Lecture Outline ()
... • Injured tissues release chemicals that stimulate pain fibers (bradykinin, histamine, prostaglandin) ...
... • Injured tissues release chemicals that stimulate pain fibers (bradykinin, histamine, prostaglandin) ...
Central nervous system
... microtubules at about 200 mm/day. Synaptic vesicles recycle in the membrane, but some used vesicles are carried back to the cell body and deposited in lysosomes. ...
... microtubules at about 200 mm/day. Synaptic vesicles recycle in the membrane, but some used vesicles are carried back to the cell body and deposited in lysosomes. ...
Reflexes
... General a. Description b. Components: i. receptor, ii. sensory neuron, iii. integration center- generally within CNS; may involve simply a synapse (monosynaptic) or may involve interneurons (polysynaptic) iv. motor neuron v. effector c. Somatic reflexes involve skeletal muscle responses; when they o ...
... General a. Description b. Components: i. receptor, ii. sensory neuron, iii. integration center- generally within CNS; may involve simply a synapse (monosynaptic) or may involve interneurons (polysynaptic) iv. motor neuron v. effector c. Somatic reflexes involve skeletal muscle responses; when they o ...
Brain Chips - IndiaStudyChannel.com
... The study of artificial neural networks has also added to the data required to create brain chips. They crudely mimic the fundamental properties of the brain. When eventually a network model which resembles the brain in every aspect is created, it will be a major breakthrough in the evolution towar ...
... The study of artificial neural networks has also added to the data required to create brain chips. They crudely mimic the fundamental properties of the brain. When eventually a network model which resembles the brain in every aspect is created, it will be a major breakthrough in the evolution towar ...
Chapter Three - New Providence School District
... (ACh). Like other neurotransmitters, ACh can movement of all muscles depends on . However, other chemical substances can only bind to specific sites, much like a lock and fool the receptor sites. For example, an agonist like nicotine can (~ the action of ACh, while an antagonist like curare can (bio ...
... (ACh). Like other neurotransmitters, ACh can movement of all muscles depends on . However, other chemical substances can only bind to specific sites, much like a lock and fool the receptor sites. For example, an agonist like nicotine can (~ the action of ACh, while an antagonist like curare can (bio ...
Therapeutic Restoration of Spinal Inhibition via
... Dysfunction of γ-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA)–ergic Signaling in the Superficial Dorsal Horn in Neuropathic PainIn normal function, nociceptive fibers innervate peripheral tissues and form excitatory (glutamatergic) synapses onto secondary sensory neurons in superficial laminae (I and II) of the dorsal ...
... Dysfunction of γ-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA)–ergic Signaling in the Superficial Dorsal Horn in Neuropathic PainIn normal function, nociceptive fibers innervate peripheral tissues and form excitatory (glutamatergic) synapses onto secondary sensory neurons in superficial laminae (I and II) of the dorsal ...
Neuron Preview
... effects on other, antagonist motor neurons. The synaptic effects of direct M1 input onto ␣ motor neurons have been well characterized. Axons of individual CM cells also branch to contact neurons in other motor neuron pools; their aggregate branching pattern yields a muscle field that describes the f ...
... effects on other, antagonist motor neurons. The synaptic effects of direct M1 input onto ␣ motor neurons have been well characterized. Axons of individual CM cells also branch to contact neurons in other motor neuron pools; their aggregate branching pattern yields a muscle field that describes the f ...
Central Nervous System
... nerves, making 62 nerves composed of sensory and motor neurons. The nerves are named off of where they leave the spine. They are divided into 5 groups, cranial, thoraic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal. 8 in the cervical region 12 in the thoracic region 5 in the lumbar 5 in the sacral 1 in t ...
... nerves, making 62 nerves composed of sensory and motor neurons. The nerves are named off of where they leave the spine. They are divided into 5 groups, cranial, thoraic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal. 8 in the cervical region 12 in the thoracic region 5 in the lumbar 5 in the sacral 1 in t ...
Modulation of Cortical Activation and Behavioral Arousal by
... (Orx) or hypocretin, contained in diffusely projecting neurons of the hypothalamus, was found to be essential for the maintenance of waking with muscle tone, since in its absence narcolepsy with cataplexy occurred. Orx neurons discharge during active waking and cease firing during sleep. Since choli ...
... (Orx) or hypocretin, contained in diffusely projecting neurons of the hypothalamus, was found to be essential for the maintenance of waking with muscle tone, since in its absence narcolepsy with cataplexy occurred. Orx neurons discharge during active waking and cease firing during sleep. Since choli ...
Cells of the Nervous System
... good example is schizophrenia which includes hallucinations and delusions. • Some therapeutic drugs (chlorpromazine = thorazine and halprodol) work to block dopamine receptors therefore reducing dopamine exposure. • Amphetamines worsen the schizophrenic condition because they promote dopamine produc ...
... good example is schizophrenia which includes hallucinations and delusions. • Some therapeutic drugs (chlorpromazine = thorazine and halprodol) work to block dopamine receptors therefore reducing dopamine exposure. • Amphetamines worsen the schizophrenic condition because they promote dopamine produc ...
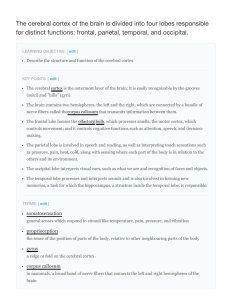
The cerebral cortex of the brain is divided into four lobes
... The parietal lobe is located at the top of the brain. Neurons in the parietal lobe are involved in speech and reading. Two of the parietal lobe's main functions are processing somatosensation(touch sensations such as pressure, pain, heat, cold) and processing proprioception (the sense of how parts o ...
... The parietal lobe is located at the top of the brain. Neurons in the parietal lobe are involved in speech and reading. Two of the parietal lobe's main functions are processing somatosensation(touch sensations such as pressure, pain, heat, cold) and processing proprioception (the sense of how parts o ...
Medical Reference Guide
... Stroke – a vascular event, either embolic (blood clot) or hemorrhagic (bleeding), which results in permanent damage to the brain and a disturbance of cerebral function . The symptoms are unilateral neurological symptoms such as paralysis, weakness and loss of coordination affecting the face, arm, le ...
... Stroke – a vascular event, either embolic (blood clot) or hemorrhagic (bleeding), which results in permanent damage to the brain and a disturbance of cerebral function . The symptoms are unilateral neurological symptoms such as paralysis, weakness and loss of coordination affecting the face, arm, le ...
Target Selection
... Rotation of the eye 180 degrees results in the formation of an inverted image in the frog’s brain because dorsal (or ventral) axons always project to one specific area of the tectum It appears that retinal fibers are guided to the tectum by biochemical tags present across the retina and the tectum. ...
... Rotation of the eye 180 degrees results in the formation of an inverted image in the frog’s brain because dorsal (or ventral) axons always project to one specific area of the tectum It appears that retinal fibers are guided to the tectum by biochemical tags present across the retina and the tectum. ...
Motor Neuron - papbiobellaire
... Stimulus - environmental change which causes a response; usually a form of energy a) radiant (heat, light) ...
... Stimulus - environmental change which causes a response; usually a form of energy a) radiant (heat, light) ...
No Slide Title
... -cAMP acts as a signal within the cell = second messenger – effects cell activity -BUT some G proteins can inhibit this pathway!!!! (no AC activation, no cAMP production) 5 players in this mechanism: ...
... -cAMP acts as a signal within the cell = second messenger – effects cell activity -BUT some G proteins can inhibit this pathway!!!! (no AC activation, no cAMP production) 5 players in this mechanism: ...
The Brain`s Response to Drugs Teacher`s Guide
... to the axon. The axons then transmit the messages, which are in the form of electrical impulses, to other neurons or body tissues. The axons of many neurons are covered in a fatty substance known as myelin. Myelin has several functions. One of its most important is to increase the rate at which nerv ...
... to the axon. The axons then transmit the messages, which are in the form of electrical impulses, to other neurons or body tissues. The axons of many neurons are covered in a fatty substance known as myelin. Myelin has several functions. One of its most important is to increase the rate at which nerv ...
slides - NYU Computation and Cognition Lab
... Information flows between neurons with action potentials and synaptic transmission (involving neurotransmitters) The likely mechanism for memory is the changes at the synapses in the form of LTP, dendritic growth, etc.. Circuits represent the collective action of interconnected networks of neurons C ...
... Information flows between neurons with action potentials and synaptic transmission (involving neurotransmitters) The likely mechanism for memory is the changes at the synapses in the form of LTP, dendritic growth, etc.. Circuits represent the collective action of interconnected networks of neurons C ...
Cellular and Systems Neurophysiology Part 13: The Motor
... • The data below are from motor neurons that are mediating repetitive scratching behavior in a turtle • It seemed strange to most people that inhibition and excitation should occur at the same time • That is why this was published in Science • This observation fits well with the theory ...
... • The data below are from motor neurons that are mediating repetitive scratching behavior in a turtle • It seemed strange to most people that inhibition and excitation should occur at the same time • That is why this was published in Science • This observation fits well with the theory ...
LSU Seminar Neuroscience Center of Excellence
... The fine-tuning of circuits in sensory cortex requires sensory experience during an early critical period. Visual deprivation (VD) during the critical period has atastrophic effects on visual function, including loss of visual responsiveness to the deprived eye, reduced visual acuity, and loss of tu ...
... The fine-tuning of circuits in sensory cortex requires sensory experience during an early critical period. Visual deprivation (VD) during the critical period has atastrophic effects on visual function, including loss of visual responsiveness to the deprived eye, reduced visual acuity, and loss of tu ...
Parenteral Administration of Medication in Small Animals
... Skin is usually shaved Animals are usually sedated Drug does not go systemic ...
... Skin is usually shaved Animals are usually sedated Drug does not go systemic ...
Genit 7
... Central Dogma of Genetics Slide 4 Info comes from DNA which can replicate and duplicate itself. Then DNA transcription to produce mRNA which is translated into amino acids that produce proteins. Sometimes we have reverse transcription condition. Slide 5 Each step in protein synthesis there is a gene ...
... Central Dogma of Genetics Slide 4 Info comes from DNA which can replicate and duplicate itself. Then DNA transcription to produce mRNA which is translated into amino acids that produce proteins. Sometimes we have reverse transcription condition. Slide 5 Each step in protein synthesis there is a gene ...
chapter 11 the somatosensory system and topographic organization
... cutaneous receptors is transmitted from the spinal cord to the ventral posterior nucleus of the thalamus, and from there to the somatosensory cortex. As in the case of the visual system, each level of the somatosensory system contains a topographic representation or "map" of the body surface, and th ...
... cutaneous receptors is transmitted from the spinal cord to the ventral posterior nucleus of the thalamus, and from there to the somatosensory cortex. As in the case of the visual system, each level of the somatosensory system contains a topographic representation or "map" of the body surface, and th ...
OCR Document - MrsGorukhomework
... resting potential. This charge or difference in electrical potential, can actually be measured at -70mV,about 5% of the voltage of AA battery. How does it achieve this potential? The resting potential arises from two things - difference in the ionic composition of the intracellular and intracellular ...
... resting potential. This charge or difference in electrical potential, can actually be measured at -70mV,about 5% of the voltage of AA battery. How does it achieve this potential? The resting potential arises from two things - difference in the ionic composition of the intracellular and intracellular ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.