CHAPTER 20 Principles of Biogeography
... beginning of the widespread clearances by the first farmers. The woodland provinces of this map denote the principal species of woodland tree, but not their density of coverage. One can ask the question: was it wall-to-wall forest, as Sir Arthur Tansley (1939) claimed, or was it more open woodland, ...
... beginning of the widespread clearances by the first farmers. The woodland provinces of this map denote the principal species of woodland tree, but not their density of coverage. One can ask the question: was it wall-to-wall forest, as Sir Arthur Tansley (1939) claimed, or was it more open woodland, ...
Riparian Habitat Management for Reptiles and Amphibians on
... vegetation, plant species, and soil. Microhabitat components are site-specific, physical entities that provide environmental conditions necessary for a wide variety of ecological functions such as reproduction, foraging, predator avoidance or escape, thermoregulation, and resting. Litter (e.g., fall ...
... vegetation, plant species, and soil. Microhabitat components are site-specific, physical entities that provide environmental conditions necessary for a wide variety of ecological functions such as reproduction, foraging, predator avoidance or escape, thermoregulation, and resting. Litter (e.g., fall ...
University of Chester Department of Biological Sciences For general
... Dr Christina Stanley [email protected] Grazing is essential for the maintenance of biodiversity in habitats such as grasslands, meadows, moorland and heathland which have historically been shaped by human activity. Ponies are often used for conservation grazing schemes as they are high ...
... Dr Christina Stanley [email protected] Grazing is essential for the maintenance of biodiversity in habitats such as grasslands, meadows, moorland and heathland which have historically been shaped by human activity. Ponies are often used for conservation grazing schemes as they are high ...
North Fulton Masters Gardeners
... beautiful environments. Several other species of pitcher plants are found here too including hooded, trumpet, purple, and parrot varieties. Other plants that can be found in the bogs are slash and longleaf pines, wax myrtle, gall berry and dwarfed red maple. We are delighted that our volunteer hours ...
... beautiful environments. Several other species of pitcher plants are found here too including hooded, trumpet, purple, and parrot varieties. Other plants that can be found in the bogs are slash and longleaf pines, wax myrtle, gall berry and dwarfed red maple. We are delighted that our volunteer hours ...
Forest 1
... This laboratory exercise is designed to provide you with an opportunity to increase your observation and quantitative skills, and more specifically, to provide you with an introduction to general habitat analysis on a macro and micro scale. After your walk through Veit's woods and the associated old ...
... This laboratory exercise is designed to provide you with an opportunity to increase your observation and quantitative skills, and more specifically, to provide you with an introduction to general habitat analysis on a macro and micro scale. After your walk through Veit's woods and the associated old ...
CyanoHAB FAQ Brochure
... may be present. If your pet becomes sick, tell your veterinarian that there may have been exposure to CyanoHAB toxins. Are CyanoHABs visible? Dense blooms of cyanobacteria can turn the water bright green and be clearly visible. However, presence of toxins can not be determined from appearance, odor, ...
... may be present. If your pet becomes sick, tell your veterinarian that there may have been exposure to CyanoHAB toxins. Are CyanoHABs visible? Dense blooms of cyanobacteria can turn the water bright green and be clearly visible. However, presence of toxins can not be determined from appearance, odor, ...
Marine Biome
... Unique fact: Coral reefs support a greater number of fish and invertebrate species than any other ocean ecosystem. ...
... Unique fact: Coral reefs support a greater number of fish and invertebrate species than any other ocean ecosystem. ...
Chapter 14 - FacStaff Home Page for CBU
... great Lakes region by mallards Undisturbed areas with high biodiversity of species are highly resistant to invasion by new species. Competition may be the factor that limits the geographical range of a species. Convincing cases are scarce. Competitive exclusion is most evident when exotic species su ...
... great Lakes region by mallards Undisturbed areas with high biodiversity of species are highly resistant to invasion by new species. Competition may be the factor that limits the geographical range of a species. Convincing cases are scarce. Competitive exclusion is most evident when exotic species su ...
Background document to protected areas policy brief
... marine ecosystem. Fishing is pointed out as one of the main threats to vulnerable species and habitats in the Baltic Sea (HELCOM 2013a), so the frequent occurrence of fishing in MPAs may be in conflict with nature conservation. There is a growing scientific understanding of the direct and indirect e ...
... marine ecosystem. Fishing is pointed out as one of the main threats to vulnerable species and habitats in the Baltic Sea (HELCOM 2013a), so the frequent occurrence of fishing in MPAs may be in conflict with nature conservation. There is a growing scientific understanding of the direct and indirect e ...
biology_-_module_4_-_notes
... This is found in Australia, New Guinea, New Zealand and South America and its presence on the southern continents led scientists to believe that these continents had once been joined. It evolved after Africa separated from Gondwana and it formed large rainforests. Fossil pollen of Nothofagus from Au ...
... This is found in Australia, New Guinea, New Zealand and South America and its presence on the southern continents led scientists to believe that these continents had once been joined. It evolved after Africa separated from Gondwana and it formed large rainforests. Fossil pollen of Nothofagus from Au ...
Ch 5 PPT
... extinction 250 million years ago, 70% of all land species and 90% of all marine species went extinct. ...
... extinction 250 million years ago, 70% of all land species and 90% of all marine species went extinct. ...
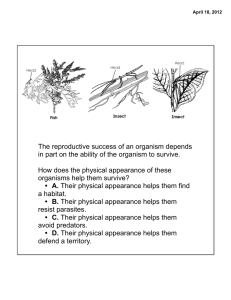
The reproductive success of an organism depends in part on the
... C. Sexual reproduction increases variation in the population and provides for adaptability in a changing environment. ...
... C. Sexual reproduction increases variation in the population and provides for adaptability in a changing environment. ...
Nature Trail Guide - Marianist Environmental Education Center
... hickory/ dogwood woodland. Its dryness is a function of the topography – the surface features which are a legacy of glacial activity which shaped this land thousands of years ago – and drainage. The soil of Mount St. John is well drained as it lies on top of 100-200 feet of sand and rock, deposited ...
... hickory/ dogwood woodland. Its dryness is a function of the topography – the surface features which are a legacy of glacial activity which shaped this land thousands of years ago – and drainage. The soil of Mount St. John is well drained as it lies on top of 100-200 feet of sand and rock, deposited ...
Denman Interpretive Trail
... the absence of oxygen. One byproduct of this process is hydrogen sulfide that, when released into the air, gives marshes their CA characteristic rotten egg odor. Detritivore activity converts organic matter into nutrients available in the soil and water for primary producers. Detritivores are Earth’ ...
... the absence of oxygen. One byproduct of this process is hydrogen sulfide that, when released into the air, gives marshes their CA characteristic rotten egg odor. Detritivore activity converts organic matter into nutrients available in the soil and water for primary producers. Detritivores are Earth’ ...
Ecology Population
... Biotic factor - any living component that affects another organism - needs energy to do work and food for proper growth - Plants, animals, fungi, protiste and bacteria ...
... Biotic factor - any living component that affects another organism - needs energy to do work and food for proper growth - Plants, animals, fungi, protiste and bacteria ...
1. Primary Production
... – the use of biomass to release energy that can be used to do work – In other words, the use of energy from organic matter by most heterotrophic and autotrophic organisms is accomplished through respiration. – An organic compound such as sugar is combined with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and wa ...
... – the use of biomass to release energy that can be used to do work – In other words, the use of energy from organic matter by most heterotrophic and autotrophic organisms is accomplished through respiration. – An organic compound such as sugar is combined with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and wa ...
AP Biology Review Chapters 43-47 Review Questions
... 10. Compare the flow of energy to the flow of chemicals through an ecosystem. 11. Differentiate among nitrogen fixation, nitrification, and denitrification. Identify the organism that performs these functions. 12. Provide examples of how human activities can alter the biogeochemical cycles. Be sure ...
... 10. Compare the flow of energy to the flow of chemicals through an ecosystem. 11. Differentiate among nitrogen fixation, nitrification, and denitrification. Identify the organism that performs these functions. 12. Provide examples of how human activities can alter the biogeochemical cycles. Be sure ...
Insect communities and biotic interactions on
... and Holt, 2000). In the following we evaluate existing evidence for each hypothesis (Table 1). 2.1. Species diversity increases with habitat area and decreases with habitat isolation Although species–area relationships are generally a well known and often described ecological pattern, only a few stu ...
... and Holt, 2000). In the following we evaluate existing evidence for each hypothesis (Table 1). 2.1. Species diversity increases with habitat area and decreases with habitat isolation Although species–area relationships are generally a well known and often described ecological pattern, only a few stu ...
Biology Topic 4
... response to environmental change; one must be multiple antibiotic resistance in bacteria Example 1: Two varieties of the moth Biston betularia exist in the forms of different body color. One is black, the other is speckled. The black moth is easily seen by predators while the speckled one is camoulf ...
... response to environmental change; one must be multiple antibiotic resistance in bacteria Example 1: Two varieties of the moth Biston betularia exist in the forms of different body color. One is black, the other is speckled. The black moth is easily seen by predators while the speckled one is camoulf ...
Chapter 7
... In mutualism, two species interact in a way that benefits both. Commensalism is an interaction that benefits one species but has little, if any, effect on the other species. ...
... In mutualism, two species interact in a way that benefits both. Commensalism is an interaction that benefits one species but has little, if any, effect on the other species. ...
Fish Introductions into Southern Florida: Species, pathways, and
... emphasis placed on additional monitoring of under-sampled habitats such as canals. We also suggest that more efforts be made to educate the public about introduced species and in closing newly identified pathways for the introduction of additional species identified as potential threats. Although th ...
... emphasis placed on additional monitoring of under-sampled habitats such as canals. We also suggest that more efforts be made to educate the public about introduced species and in closing newly identified pathways for the introduction of additional species identified as potential threats. Although th ...
The Realized Niche
... is the sum total of all the ways it utilizes the resources of its environment. A niche may be described in terms of space utilization, food consumption, temperature range, appropriate conditions for mating, requirements for moisture, and other factors. Niche is not synonymous with habitat, the place ...
... is the sum total of all the ways it utilizes the resources of its environment. A niche may be described in terms of space utilization, food consumption, temperature range, appropriate conditions for mating, requirements for moisture, and other factors. Niche is not synonymous with habitat, the place ...
Answers to STUDY BREAK Questions Essentials 5th Chapter 13
... surface nutrients because the strong thermocline discourages the vertical mixing necessary to bring nutrients from the lower depths. The tropical oceans away from land are therefore oceanic deserts nearly devoid of visible (that is, non-cyanobacterial) plankton. The typical clarity of tropical water ...
... surface nutrients because the strong thermocline discourages the vertical mixing necessary to bring nutrients from the lower depths. The tropical oceans away from land are therefore oceanic deserts nearly devoid of visible (that is, non-cyanobacterial) plankton. The typical clarity of tropical water ...
Habitat
A habitat is an ecological or environmental area that is inhabited by human, a particular species of animal, plant, or other type of organism.A place where a living thing lives is its habitat. It is a place where it can find food, shelter, protection and mates for reproduction. It is the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the physical environment that surrounds a species population.A habitat is made up of physical factors such as soil, moisture, range of temperature, and availability of light as well as biotic factors such as the availability of food and the presence of predators. A habitat is not necessarily a geographic area—for a parasitic organism it is the body of its host, part of the host's body such as the digestive tract, or a cell within the host's body.