Nerve activates contraction - Silver Falls School District
... and unmylenated fibers 2. Nuclei – clusters of cell bodies within the white matter of the central nervous system ...
... and unmylenated fibers 2. Nuclei – clusters of cell bodies within the white matter of the central nervous system ...
15_Neuro
... continuos with brain stem ascending and descending nerve tracts protected by CSF and meninges gray matter in internal section - not protected by myelin sheath myelinated white matter in outer area ...
... continuos with brain stem ascending and descending nerve tracts protected by CSF and meninges gray matter in internal section - not protected by myelin sheath myelinated white matter in outer area ...
psyc223
... Placebos and opioid agonist have a related analgesia mechanism, the same regions of the brain are affected by both treatments Hidden Treatment: the patient is not aware of when a drug is administered ...
... Placebos and opioid agonist have a related analgesia mechanism, the same regions of the brain are affected by both treatments Hidden Treatment: the patient is not aware of when a drug is administered ...
Sleep and Biological Rhythms
... desynchrony), and to the tectum (rapid eye movements) Pontine cells project via magnocellular cells within medulla to the spinal cord: release glycine to inhibit alpha-motoneurons (induce REM motor paralysis or atonia) ...
... desynchrony), and to the tectum (rapid eye movements) Pontine cells project via magnocellular cells within medulla to the spinal cord: release glycine to inhibit alpha-motoneurons (induce REM motor paralysis or atonia) ...
Slide ()
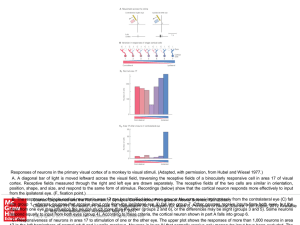
... Responses of neurons in the primary visual cortex of a monkey to visual stimuli. (Adapted, with permission, from Hubel and Wiesel 1977.) A. A diagonal bar of light is moved leftward across the visual field, traversing the receptive fields of a binocularly responsive cell in area 17 of visual cortex. ...
... Responses of neurons in the primary visual cortex of a monkey to visual stimuli. (Adapted, with permission, from Hubel and Wiesel 1977.) A. A diagonal bar of light is moved leftward across the visual field, traversing the receptive fields of a binocularly responsive cell in area 17 of visual cortex. ...
True or False: Write “True” or “False”
... signals in sensory neurons. The signals then travel along precise pathways to the brain, passing through several processing or relay stages in the brain stem and thalamus before terminating in the somatosensory cortex. At each stage the signals travelling from adjacent points on the skin are carried ...
... signals in sensory neurons. The signals then travel along precise pathways to the brain, passing through several processing or relay stages in the brain stem and thalamus before terminating in the somatosensory cortex. At each stage the signals travelling from adjacent points on the skin are carried ...
Chapter 28: Nervous System
... 3. Motor Output: Conduction of signals from brain or spinal cord to effector organs (muscles or glands). Controls the activity of muscles and glands, and allows the animal to respond to its ...
... 3. Motor Output: Conduction of signals from brain or spinal cord to effector organs (muscles or glands). Controls the activity of muscles and glands, and allows the animal to respond to its ...
I. Introduction to class
... 3. Motor Output: Conduction of signals from brain or spinal cord to effector organs (muscles or glands). Controls the activity of muscles and glands, and allows the animal to respond to its ...
... 3. Motor Output: Conduction of signals from brain or spinal cord to effector organs (muscles or glands). Controls the activity of muscles and glands, and allows the animal to respond to its ...
Electronic supplementary material consisting of: ... figures, Supplementary materials and methods, and Supplementary reference
... Representative pictures taken after 2 days. (d) Invasion was quantified as area difference on day 2 minus day 0. Results are expressed as mean ± s.d. ...
... Representative pictures taken after 2 days. (d) Invasion was quantified as area difference on day 2 minus day 0. Results are expressed as mean ± s.d. ...
Drugs - Warren County Schools
... Bacterial Toxins • Botulism is the most poisonous toxin known to humans. • It acts as a neurotoxin, paralyzing muscles by releasing a neurotransmitter, acetylcholine. An antitoxin made from horse serum can be administered if caught in time. • If not caught in time, painful muscle spasms occur befor ...
... Bacterial Toxins • Botulism is the most poisonous toxin known to humans. • It acts as a neurotoxin, paralyzing muscles by releasing a neurotransmitter, acetylcholine. An antitoxin made from horse serum can be administered if caught in time. • If not caught in time, painful muscle spasms occur befor ...
The Nervous System
... Ø Do not transfer any information Ø Provide metabolic support and protection for neurons in the central and peripheral nervous systems Ø More numerous than neurons? ...
... Ø Do not transfer any information Ø Provide metabolic support and protection for neurons in the central and peripheral nervous systems Ø More numerous than neurons? ...
Hair cells
... damage is most likely to occur Temperature extremes affect the transient receptor potential (TRP) ion channel -Produces depolarization by an inward flow of Na+ and Ca2+, which in turn causes the sensory neuron to fire -Leads to a release of glutamate and an EPSP in neurons in spinal cord, which ulti ...
... damage is most likely to occur Temperature extremes affect the transient receptor potential (TRP) ion channel -Produces depolarization by an inward flow of Na+ and Ca2+, which in turn causes the sensory neuron to fire -Leads to a release of glutamate and an EPSP in neurons in spinal cord, which ulti ...
Powerpoint
... • The truth is we know very little about how the major drugs we take work – receptors are unknown • We know even less about what side effects they might have - receptors are unknown • Drug discovery seems to be approached in a very consistent and conventional way • The cost of bringing a drug to mar ...
... • The truth is we know very little about how the major drugs we take work – receptors are unknown • We know even less about what side effects they might have - receptors are unknown • Drug discovery seems to be approached in a very consistent and conventional way • The cost of bringing a drug to mar ...
Developing a diagnostic service for Stargardt disease – a feasibility
... No mutation hotspots 500+ variants identified ...
... No mutation hotspots 500+ variants identified ...
Nervous System and Senses - Avon Community School Corporation
... Ca rushes in and cause the synaptic vesicles to fuse with the cell membrane and release the neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft After binding, neurotransmitters will either be destroyed in the synaptic cleft or taken back in to surrounding neurons ...
... Ca rushes in and cause the synaptic vesicles to fuse with the cell membrane and release the neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft After binding, neurotransmitters will either be destroyed in the synaptic cleft or taken back in to surrounding neurons ...
Cognitive Psychology
... • All action potentials are the same magnitude (strength). • We determine how excited a neuron is by its firing rate - how many action potentials per second it generates. ...
... • All action potentials are the same magnitude (strength). • We determine how excited a neuron is by its firing rate - how many action potentials per second it generates. ...
Senses presentation
... received by receptor. • Receptors transduce (change) different forms of energy into nerve impulses • Nerve impulses are conducted to the brain – Stimulus must initiate and action potential in the cerebral cortex – The brain interprets these impulses as sound or sight even though the impulses themsel ...
... received by receptor. • Receptors transduce (change) different forms of energy into nerve impulses • Nerve impulses are conducted to the brain – Stimulus must initiate and action potential in the cerebral cortex – The brain interprets these impulses as sound or sight even though the impulses themsel ...
hendrick
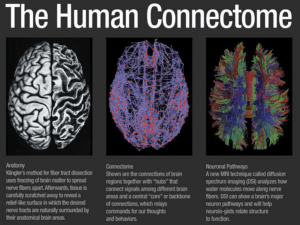
... identify the two neurons would take 37 + 37 = 74 bits per connection, or 518,000 bits (65 kilobytes) per neuron. Multiplying by 86 billion neurons gives a total of 5.59 petabytes (PB) of information. That’s just for the basic connectivity map: a record of which neurons are connected to which. More i ...
... identify the two neurons would take 37 + 37 = 74 bits per connection, or 518,000 bits (65 kilobytes) per neuron. Multiplying by 86 billion neurons gives a total of 5.59 petabytes (PB) of information. That’s just for the basic connectivity map: a record of which neurons are connected to which. More i ...
figures from Lin et al.
... a. In this study, what are projection neurons (PNs)? [3 pts.] Projection neurons convey sensory information from the antennal lobes to the deeper parts of the brain (lateral horns, superior dorsofrontal protocerebrum, etc.) b. What do PNv-3’s do in Drosophila, according to this study? [3 pts.] P ...
... a. In this study, what are projection neurons (PNs)? [3 pts.] Projection neurons convey sensory information from the antennal lobes to the deeper parts of the brain (lateral horns, superior dorsofrontal protocerebrum, etc.) b. What do PNv-3’s do in Drosophila, according to this study? [3 pts.] P ...
Sample Midterm Exam
... B. whether or not the cribriform plate is covered with scar tissue C. whether or not the supporting cells were destroyed D. A & B 5. Which of the sensory systems discussed in class is unusual because the incoming sensory information does not make a synapse in the thalamus, and also remains predomina ...
... B. whether or not the cribriform plate is covered with scar tissue C. whether or not the supporting cells were destroyed D. A & B 5. Which of the sensory systems discussed in class is unusual because the incoming sensory information does not make a synapse in the thalamus, and also remains predomina ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... Small-diameter pain fibers synapse with superficially located substantia gelatinosa neurons in the dorsal horn The large myelinated fibers from pressure and touch receptors make collateral synapses with interneurons in the dorsal horns ...
... Small-diameter pain fibers synapse with superficially located substantia gelatinosa neurons in the dorsal horn The large myelinated fibers from pressure and touch receptors make collateral synapses with interneurons in the dorsal horns ...
Skeletal System
... Small-diameter pain fibers synapse with superficially located substantia gelatinosa neurons in the dorsal horn The large myelinated fibers from pressure and touch receptors make collateral synapses with interneurons in the dorsal horns ...
... Small-diameter pain fibers synapse with superficially located substantia gelatinosa neurons in the dorsal horn The large myelinated fibers from pressure and touch receptors make collateral synapses with interneurons in the dorsal horns ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.