Essentials of Human Anatomy Special Senses Special Senses
... • olfactory organs located high in the nasal cavity above the usual pathway of inhaled air • olfactory receptors undergo sensory adaptation rapidly • sense of smell drops by 50% within a second after stimulation ...
... • olfactory organs located high in the nasal cavity above the usual pathway of inhaled air • olfactory receptors undergo sensory adaptation rapidly • sense of smell drops by 50% within a second after stimulation ...
to find the lecture notes for lecture 5 cellular communication click here
... these compounds exert their effects by binding to the target cells and/or entering the cell the ultimate goal is to affect the function of the cell – through modifying the expression of genes/proteins ...
... these compounds exert their effects by binding to the target cells and/or entering the cell the ultimate goal is to affect the function of the cell – through modifying the expression of genes/proteins ...
High Throughput Screening Proposal
... Screen Charge to information (charge code or bill to information): _____________________________________________________________________________________ E-mail:_______________________________________________________________________________ Phone #:____________________________________________________ ...
... Screen Charge to information (charge code or bill to information): _____________________________________________________________________________________ E-mail:_______________________________________________________________________________ Phone #:____________________________________________________ ...
STATUS DECISION OF CONTROLLED AND NON
... US: 4-Fluorotropacocaine is not listed specifically in the Schedules to the US Controlled Substances Act and is not mentioned anywhere on the DEA website. United Nations: The substance is not listed on the Yellow List - List of Narcotic Drugs under International Control, the Green List - List of Psy ...
... US: 4-Fluorotropacocaine is not listed specifically in the Schedules to the US Controlled Substances Act and is not mentioned anywhere on the DEA website. United Nations: The substance is not listed on the Yellow List - List of Narcotic Drugs under International Control, the Green List - List of Psy ...
Graded Potentials
... Sketch and label the structure of a typical neuron, describe the functions of each component, and classify neurons on the basis of their structure and function. Describe the locations and functions of the various types of neuroglia. Explain how the resting potential is created and maintained. ...
... Sketch and label the structure of a typical neuron, describe the functions of each component, and classify neurons on the basis of their structure and function. Describe the locations and functions of the various types of neuroglia. Explain how the resting potential is created and maintained. ...
Oral Pharmacotherapy of Childhood Movement Disorders
... the consequences of therapy may be worse than any shortterm relief. There is no consensus on the optimal management of autoimmune chorea, but both corticosteroids10 and intravenous immunoglobulins have been used. Corticosteroids appear to be effective in the treatment of chorea associated with heart ...
... the consequences of therapy may be worse than any shortterm relief. There is no consensus on the optimal management of autoimmune chorea, but both corticosteroids10 and intravenous immunoglobulins have been used. Corticosteroids appear to be effective in the treatment of chorea associated with heart ...
Neuroscience 14c – The Limbic System and Drugs of Abuse
... These project into the hypothalamus via the stria terminalis and the ventral amygdalofugal pathway. It also projects onto the reticular nucleus for increased reflexes, to the nuclei of the trigeminal nerve and facial nerve for facial expressions of fear, and to the ventral tegmental area, locus coer ...
... These project into the hypothalamus via the stria terminalis and the ventral amygdalofugal pathway. It also projects onto the reticular nucleus for increased reflexes, to the nuclei of the trigeminal nerve and facial nerve for facial expressions of fear, and to the ventral tegmental area, locus coer ...
Homeostasis Review Definitions
... A system that shuts off a response that the body originally had because it was out of balance. i.e. water balance and hypothalamus stops releasing vasopressin ...
... A system that shuts off a response that the body originally had because it was out of balance. i.e. water balance and hypothalamus stops releasing vasopressin ...
Respiratory Regulation - Warner Pacific College
... a feedback that ”switches off” the respirator ramp and stop further inspiration ○ can also increase the rate of respiration Not activated until tidal volume increases Can appear to be a protective mechanism for preventing lung inflation ...
... a feedback that ”switches off” the respirator ramp and stop further inspiration ○ can also increase the rate of respiration Not activated until tidal volume increases Can appear to be a protective mechanism for preventing lung inflation ...
What do you want to know about the brain?
... Facts about the right side of the brain What does the left side of your brain do? Pictures of your brain The 3 different sides of your brain The reptilian brain The limbic ...
... Facts about the right side of the brain What does the left side of your brain do? Pictures of your brain The 3 different sides of your brain The reptilian brain The limbic ...
Study Questions
... for example by switching the correct lever to press to obtain a reward to the previously incorrect lever. The rationale for this strategy is that the action system would facilitate learning changes in the outcome but the habit system would interfere because it is slow to change. 9. Explain the conce ...
... for example by switching the correct lever to press to obtain a reward to the previously incorrect lever. The rationale for this strategy is that the action system would facilitate learning changes in the outcome but the habit system would interfere because it is slow to change. 9. Explain the conce ...
Lecture 3 Review
... Once a PSP is initiated it spreads through the cytoplasm of the post-synaptic cell. For the most part, the spread of the PSP is passive; i.e. it is not conducted. Some longer dendrites have voltage-sensitive Na+/K+ channels that help the PSP along, however, this not typical. As it spreads away from ...
... Once a PSP is initiated it spreads through the cytoplasm of the post-synaptic cell. For the most part, the spread of the PSP is passive; i.e. it is not conducted. Some longer dendrites have voltage-sensitive Na+/K+ channels that help the PSP along, however, this not typical. As it spreads away from ...
14-Nervous System - Savita Pall and Chemistry
... An organ system is a group of organs that are co-ordinated to work together to perform specific tasks in the body. Organ systems are made up of groups of organs. Tissues are made up of specialized cells. Organs are made up of tissues. The nervous system is an intricate communications network fueled ...
... An organ system is a group of organs that are co-ordinated to work together to perform specific tasks in the body. Organ systems are made up of groups of organs. Tissues are made up of specialized cells. Organs are made up of tissues. The nervous system is an intricate communications network fueled ...
Overview Functions of the Nervous System
... • travel across the synapse to the postsynaptic cells, where they are converted back into electrical signals • Axon terminal: contains many tiny, membrane-bounded sacs (synaptic vesicles) containing thousands of neurotransmitter molecules • Neurotransmitter receptor region on the membrane of a dendr ...
... • travel across the synapse to the postsynaptic cells, where they are converted back into electrical signals • Axon terminal: contains many tiny, membrane-bounded sacs (synaptic vesicles) containing thousands of neurotransmitter molecules • Neurotransmitter receptor region on the membrane of a dendr ...
Chapter 12- Intro to NS
... and transfer a signal onto the cendrite of the sensory neuron. The dendrite then connects tot eh cell body that sends an axon into the CNS (spinal cord). The bodies of sensory neurons are in ganglia outside the CNS. peripheral process going to receptors in the body (axon and dendrites). e. Motor neu ...
... and transfer a signal onto the cendrite of the sensory neuron. The dendrite then connects tot eh cell body that sends an axon into the CNS (spinal cord). The bodies of sensory neurons are in ganglia outside the CNS. peripheral process going to receptors in the body (axon and dendrites). e. Motor neu ...
Psychology 10th Edition David Myers - AP Psychology
... ACh-producing neurons deteriorate as Alzheimer’s disease progresses ...
... ACh-producing neurons deteriorate as Alzheimer’s disease progresses ...
Chapter 4 – Sensation
... Rods – Photoreceptors in the retina that respond to lower light intensities and give rise to achromatic (colorless) sensations Cones – Visual receptors that respond to greater light intensities and give rise to chromatic sensations Fovea – The area roughly at the retina’s center where cones ar ...
... Rods – Photoreceptors in the retina that respond to lower light intensities and give rise to achromatic (colorless) sensations Cones – Visual receptors that respond to greater light intensities and give rise to chromatic sensations Fovea – The area roughly at the retina’s center where cones ar ...
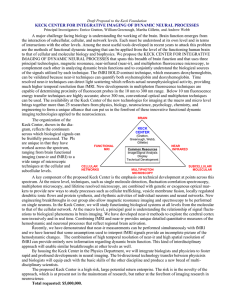
Draft Proposal to the Keck Foundation KECK CENTER FOR
... multiphoton microscopy, and lifetime resolved microscopy, are combined with genetic or exogenous optical markers to provide new ways to study processes such as cellular trafficking, vesicle membrane fusion, locally regulated dendritic ionic flows and protein synthesis, and rhythmic activities of ind ...
... multiphoton microscopy, and lifetime resolved microscopy, are combined with genetic or exogenous optical markers to provide new ways to study processes such as cellular trafficking, vesicle membrane fusion, locally regulated dendritic ionic flows and protein synthesis, and rhythmic activities of ind ...
the PDF file
... 7. Which signals will get disrupted in case of a spinal cord injury? Answer In case of the spinal cord injury, the signals coming from the nerves as well as the signals coming to the receptors will be disrupted. As both these signals meet in a bundle in spinal cord so there is any spinal cord injury ...
... 7. Which signals will get disrupted in case of a spinal cord injury? Answer In case of the spinal cord injury, the signals coming from the nerves as well as the signals coming to the receptors will be disrupted. As both these signals meet in a bundle in spinal cord so there is any spinal cord injury ...
Topic 4 Proteins as Drug Targets
... travel across a nerve synapse to bind with receptors on target cells, such as muscle cells or another nerve. Usually short lived and responsible for messages between individual cells Hormones: Chemicals released from cells or glands and which travel some distance to bind with receptors on target cel ...
... travel across a nerve synapse to bind with receptors on target cells, such as muscle cells or another nerve. Usually short lived and responsible for messages between individual cells Hormones: Chemicals released from cells or glands and which travel some distance to bind with receptors on target cel ...
NMDA Receptors Contribute to Primary Visceral Afferent
... non-NMDA receptors transmit primary sensory afferent signals to second-order neurons in the NTS, then the secondorder neurons most likely serve to simply relay information from visceral sensory endings to higher-order neurons, as has been classically described (Spyer 1981). If, on the other hand, NM ...
... non-NMDA receptors transmit primary sensory afferent signals to second-order neurons in the NTS, then the secondorder neurons most likely serve to simply relay information from visceral sensory endings to higher-order neurons, as has been classically described (Spyer 1981). If, on the other hand, NM ...
Summary - SCIENCE HELP @ ne3me.com
... heart rate. Stimulants also increase the release of neurotransmitters in the brain. Depressants decrease actions, such as heart rate, that are controlled by the brain. Cocaine causes the sudden release in the brain of a neurotransmitter called dopamine. Opiates act like natural brain chemicals calle ...
... heart rate. Stimulants also increase the release of neurotransmitters in the brain. Depressants decrease actions, such as heart rate, that are controlled by the brain. Cocaine causes the sudden release in the brain of a neurotransmitter called dopamine. Opiates act like natural brain chemicals calle ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.