* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Population notes.
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
World population wikipedia , lookup
The Population Bomb wikipedia , lookup
Human overpopulation wikipedia , lookup
Source–sink dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Maximum sustainable yield wikipedia , lookup
Human population planning wikipedia , lookup
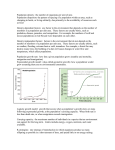
Populations Populations = groups of individuals of the same species living in the same place • Individuals within a population: ▫ occupy the same general area ▫ rely on the same resources ▫ influenced by the same environmental conditions Population Dynamics • Three Key Features of Populations ▫ Size ▫ Density ▫ Dispersion Three Key Features of Populations 1. Size: number of individuals in an area Population Size Depends on 4 Factors: Natality – number of births (increase population) Mortality – number of deaths (decrease population) Immigration – number of individuals moving into an area (increase population). Emigration – number of individuals moving out of an area (decrease population). Population Change • Population size increases and decreases over time. • population change = (natality + immigration) – (mortality + emigration) Population Limiting Factors • Density-dependent factors ▫ Any factor in the environment that depends on the number of members in a population per unit area ▫ Usually biotic (living) factors ▫ These include Predation Disease Parasites Competition (for mates, resources) Food shortage Population Limiting Factors • Density-independent factors ▫ Factors that limit population size, regardless of population density. ▫ These are usually abiotic (non-living) factors Natural weather events: Drought, flooding, extreme heat or cold, tornadoes, hurricanes, fires Pesticides Destruction of habitat Pollution Three Key Features of Populations 2. Density: measurement of population per unit area or unit volume Pop. Density = # of individuals ÷ unit of space Three Key Features of Populations 3. Dispersion: The pattern of spacing a population within an area ▫ 3 main types of dispersion ▫ Clumped Uniform Random The primary cause of dispersion is resource availability Clumped Distribution • Most common pattern in nature. • Result of unreliable resources. ▫ Individuals of the population will clump around resources. ▫ Also found among many animals to aid predation or fend off predators. Uniform Distribution • Uniform Distribution = The tendency for populations to be found evenly distributed about their habitat. • Individuals use the resources found immediately around them, and spread out as to use all of the available resources • Happens because of interactions between individuals in the population. Random Distribution • Uncommon in nature. • Is the tendency for populations to be found randomly about their habitat. • This pattern occurs in the absence of strong attraction or repulsion from another individual. • Animals ▫ Able to move about their habitat, so that at any given instance, they can be found anywhere about their environment. • Plants ▫ Spores are randomly distributed by the wind ▫ Usually have the ability to live anywhere in a given habitat. Carrying Capacity • Carrying Capacity = the size of a population that can live indefinitely using the resources available where that population lives. Factors that Affect Carrying Capacity 1. Materials and energy – populations are limited by the amount of usable energy from the sun and the supply of water, carbon, etc. 2. Food chains – populations are limited by food supply and their predators. 3. Competition – each species shares the same needs. Competition for food, water, mates, space, etc. can limit population growth. Intraspecific competition – among members of the same species Interspecific competition – between different species 4. Density – species have differing needs for space. This determines an organism’s population density. Overcrowding can increase stress, promote disease, increase aggression, neglect of offspring, etc. Death rates increase and birth rates decrease so that the population goes down. Alien and Invasive Species • Alien species – a species that is accidentally or deliberately introduced into a new location • Invasive species – a species that can take over the habitat of native species Deer: Predation of Starvation • Graphing Exercise Human Population Growth • http://video.nationalgeographic.com/vid eo/the-magazine/the-magazinelatest/ngm-7billion/ World population density- 7 billion http://www.worldometers.info/world-population/ Graphing Question (submit response) •Does the Human Population have a carrying capacity?