemblage with the exception of reptiles e. Neotropical Region: all of South America and tropical North America with a rich and distinctive fauna that reflects both a variety of habitats and a considerable degree of isolatio ...
Marine habitats: fauna and ecology
... and biotic features, whether entirely natural or semi-natural”. The Directive also identifies the habitat types of Bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) European interest. Clearly, this definition of habitat in the Directive is very general and does not regard the biota, but only where living org ...
... and biotic features, whether entirely natural or semi-natural”. The Directive also identifies the habitat types of Bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) European interest. Clearly, this definition of habitat in the Directive is very general and does not regard the biota, but only where living org ...
Energy Pyramid Diagram showing the loss of energy in ecosystems
... Deer, rabbits, grasshopper Raccoon, bear, or human Lion, wolf, owl Mushrooms and bacteria ...
... Deer, rabbits, grasshopper Raccoon, bear, or human Lion, wolf, owl Mushrooms and bacteria ...
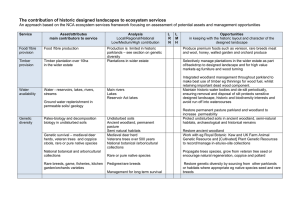
The contribution of historic designed landscapes to ecosystem
... Large areas of unimproved and semiimproved habitats Rivers and water bodies with good WFD ecological status ...
... Large areas of unimproved and semiimproved habitats Rivers and water bodies with good WFD ecological status ...
The Importance of the Natural Sciences to Conservation
... Important nutrient cycling and fluxes, primary and secondary productivity, nursery areas, and critical habitats of many birds and mammals are examples of essential services provided by these once ubiquitous habitats. Most of these functions are mediated via sediment-associated biota, including macro ...
... Important nutrient cycling and fluxes, primary and secondary productivity, nursery areas, and critical habitats of many birds and mammals are examples of essential services provided by these once ubiquitous habitats. Most of these functions are mediated via sediment-associated biota, including macro ...
Habitat
A habitat is an ecological or environmental area that is inhabited by human, a particular species of animal, plant, or other type of organism.A place where a living thing lives is its habitat. It is a place where it can find food, shelter, protection and mates for reproduction. It is the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the physical environment that surrounds a species population.A habitat is made up of physical factors such as soil, moisture, range of temperature, and availability of light as well as biotic factors such as the availability of food and the presence of predators. A habitat is not necessarily a geographic area—for a parasitic organism it is the body of its host, part of the host's body such as the digestive tract, or a cell within the host's body.