MRS study on lentiform nucleus in idiopathic Parkinson`s disease
... Journal of Zhejiang University SCIENCE (ISSN 1009-3095, Monthly) ♦ The Journal has been accepted by Ei Compendex, Index Medicus/MEDLINE, CA, BIOSIS, AJ, CBA, ZB1, INSPEC, and CSA for abstracting and indexing respectively, since founded in 2000. ♦ The Journal aims to present the latest development an ...
... Journal of Zhejiang University SCIENCE (ISSN 1009-3095, Monthly) ♦ The Journal has been accepted by Ei Compendex, Index Medicus/MEDLINE, CA, BIOSIS, AJ, CBA, ZB1, INSPEC, and CSA for abstracting and indexing respectively, since founded in 2000. ♦ The Journal aims to present the latest development an ...
cro appointed for hepatitis c trial
... TT-034 is a ddRNAi molecule that was created by Tacere Therapeutics and advanced through the development pathway in collaboration with Pfizer. The molecule is designed to express three independently transcribed short hairpin RNA (shRNA) elements that simultaneously target and cleave three separate r ...
... TT-034 is a ddRNAi molecule that was created by Tacere Therapeutics and advanced through the development pathway in collaboration with Pfizer. The molecule is designed to express three independently transcribed short hairpin RNA (shRNA) elements that simultaneously target and cleave three separate r ...
What is Your Reaction Time?
... as several threadlike "arms" called axons and dendrites, which transmit nerve impulses. Scientists estimate there are more than 100 billion neurons in the brain. Neurotransmitter: A chemical that acts as a messenger between neurons, and is released into the synaptic cleft when a nerve impulse reache ...
... as several threadlike "arms" called axons and dendrites, which transmit nerve impulses. Scientists estimate there are more than 100 billion neurons in the brain. Neurotransmitter: A chemical that acts as a messenger between neurons, and is released into the synaptic cleft when a nerve impulse reache ...
Section 35-2: The Nervous System The nervous system controls and
... Section 35-5: Drugs and the Nervous System A drug is any substance, other than food, that changes the structure or function of the body. Some drugs, such as cocaine and heroin are illegal. Other drugs, such as penicillin and codeine are prescribed by doctors. Still other drugs, including cough medic ...
... Section 35-5: Drugs and the Nervous System A drug is any substance, other than food, that changes the structure or function of the body. Some drugs, such as cocaine and heroin are illegal. Other drugs, such as penicillin and codeine are prescribed by doctors. Still other drugs, including cough medic ...
File
... Section 35-5: Drugs and the Nervous System A drug is any substance, other than food, that changes the structure or function of the body. Some drugs, such as cocaine and heroin are illegal. Other drugs, such as penicillin and codeine are prescribed by doctors. Still other drugs, including cough medic ...
... Section 35-5: Drugs and the Nervous System A drug is any substance, other than food, that changes the structure or function of the body. Some drugs, such as cocaine and heroin are illegal. Other drugs, such as penicillin and codeine are prescribed by doctors. Still other drugs, including cough medic ...
Document
... extremely serious. It is fatal in one in ten cases and in one in seven survivors is left with severe handicap, such as deafness or brain injury. The bacteria that causes both meningococcal and and pneummococcal meningitis are vary common and live in the back of the nose and throat. People of any age ...
... extremely serious. It is fatal in one in ten cases and in one in seven survivors is left with severe handicap, such as deafness or brain injury. The bacteria that causes both meningococcal and and pneummococcal meningitis are vary common and live in the back of the nose and throat. People of any age ...
The NERVOUS System
... decides on response based on past experience, reflexes, and current conditions. ...
... decides on response based on past experience, reflexes, and current conditions. ...
Nervous System Study Guide 1
... 8. It seems like a stranger is following you as you walk to your car in the parking lot. Your heart starts beating faster. Write out the pathway that the nervous system has taken during this experience. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 9. What are the 2 main types of cell ...
... 8. It seems like a stranger is following you as you walk to your car in the parking lot. Your heart starts beating faster. Write out the pathway that the nervous system has taken during this experience. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 9. What are the 2 main types of cell ...
chapt08_lecture
... 3) This cycle repeats every 90 minutes, and most people go through five per night. 4) If allowed to awaken naturally, people usually do so during REM sleep. 5) Slow-wave is prominent in the first part of sleep, while REM is prominent in the second half ...
... 3) This cycle repeats every 90 minutes, and most people go through five per night. 4) If allowed to awaken naturally, people usually do so during REM sleep. 5) Slow-wave is prominent in the first part of sleep, while REM is prominent in the second half ...
Slide ()
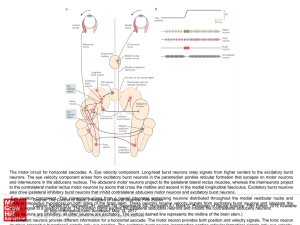
... The motor circuit for horizontal saccades. A. Eye velocity component. Long-lead burst neurons relay signals from higher centers to the excitatory burst neurons. The eye velocity component arises from excitatory burst neurons in the paramedian pontine reticular formation that synapse on motor neurons ...
... The motor circuit for horizontal saccades. A. Eye velocity component. Long-lead burst neurons relay signals from higher centers to the excitatory burst neurons. The eye velocity component arises from excitatory burst neurons in the paramedian pontine reticular formation that synapse on motor neurons ...
Supplement: A Heuristic Model of Alcohol Dependence
... no targeted study has shed light on the quantification of relative functional weights, and a firm definition of the term “functional weight” has not yet been established. One challenge for the quantification of relative functional weights is that it is not known whether each disease phenomenon (e.g. ...
... no targeted study has shed light on the quantification of relative functional weights, and a firm definition of the term “functional weight” has not yet been established. One challenge for the quantification of relative functional weights is that it is not known whether each disease phenomenon (e.g. ...
NEUROSCIENCE FACTS
... granule cell surface (Han et al. , Eur. J. Neurosci., in press; Halasy and Somogyi, ibid., in press): (i) Hilar cells whose cell bodies and dendrites are restricted to the hilus and which have ascending axons to the outer two-thirds of the molecular layer terminate in conjunction with the perforant ...
... granule cell surface (Han et al. , Eur. J. Neurosci., in press; Halasy and Somogyi, ibid., in press): (i) Hilar cells whose cell bodies and dendrites are restricted to the hilus and which have ascending axons to the outer two-thirds of the molecular layer terminate in conjunction with the perforant ...
• - Frankfort-Schuyler Central School District
... The central canal and the four ventricles are filled with cerebrospinal fluid, formed in the brain by filtration of the blood. o The cerebrospinal fluid circulates slowly through the central canal and the ventricles and then drains into the veins, bringing nutrients and hormones to the brain and cle ...
... The central canal and the four ventricles are filled with cerebrospinal fluid, formed in the brain by filtration of the blood. o The cerebrospinal fluid circulates slowly through the central canal and the ventricles and then drains into the veins, bringing nutrients and hormones to the brain and cle ...
Class Notes
... The central canal and the four ventricles are filled with cerebrospinal fluid, formed in the brain by filtration of the blood. o The cerebrospinal fluid circulates slowly through the central canal and the ventricles and then drains into the veins, bringing nutrients and hormones to the brain and cle ...
... The central canal and the four ventricles are filled with cerebrospinal fluid, formed in the brain by filtration of the blood. o The cerebrospinal fluid circulates slowly through the central canal and the ventricles and then drains into the veins, bringing nutrients and hormones to the brain and cle ...
Title: Nervous System
... intracellular second-messenger molecules. One second messenger activates many enzymes, and each activated enzyme can regulate many target proteins (amplification). Second-messengers may activate certain enzymes that catalyze the phosphorylation of certain proteins, which in turn produce the physiolo ...
... intracellular second-messenger molecules. One second messenger activates many enzymes, and each activated enzyme can regulate many target proteins (amplification). Second-messengers may activate certain enzymes that catalyze the phosphorylation of certain proteins, which in turn produce the physiolo ...
Somatic Sensory System
... without looking in the mirror • Muscle spindles- intrafusal fibers and • Golgi Tendon organs are specialized structures that are innervated by DRGNs and send information to the spinal cord ...
... without looking in the mirror • Muscle spindles- intrafusal fibers and • Golgi Tendon organs are specialized structures that are innervated by DRGNs and send information to the spinal cord ...
NervousSystem2
... of these cortical neurons results in action, that action is designated a response or a conditioned reflex. Such an action’s taking place due to the animal’s perception of stimuli is a learned response. Such actions are present only after the animal has learned the appropriate response. They are to b ...
... of these cortical neurons results in action, that action is designated a response or a conditioned reflex. Such an action’s taking place due to the animal’s perception of stimuli is a learned response. Such actions are present only after the animal has learned the appropriate response. They are to b ...
Regulation of Respiration
... CO2 excites respiratory center greatly the first few hours after the PCO2 first increases, but then it gradually declines over the next 1 to 2 days to 1/5 the initial effect action of the kidneys (increased levels of HCO3-) – in blood, cerebrospinal fluid and ...
... CO2 excites respiratory center greatly the first few hours after the PCO2 first increases, but then it gradually declines over the next 1 to 2 days to 1/5 the initial effect action of the kidneys (increased levels of HCO3-) – in blood, cerebrospinal fluid and ...
Chapter 5: SENSATION - Charles Best Library
... A difference threshold is the minimum difference between two stimuli that a person can detect 50 percent of the time. In humans, difference thresholds (experienced as a just noticeable difference, increase in proportion to the size of the stimulus—a principle known as Weber’s law. ...
... A difference threshold is the minimum difference between two stimuli that a person can detect 50 percent of the time. In humans, difference thresholds (experienced as a just noticeable difference, increase in proportion to the size of the stimulus—a principle known as Weber’s law. ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.