SENSATION AND PERCEPTION
... • Messages from senses are called sensations – For example, vision is the system through which the eyes convert light into neural activity. This tells the brain something about the source of the light (brightness) or about the objects from which the light is reflected (round, red, etc). ...
... • Messages from senses are called sensations – For example, vision is the system through which the eyes convert light into neural activity. This tells the brain something about the source of the light (brightness) or about the objects from which the light is reflected (round, red, etc). ...
VI. The vertebrate nervous system is a hierarchy of structural and
... branched to increase surface area where the cell is most likely to be stimulated. ⇒ Axons conduct impulses away from the cell body; are long, single processes. ◊ Vertebrate axons in PNS are wrapped in concentric layers of Schwann cells which form an insulating myelin sheath. ◊ Axons extend from the ...
... branched to increase surface area where the cell is most likely to be stimulated. ⇒ Axons conduct impulses away from the cell body; are long, single processes. ◊ Vertebrate axons in PNS are wrapped in concentric layers of Schwann cells which form an insulating myelin sheath. ◊ Axons extend from the ...
nervous system
... • Synaptic knob- slightly enlarged bulb at end of axon • Vesicles contain neurotransmitter (a chemical messenger) • When depolarization wave reaches axon terminal, calcium channels open and ...
... • Synaptic knob- slightly enlarged bulb at end of axon • Vesicles contain neurotransmitter (a chemical messenger) • When depolarization wave reaches axon terminal, calcium channels open and ...
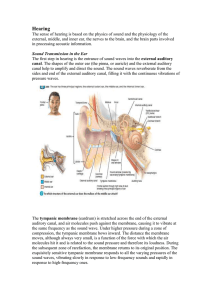
Ear
... inner ear must be amplified. This is achieved by a movable chain of three small bones, the malleus, incus, and stapes; these bones act as a piston and couple the motions of the tympanic membrane to the oval window, a membrane covered opening separating the middle and inner ear. The total force of a ...
... inner ear must be amplified. This is achieved by a movable chain of three small bones, the malleus, incus, and stapes; these bones act as a piston and couple the motions of the tympanic membrane to the oval window, a membrane covered opening separating the middle and inner ear. The total force of a ...
doc GIT
... 1- Submucosal plexus – in the submucosa 2- Myenteric plexus - b/w the circular and longitudinal muscle Structurally they are different; but for our purposes, the plexuses are considered as 1: ~ enteric plexus/innervation - a functional unit that comprises the submucosal and myenteric plexus. This is ...
... 1- Submucosal plexus – in the submucosa 2- Myenteric plexus - b/w the circular and longitudinal muscle Structurally they are different; but for our purposes, the plexuses are considered as 1: ~ enteric plexus/innervation - a functional unit that comprises the submucosal and myenteric plexus. This is ...
as a PDF - University of Sussex
... than through external means such as TMS. It is turned off to save energy. Snyder et al [25] and Bossomaier and Snyder [3] propose a concept model for how inhibition mechanisms might generate the observed effects of TMS. The effect is to turn off the inhibitory mechanisms, dis-inhibiting their target ...
... than through external means such as TMS. It is turned off to save energy. Snyder et al [25] and Bossomaier and Snyder [3] propose a concept model for how inhibition mechanisms might generate the observed effects of TMS. The effect is to turn off the inhibitory mechanisms, dis-inhibiting their target ...
Limitations in anti-obesity drug development: the critical role of
... behaviour by acting on neurons in the hypothalamus and the brainstem. During periods of satiety, the body works towards storage of the acquired nutrients. Satiety is associated with increased sympathetic activity, which promotes both insulin release by the pancreas (and thus stimulates glucose stora ...
... behaviour by acting on neurons in the hypothalamus and the brainstem. During periods of satiety, the body works towards storage of the acquired nutrients. Satiety is associated with increased sympathetic activity, which promotes both insulin release by the pancreas (and thus stimulates glucose stora ...
Theme 6. Vision
... Can you describe how myelination occurs in the peripheral nervous system and by which mechanism this can have an impact on speed of transmission. (6p) ...
... Can you describe how myelination occurs in the peripheral nervous system and by which mechanism this can have an impact on speed of transmission. (6p) ...
Comparative approaches to cortical microcircuits
... Drosophila is implemented by high-quantal EPSPs, high basal release rate [59], and olfactory receptor neuron (ORN) convergence on projection neurons (PNs) [60,61]. Gain reduction for strong signals, by contrast, relies on fast vesicle depletion (hence strong short term depression) at the ORN-PN syna ...
... Drosophila is implemented by high-quantal EPSPs, high basal release rate [59], and olfactory receptor neuron (ORN) convergence on projection neurons (PNs) [60,61]. Gain reduction for strong signals, by contrast, relies on fast vesicle depletion (hence strong short term depression) at the ORN-PN syna ...
Somatosensory system
... felt at the correct location. The point-to-point mapping of the body surfaces in the brain is called a homunculus and is essential in the creation of a body image. This brain-surface ("cortical") map is not immutable, however. Dramatic shifts can occur in response to stroke or injury. ...
... felt at the correct location. The point-to-point mapping of the body surfaces in the brain is called a homunculus and is essential in the creation of a body image. This brain-surface ("cortical") map is not immutable, however. Dramatic shifts can occur in response to stroke or injury. ...
nervous system
... communicate with each other. Since the brain is so important, it is protected by the skull, cerebrospinal fluid which cushions it, and meninges which are membranes that surround the brain and only let certain substances cross through to the brain. The brain is one of the few organs that can only use ...
... communicate with each other. Since the brain is so important, it is protected by the skull, cerebrospinal fluid which cushions it, and meninges which are membranes that surround the brain and only let certain substances cross through to the brain. The brain is one of the few organs that can only use ...
False - UPM EduTrain Interactive Learning
... the brain are either on or off by either firing an action potential or not firing an action potential. However, neurons are more than just on or off because the "excitability" of a neuron is always changing. This is because a neuron is constantly getting information from other cells through synapt ...
... the brain are either on or off by either firing an action potential or not firing an action potential. However, neurons are more than just on or off because the "excitability" of a neuron is always changing. This is because a neuron is constantly getting information from other cells through synapt ...
Clinicals - Website of Neelay Gandhi
... charges to cross membrane, which acts as a depolarization. Also, Ca helps to maintain cell membrane integrity. Low calcium leads to leakiness of membrane. Two major changes: ...
... charges to cross membrane, which acts as a depolarization. Also, Ca helps to maintain cell membrane integrity. Low calcium leads to leakiness of membrane. Two major changes: ...
PC 11 - exam 3 (2:00-3:15) Students can and will be tested on the
... 2. An axon transmits messages ________ the cell body and a dendrite transmits messages ________ the cell body. A) away from; toward B) away from; away from C) toward; away from D) toward; toward ...
... 2. An axon transmits messages ________ the cell body and a dendrite transmits messages ________ the cell body. A) away from; toward B) away from; away from C) toward; away from D) toward; toward ...
Lecture 27 Powerpoint File
... with intention to eat it – or when monkey observes a human grasping food to eat it – Some cells fire more when monkey grasps food with intention to place it in a container – or when monkey observes a human placing food in a container ...
... with intention to eat it – or when monkey observes a human grasping food to eat it – Some cells fire more when monkey grasps food with intention to place it in a container – or when monkey observes a human placing food in a container ...
Nervous System
... Homeostasis - The relatively constant state of the internal environment of the body that is maintained by adaptive responses. Specific control and feedback mechanisms are responsible for adjusting body systems to maintain this state. Sense organs – specialized cells that can detect environmental cha ...
... Homeostasis - The relatively constant state of the internal environment of the body that is maintained by adaptive responses. Specific control and feedback mechanisms are responsible for adjusting body systems to maintain this state. Sense organs – specialized cells that can detect environmental cha ...
Cell Assemblies - CAAM @ Rice
... these questions in terms of cell assemblies in his book The Organization of Behavior. Hebb asserts that a cell assembly is a group of neurons wired in a specific manner such that when a sufficient amount of neurons in this group are excited, the entire group becomes excited in a synchronized manner. ...
... these questions in terms of cell assemblies in his book The Organization of Behavior. Hebb asserts that a cell assembly is a group of neurons wired in a specific manner such that when a sufficient amount of neurons in this group are excited, the entire group becomes excited in a synchronized manner. ...
DNA Replication Precedes Neuronal Cell Death
... Alzheimer’s disease cases. As with the chromosome 11 probes, three and four spots of FISH hybridization were found with this second probe in Alzheimer’s disease cases (Fig. 6 A). The BACE2 locus is near the end of the long arm of human chromosome 21 (q22.3) (Fig. 2), and thus, at least two chromosom ...
... Alzheimer’s disease cases. As with the chromosome 11 probes, three and four spots of FISH hybridization were found with this second probe in Alzheimer’s disease cases (Fig. 6 A). The BACE2 locus is near the end of the long arm of human chromosome 21 (q22.3) (Fig. 2), and thus, at least two chromosom ...
Learning, Memory and Amnesia
... • Can affect short-term, long-term, or both. • Usually accompanied by retrograde amnesia. ...
... • Can affect short-term, long-term, or both. • Usually accompanied by retrograde amnesia. ...
Ch. 2 - WordPress.com
... Organelles: Membrane-enclosed structures within the soma Cytoplasm: Contents within a cell membrane (e.g., organelles, excluding the nucleus) ...
... Organelles: Membrane-enclosed structures within the soma Cytoplasm: Contents within a cell membrane (e.g., organelles, excluding the nucleus) ...
ANSWERS TO CHAPTER 8
... formation is a major component of the reticular activating system, which plays an important role in arousing and maintaining consciousness and in regulating the sleep/wake cycle. ...
... formation is a major component of the reticular activating system, which plays an important role in arousing and maintaining consciousness and in regulating the sleep/wake cycle. ...
The vertebrate nervous system is regionally specialized
... neurotransmitter diffuses out of the synaptic cleft, is taken up by surrounding cells, or is degraded by enzymes. A single neuron has many synapses on its dendrites and cell body. Whether it generates an action potential depends on the temporal and spatial summation of EPSPs and IPSPs at the axon hi ...
... neurotransmitter diffuses out of the synaptic cleft, is taken up by surrounding cells, or is degraded by enzymes. A single neuron has many synapses on its dendrites and cell body. Whether it generates an action potential depends on the temporal and spatial summation of EPSPs and IPSPs at the axon hi ...
Design Features in Vertebrate Sensory Systems
... use directed eye movements to center a visual stimulus on the fovea or when rodents use their whiskers to sample physical objects in the environment. There are in some cases feedback projections from the central nervous system to receptors (Fig. 1). This occurs, for example, in many hair cells in th ...
... use directed eye movements to center a visual stimulus on the fovea or when rodents use their whiskers to sample physical objects in the environment. There are in some cases feedback projections from the central nervous system to receptors (Fig. 1). This occurs, for example, in many hair cells in th ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.